 The disease is characterized by the defeat of the cranial nerves, conductive disorders of motor and sensory functions.
The disease is characterized by the defeat of the cranial nerves, conductive disorders of motor and sensory functions.
Multiple alternating syndromes are caused by circulatory disorders in the spinal cord system, the appearance of tumors with localization in the brainstem, especially after craniocerebral trauma.
Stem symptom complexes are quite common, due to dysfunction of nuclei or brain processes.
The main cause of the appearance of the syndrome are changes in the functioning of the cerebral blood flow , with the appearance of tumors, injuries, in people with the disease - diabetes mellitus.
Paralysis or a cut of limbs develops due to the cortical-spinal path, and cross-hemianesthesia - when the sensitive conductive channels of the lower part of the brainstem are damaged.
Content
- Known types of syndromes
- bulbar syndromes
- Pontin violation
- brain stem lesions
- overall picture of symptoms
- Syndrome Benedict
- Pathology Notnagelya
- syndromes in diabetic neuropathy
- Syndromes lesions of the midbrain
- Syndromes medulla dysfunction
- Summary
Known types
syndromes in neurologyIsolate the following alternating syndromes:
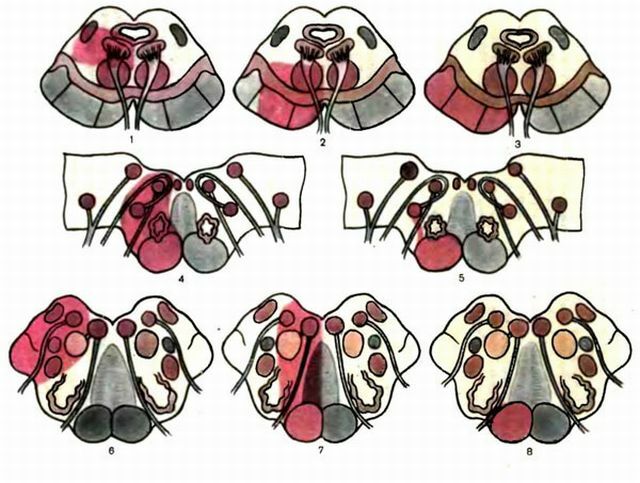
- bulbar disease ( with damage to the medulla oblongata) -Indra Jackson Avellisa, Schmidt, Wallenberg Zakharchenko, Babinski Nageotte.
- pontinous violations of ( in case of bridge failure) - the syndrome of Goebler, Fauville, Reymond Sestan, Brissot.
- peduncular syndromes ( in the presence of a defect on the brain stem) - Weber, Claude, Benedict, Notnagel.
 A sure sign of cerebellar involvement is intentional tremor - a characteristic symptom and approach to treating the disorder.
A sure sign of cerebellar involvement is intentional tremor - a characteristic symptom and approach to treating the disorder. Causalgia is a symptom characterized by the appearance of burning pain at the site of damage to the peripheral nerves. How to stop the pain?
Bulbar syndromes
Major bulbar alternating syndromes:
- Jackson's disease is characterized by damage to the sublingual nerve and paralysis of the extremities on the opposite side. There are deviations of the tongue to the side, or its complete atrophy. Sometimes its fibrillar twitchings are observed with muscle excitability. A person can not speak clearly, stammers and swallows half the words. Disassemble the speech of the patient is almost impossible.
- The Avellis syndrome affects the lingual-pharyngeal nerves, there is a paralysis of the palate and vocal cords, a swallowing disorder. In such patients, food intake is painful, liquid food enters the nasal passage, and the hard one goes to the intestines with difficulty, while the patient often coughs and suffocates while eating.
- The Schmidt's disease consists of the previous symptoms and the paresis of the vocal fold. A person can not talk, hardly uses food.
- The syndrome of Valenberg Zakharchenko is manifested by the appearance on the side of the focus of the symptoms of the defeat of the vagus nerve, a disorder of the sensation of the muscles throughout the face. In such cases, the patient's eyes, cheeks, nose are skewed, he does not see well, he breathes and hears. Appearance for a short time is distorted beyond recognition.
- Disease of the Babinsky Najott consists of cerebellar traits in the form of lesions of the olive-cerebellar path. The patient does not develop musculature. He hardly moves, the whole body is weakened and exhausted.
Pontine disorders
All types of disease manifest themselves as paralysis of the facial nerve, distortion of the outer shell of the face.
Pontine Alternating Syndromes:
- Gübler's syndrome is a pathological process associated with circulatory disorders in the paramedical arteries, a lagophthalmus arises, severe lachrymation.
- Fauville disease occurs due to thrombosis of the basilar artery, with metastases of cancer and sarcoma. There is a squint, the eye nerve expands. In the patient, one eye becomes larger than the other, it may not close at all during blinking and during sleep.
- The seizure's discomfort of Sestan is manifested by the paresis of the field of eyeballs, impaired sensation during movement, hemiparesis on the opposite side. Such people can lie for years on a medical cot in one position, not daring to turn half of the body.
- Brissot's syndrome distorts facial muscles on the facial nerve side, distortions of the pyramidal path appear. Irritation of the cells of the roots or nucleus of the facial nerve occurs, reflex spasms appear in the opposite area of the lesion.
