 Solarar, or as it is called medical literature, solar plexitis( idiomatic peripheral vegetative neuropathy) is the defeat of the solar plexus( also called celiac or plannic).
Solarar, or as it is called medical literature, solar plexitis( idiomatic peripheral vegetative neuropathy) is the defeat of the solar plexus( also called celiac or plannic).
The disease is associated with degenerative or inflammatory processes occurring in the nodes of the solar plexus.
The name of the disease comes from the word solaritis, in translation meaning "sunny."
Contents
- Anatomical and physiological information
- Etiology and causes
- Clinical picture and symptoms
- Diagnostic criteria
- Medical care complex
- Physical methods and medicines
- Folk methods
- Prevention of disease
Anatomical and physiological information
The pulmonary plexus is located in the abdominal cavity near the source of the celiacand the superior mesenteric arteries and is a multiple plexus of nerve cells that are located outside the nervous system.
It is located behind the stomach, on the left and right sides of the spinal column. Not many people know that the splanchnic plexus is the most important support of the body, of which only 16. This fact explains why a person permanently goes out of order, injured in the solar plexus area.
The celiac plexus is represented by several nerve nodes and a large number of nerves that connect these nodes to each other. Visually the whole system looks like the sun, framed by numerous rays. This association formed the basis of the name.
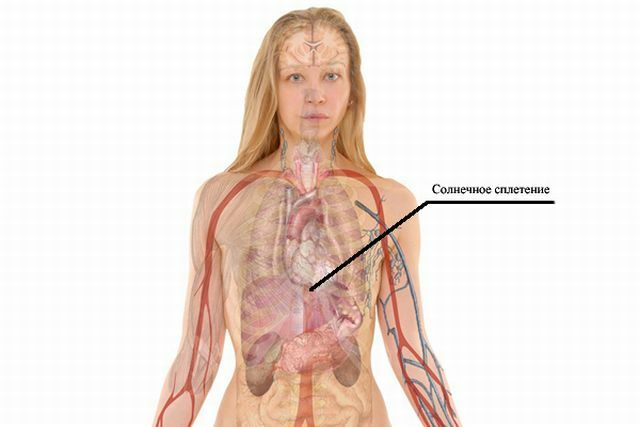
Components of the solar plexus:
- two celiac nodes( right and left) , they have a semilunar shape and are located, respectively, on both sides of the celiac trunk;
- the superior mesenteric node , located at the base of the same artery;
- two internal nerve : large and small.
These are the main components. And around the knots is still a lot of other nerves.
Etiology and causes of
The following factors can cause neuritis of the solar plexus:
- Mechanical .This item includes damage to the epigastric region as a result of impact or fall. Internal Diseases .Most often, solariitis is caused by lordosis, an aneurysm of the abdominal aorta, enteroptosis, and degenerative or dystrophic vertebral diseases. The risk of the disease increases with inflammatory processes in the peritoneum: in the stomach, intestine, gall bladder.
- Chronic or acute form of the following infectious diseases : peritonitis, influenza, syphilis, tuberculosis.
- Different kinds of intoxication .Endogenous: defeat by parasites( worms), intestinal dysfunction, colitis. Exogenous: alcohol and nicotine abuse, lead poisoning or any chemical poisonous substances.
- Disruption of the work of higher vegetative centers .The most frequent culprit is the hypothalamic region. Solaris can also develop against a background of mental trauma( stress, nervous breakdown).
There are three stages of the course of the disease: subacute, acute and chronic. Degree of seriousness - from the initial to the final. The last stage is the hardest to treat, with prolonged treatment and a high probability of relapse.
Clinical picture and symptoms
The clinical picture of the solaris can be of two types: with persistent or short-term symptoms.
Constant discomfort is characterized by persistent aching, drilling or spasmodic pain in the epigastric region. And the pain sensations increase with the change in the position of the body - standing or lying on the back. Food intake does not affect the intensity and nature of the pain.
Short-term, sudden and sudden abnormalities, which tend to recur, are called paroxysmal symptoms. These include the solar crisis, characterized by sudden intense pains in the  area of the solar plexus, secretory and cardiovascular disorders, increased pulsation of the abdominal aorta.
area of the solar plexus, secretory and cardiovascular disorders, increased pulsation of the abdominal aorta.
Crisis has an undetermined repetition rate. It can occur several times a month or be repeated daily. The duration of the attack can be different - from a couple of hours to several days. Depends on the etiology of the disease and its stage.
Recognize the solar crisis can be by burning, drilling pains, giving in the lower back, lower thoracic vertebrae or throughout the abdominal cavity. Food intake and time of day do not matter. To facilitate the crisis period will help the situation lying with the knees drawn to the chest.
Against the background of the above symptoms of a solyaritis, there may be:
- increased blood pressure;
- heaviness and bloating;
- heart palpitations( tachycardia);
- diarrhea or constipation;
- headache;
- fast fatigue;
- sleep disturbance;
- possible nausea and vomiting.
