In the pulmonological section of medicine, among the many pathologies of the pleural cavity the most common disease is pleurisy( pleurosis).
What is it? Pleurisy is a term that generalizes several diseases that cause inflammation of the serosa of the lung - the pleura. As a rule, it develops with existing pathologies, accompanied by the outflow of exudate or clots of fibrin into the pulmonary pleural cavity.
Pleuris development process
Pleura is a two-layered( in the form of two sheets) serosa, surrounding the lungs - the internal( visceral) leaf and the outer( parietal).The pleural internal sheet covers directly the lung tissue and its structures( nerve tissue, vascular network and bronchial branches) and isolates them from other organs.
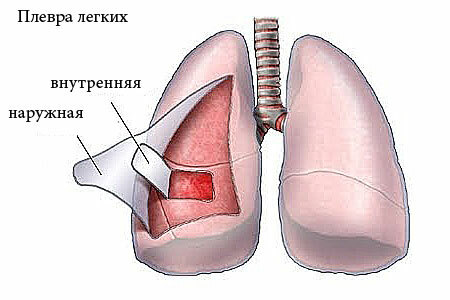 The outer pleural sheet lining the intracavitary thoracic walls. It ensures the safety of the lungs, and the sliding of the sheets, preventing their friction in the process of breathing.
The outer pleural sheet lining the intracavitary thoracic walls. It ensures the safety of the lungs, and the sliding of the sheets, preventing their friction in the process of breathing.
In a healthy, normal state, the distance between the pleural sheet shells does not exceed 2.5 cm and is filled with serous( serum) fluid.
Liquid enters between the pleura sheets from the vessels of the upper zone of the lung, resulting in processes of plasma filtration of blood. Under the influence of any injuries, serious illnesses or infections, there is a rapid accumulation of it between the pleural membranes, causing the development of inflammatory reactions in the pleura - pleurosis.
Normal operation of vascular functions, ensures the absorption of excess exudate, leaving a pleura on the pleural leaf in the form of fibrin proteins, so there is a dry( fibrinous) form of pleurisy.
The inconsistency of vascular functions provokes the formation of bloody, purulent or lymphoid fluid in the cavity of the pleural membrane - the type of exudative pleura.
Content
- 1 Causes of pleurisy, etiology
- 2 Symptoms of pleurisy lung
- 3 Therapies pleurisy
- 4 Possible complications and consequences
Causes of pleurisy, etiology
The cause of pleurisy is due to two large groups of provocative factors - infectious and non-infectious.
Infection, often becoming a causal factor in the initiation of inflammatory reactions with the formation of purulent fluid( effusion) between the membranes of the pleura. Penetration into the pathogen can occur as a result of direct contact with the infectious focus( usually in the lung), through blood and lymph, or through direct contact( surgery, injury, injury).As causative agent are:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis( pleurisy tuberculosis);
- Kokkovye bacteria;
- Parasites, protozoa and fungal infections.
The most common non-infectious factors are caused by the effect:
- Malignant neoplasms on the pleura or metastases of tumors located outside of it. The tumor process damages the membrane of the pleura, contributes to a significant increase in the secretion of exudate and the development of exudative pathology.
- Systemic diseases that cause vascular and tissue damage;
- Pulmonary embolism, when inflammation passes to the membrane of the pleura;
- Acute pathology of the heart muscle, due to a decrease in the immune factor;
- of uremic toxins in renal disease;Diseases of the blood and the digestive tract.
The manifestation of clinical forms of the disease is classified:
- according to the form or species;
- the nature of exudate and its quantity;
- at the site of inflammatory reactions;
- from clinical symptoms as shown - acute pleurisy, subacute or chronic inflammatory process with bilateral pleural or left-hand and right-pleurisy.
Symptoms of pleurisy of lungs
The disease develops, usually with a dry( fibrinous) form of pleurisy, lasting from 1 to 3 weeks. Absence of positive dynamics of treatment, facilitates its flow into exudative pleurosis, or chronic.
Dry( fibrinous) pleurresia is characterized by suddenness and severity of manifestation. The first symptoms of pleurisy are manifested especially sharp chest pain in the development of inflammatory reactions. Coughing, sneezing and vibrational movements cause an increase in pain.
Deep breathing is accompanied by a dry, hot cough. The temperature is absent, or increases slightly.
Are noted:
- a migraine, a sick status and delicacy;
- articular aches and periodical muscle pain;
- is listened to by hoarseness and noise - evidence of rubbing of pleura sheets caused by precipitation of fibrin.
Symptoms of dry pleurisy of various manifestations are distinguished by special features.
- Near-wall view of inflammation, the most common disease. Its main feature is a constant increase in pain symptoms during reflex coughing and sneezing.
- The diaphragmal inflammation process is characterized by signs of pain radiating to the shoulder area and anterior peritoneum. Hiccups and swallowing movements cause unpleasant sensations.