Brain pedal lesions
Peduncular syndromes:
- Weber-Pobler's disease develops on the basis of pathological processes in the region of the legs of the brain, due to the violation of hemorrhage in the ischemic type. And also when squeezing the legs with a developing tumor.
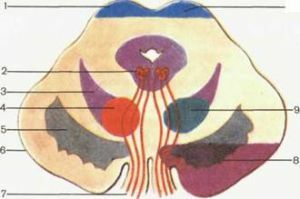
Clinical signs of the disease - paralysis of the muscles of the face, tongue and extremities by the central type. Symptoms are caused by a full or partial cut of the oculomotor nerve. In the case of muscle damage, the eyeball deviates toward the temple, and "looks" in the opposite direction of the paralyzed limbs. If pathology captures and the visual pathway, then hemianopsia occurs. The patient has an extended strabismus, he does not see well and can hardly distinguish colors. Also, the pharetic component, the clone of the hands and the foot can develop, and in the course of time there will be disturbances in flexural wrist protective reflexes. - Claud( red core) syndrome - captures the fibers of the oculomotor nerve, due to the defeat of the branches of the posterior cerebral artery, which supplies the lower parts of the red nucleus. Atherosclerosis and syphilitic endarteritis become a common cause of the onset of the disease.
The general picture of the symptoms of
There is a set of symptoms characteristic of all kinds of syndrome: 
- intensional jitter of the eyelid;
- dysarthria;
- Swallowing disorder;
- partial or complete ophthalmoplegia;
- distortion of the eye opening;
- full or partial paralysis of the face.
Benedict's syndrome
Benedict's syndrome( the upper side of the red nucleus) - affects the nucleus of the oculomotor nerve, sometimes the medial loop. Characterized by strabismus, mydriasis, trembling of the eyelid, hemiparesis.
Possible violations of associated eye movements, deviation of the eyes towards the focus of the disease. Increases the overall muscle tone, tendon reflexes, hemorrhage of the posterior cerebral artery in metastatic cancer.
Notnagel's Pathology
Notnogel's disease( quadruple) - occurs with extensive damage to the midbrain and its partial base. The main cause of the onset is a pituitary tumor, which when squeezed compresses the red nuclei and the upper legs of the cerebellum.
Clinical signs include ataxia, intentional tremor. Due to the development of the disease, central paresis of the facial and sublingual nerves appears.
A person talks badly, his speech becomes inarticulate, hardly pronounces consonant letters, and also poorly hears or does not understand speech of the interlocutor at all.
There are also eye symptoms, there is a bilateral ophthalmoplegia, medriz, ptosis. Visual disturbance occurs gradually, at first the pupillary reactions change, then paralysis of the eye appears( the patient looks up).
Later internal paralysis of the straight and upper oblique muscles adjoins.
Syndromes for diabetic neuropathy
The syndrome develops on the basis of unilateral damage to the brainstem in cases of craniocerebral trauma, peripheral paralysis on the part of the lesion in combination with the conductor disorders.
The clinical picture includes an isolated or extensive paresis of the diverting towards the angle of the lesion.
Extraocular muscles are innervated, and hemiparesis occurs.
 Vertigemigemigipichesky syndrome is a violation of the vestibular apparatus and motor area of the brain, characterized by severe noise in the ears, horizontal nystagmus in one direction, distortion of mimic muscles.
Vertigemigemigipichesky syndrome is a violation of the vestibular apparatus and motor area of the brain, characterized by severe noise in the ears, horizontal nystagmus in one direction, distortion of mimic muscles.
There is no pulsation of the carotid artery at the lesion site.
The nature of the pathological process can be judged by the dynamics of symptoms, signs of violations often develop gradually, the boundaries of the focus correspond to the zone of vascularization.
When bleeding into the brain stem, symptoms may increase due to reactive edema, accompanied by breathing disorders, cardiac activity, vomiting.
In the acute period, muscle tone decreases, certain facial features are distorted, speech changes, becomes vague and diffuse.
Syndromes of the defeat of the middle brain
Symptoms include internal, external and total ophthalmoplegia, the patient's view downwards, convergent strabismus. Discordance of eye movement, presence of paresis of limb. And also disturbances of balance, hearing, sight, swallowing and speech functions.
The syndrome of the red nucleus is manifested by symptoms of the defeat of the third pair of cranial nerves on the side of the focus.
There is ataxia, excessive reflex movements, with sharp sound stimuli.
Patients can shudder in a dream for no apparent reason, be afraid of every rustle, moan, throw up arms and legs, do not control the mimic movements.
Signs of impaired brain bridge activity:
To vegetative-trophic disorders should include:
- convulsions;
- abrupt temperature increase;
- uncontrolled weight gain( or weight loss);
- sweating disorder;
- HME;
- spasmodic defects on the affected side.
Syndrome of dysfunction of the medulla oblongata
The clinical picture can be the most diverse, except for the above mentioned syndromes there is a violation of sensitivity, paralysis of the limbs, malfunctioning in the coordination of movement, disorders in the work of the cardiovascular system.
Summary
A variety of variants of alternating syndromes are the main guarantee for their successful treatment: timely diagnostics and a professional approach to therapy.
Modern technologies allow to accurately determine the localization of the lesion and timely prevent its further development.