From the side of the psychoemotional sphere, such violations as:
- inadequate perception of reality;
- fear of death;
- unstable mood;
- unexplained crying;
- uncontrollable anger;
- suicidal thoughts.
Diagnostic criteria
The first step is to visit the therapist. Later it is necessary to undergo examinations with a surgeon, radiologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist and infectious disease specialist. Only after such comprehensive examinations the patient can be diagnosed with "solar plexite".
To make an accurate diagnosis, a patient needs to undergo comprehensive examinations. In view of the fact that the pain can be felt both in the whole of the  abdomen and in its localized part, the doctor should make sure that the problem is not the illness of other abdominal organs.
abdomen and in its localized part, the doctor should make sure that the problem is not the illness of other abdominal organs.
The examination is performed by the method of palpation of painful points, taking into account the characteristic symptoms of the disease. A particularly sensitive area for palpation is the area on the left side of the midline and slightly further than the line that connects the front end of the X ends of the ribs.
There are three more important points that allow you to determine the ailment. If visually connect the xiphoid process of the sternum to the umbilicus with a straight line, these three points will be located as follows:
- in the middle between the lower and middle third;
- in the middle and upper third;
- directly at the xiphoid process.
By palpating, the doctor morphologically determines the presence of atrophic, dystrophic or degenerative abnormalities.
Additional studies of autonomic reflexes, electrophysiological, pharmacodynamic tests, and sweating tests are also conducted.
Complex of medical care
Treatment of solarite is carried out taking into account the etiological features of the disease and is aimed at eliminating pathogenic factors. Due to the fact that the solar syndrome often develops against the background of peptic ulcer, the prescribed methods of treatment must take into account all the factors to exclude the occurrence of exacerbations. The purpose of therapeutic measures in the solar crisis is to initially stop the symptoms, and then move on to eliminate the cause.
Physical methods and medicines
Physical methods of treatment are aimed at eliminating pain depending on the cause of their occurrence.
 When inflammatory processes are prescribed UHF therapy, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of intoxication, aeroionotherapy of local purpose, antiviral and antimicrobial agents are used.
When inflammatory processes are prescribed UHF therapy, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of intoxication, aeroionotherapy of local purpose, antiviral and antimicrobial agents are used.
With degenerative abnormalities and dystrophy, vibration, vacuum therapy, segmental massage is used. Violations caused by immune malfunctions are treated with radon or hydrogen sulfide baths, conduct thalasso and aerotherapy. To maintain immunity, vitamin therapy is recommended( groups A, B, C).
In case of solar crises, it is recommended to use antispasmodic and pain medications. They use Tifen, Papaverin, No-shpu. Piroxane and Anaprilin are prescribed as adrenoblockers, and Pentamines are prescribed as ganglion blockers. 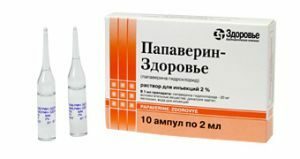
Also, when a crisis is often prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures in the form of mud applications or calcium electrophoresis on the area of pain. Well-established radon and coniferous baths. Effective is the use of ultratonotherapy, which affects the celiac plexus with the help of a mushroom-like electrode, moved along the front side of the abdominal wall from the navel to the xiphoid process.
A general recommendation for all patients is exercise therapy. Provides a selected set of exercises that help restore nerve fibers.
In addition, after a course of medical manipulations, the patient is recommended to sanatorium treatment in mud, balneo- and climatic-resorts.
Folk methods
Curing solaris with folk remedies is difficult. You can only temporarily stop the symptoms, but without proper treatment after a while, the ailment will come back again.
Traditional medicine recommends applying a fresh cabbage leaf on the site of pain localization, preparing infusions from nettle or plantain and drinking them daily. Warm warmers are also used to soothe pain in folk practice, which must be placed on the stomach. All these are temporary measures, only for a short time facilitating the state.
The prognosis for solarol does not imply a rapid cure. The disease lasts for a long time, with remissions and exacerbations. But with timely treatment and proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Patients with solar plexitis are contraindicated in excessive physical activity, contact with toxic substances, hypothermia, sedentary lifestyle.
In the period of attenuation of symptoms, suffering from plexitis recommended treatment in specialized sanatoria. The most popular resorts are Essentuki, Kislovodsk, Zheleznovodsk, Belarus.
Prevention of the disease
 To prevent the emergence of symptoms of solarite, it is necessary to treat infectious diseases in due time, to take measures for metabolic disorders.
To prevent the emergence of symptoms of solarite, it is necessary to treat infectious diseases in due time, to take measures for metabolic disorders.
In addition, you need to eat properly and fractionally, wear warm clothes in the cold season and avoid hypothermia. Doing sports help to form a muscular corset, preventing injuries of the celiac plexus.
Any pain in the solar plexus requires serious diagnosis and targeted treatment. The length and complexity of the treatment depends on how timely the patient turns to the doctor.