- Upper pleural pleurisy( dry) is recognized by the pain signs in the shoulder-scapula and neuralgic pathologies in the hands. This form develops in cases of tuberculous lesions of the lungs, which later turns into a squashed pleurosis.
Exudative, effusive form of pleurisy. Symptoms of pleurisy pleural effusive form, in its various forms, in the stage of initial development are similar to dry pleurisy. After a certain time they become "blurred", since the voids between the leaves are filled with effusion and the contact stops.
It happens that the exudative species develops without previous fibrous pleuressia.
For some time patients may not feel changes in the thoracic area, the characteristic symptomatology is manifested after a time:
- fever with very high temperatures;
- tachypnea and shortness of breath;
- swelling and cyanosis of the facial and cervical region;
- swelling of veins and venous pulsation at the neck;
- by expanding the sternum in the area of inflammation;
- by bulging, or by smoothing the intermuscular rib cracks;
- swelling in the lower skin folds in the area of manifestation of pain.
Patients try to avoid unnecessary movements, lie only on the undamaged side. Possible expectoration of bloody sputum.
Purulent pleura. It is formed in rare cases, very serious pathology with serious consequences, which, in the majority, end lethal. Very dangerous in children and old age. Purulent purulence develops on the background of inflammation, or abscess of the lungs. Shown:
- with stitching pains in the sternum, subsiding with a purulent filling of the pleural cavity;
- with subcutaneous cutting and weight;
- by the inadequacy of a deep breath and a sense of lack of air;
- gradual increase in dry cough;
- with a critical temperature and purulent expectoration.
If the disease is a consequence of lung abscess, then due to its rupture there is a painful lingering cough causing severe pain symptoms in the side.
Purulent exudate causes intoxication in the form of blanching of the skin and cold sweat. May increase pressure and build shortness of breath, making breathing difficult. With these symptoms of pleurisy of the lungs, both treatment and subsequent monitoring of its efficacy should be performed within the walls of the hospital.
Tubercular form. Characterized by the greatest frequency of development in childhood and young age. It manifests itself in three main forms - para- specific( allergic), perifocal( local) and tuberculous pleurosis.
Para-specific begins with high fever, tachycardia, dyspnea and pain symptoms in the side. Symptoms disappear immediately, after filling the pleural cavity with liquid.
Perifocal form manifests itself in the presence of tuberculosis lesions of pulmonary tissue that occurs for a long time with periods of exacerbation and spontaneous remissions.
Symptoms in the dry form of tuberculosis lesions are due to signs of friction of the pleural sheets, which cause breathing noises and pain in the sternum. The presence of effusion is accompanied by a clear symptom:
- fever and sweating;
- rapid heartbeat and suffocation;
- lateral and sternal pain muscle spasms;
- with a hoarse breath and a feverish condition;
- with a bumpy bulge and chest tightness in the area of the inflammatory reaction.
Methods for treating pleurisy

There is no single regimen for pleurisy. The basis of the therapeutic process is the physical diagnosis of the physician, after which appropriate methods of instrumental diagnostics are appointed, according to the results of which, individual therapy is selected taking into account all parameters of the pathology( form, species, localization, severity of the process, etc.
. As a conservative treatment, drug therapy is conducted.
- Antibacterial drugs, even before bacteriological results are obtained - preparations and analogues of Bigaflon, Levofloxacin, Cefepime or Ceftriaxone, followed bysubstitution for drugs for a specific pathogen
- Anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs used for inflammatory and degenerative diseases( Mephenamic acid, Indomethacin or Nurofen)
- Antifungal therapy for fungal causes of pathology
- When pleurisy, as a result of tumors, drugs are prescribednatural hormones and antitumor medications.
- In the treatment of exudative pleurisy, the use of diuretics is justified. And vascular drugs( as indicated).
- With dry form of pleurisy, cough suppressive drugs( Codeine or Dionin) are prescribed, thermal methods of physiotherapy and methods of tight bandage of the sternum.
- To prevent the development of pleural empyema, as a consequence of the complication of exudative pleurisy, puncture removal of purulent exudate is carried out, followed by washing the cavity of pleural sheets with solutions of antibiotics.
Possible complications and consequences of
The neglect of inflammatory processes in the pulmonary pleura leads to dangerous complications of pleurisy - adhesion of pleural sheets by adhesive process, local disturbances of blood circulation caused by squeezing the vessels with effusion, the development of single and multiple pulmonary pleural communications( fistula).
The most dangerous complication is pleural empyema( piothorax) in which the absence of adequate drainage of pus causes the development of multi-chamber empyema processes.
With processes of scarring and thickening of the pleural membrane, development of sepsis in adjacent tissues( septicopyemia), pathological changes in bronchi( bronchiectasis), amyloid dystrophy.
All this, in more than 50% of cases, can result in a fatal outcome. The percentage of deaths in children and elderly patients is much higher.