Often people who have a strong or prolonged cough, say that they have pneumonia. In fact, it can be a serious leaking ORZ or even tuberculosis and oncology.
It is necessary to distinguish correctly the given diseases from pneumonia in adults: their symptoms have characteristic features, and the treatment in each case is radically different.
Contents of
- 1 What is pneumonia?
- 2 Types of pneumonia and causes of infection
- 3 Symptoms of pneumonia
- 4 Features of pneumonia and its characteristic symptoms in children
- 5 Complications of pneumonia
- 6 Diagnosis of pneumonia
- 7 Therapeutic tactics
What is pneumonia?
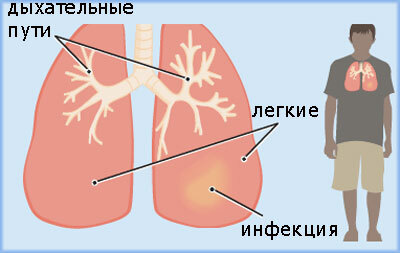
Under pneumonia, it is necessary to understand the inflammatory process in the lungs, affecting the pulmonary alveoli, the actual lung tissue( not the bronchi!).
Pneumonia is most often caused by the development in the lung tissue of pathogenic microorganisms - bacteria, viruses, fungi. However, noninfectious pneumonia is sometimes diagnosed.
Symptoms of pneumonia in an adult are always accompanied by changes in the X-ray and abnormalities in the laboratory blood test. It is on the basis of these diagnostic data that the patient is diagnosed with pneumonia.
Types of pneumonia and causes of infection
 Processes that caused pneumonia:
Processes that caused pneumonia:
- Infection with infection - primary pneumonia and secondary( occurs against the background of chronic bronchitis, influenza, acute respiratory infections);
- chemical exposure is a dangerous profession, inhaling chlorine when using household chemicals;
- severe allergic manifestations - bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis, COPD;
- high dose radiation irradiation;
- aspiration - vomiting masses, foreign bodies, food particles.
Depending on the type of infectious agent, pneumonia is distinguished:
- bacterial - pneumococcus most often, streptococcus, staphylococcus;
- atypical - klebsiella, mycoplasma, chlamydia, mycoplasma, E. coli;
- viral - cytomegalovirus, influenza virus;
- HIV-test - pneumocysts;
- fungal - candida.
The following species division of pneumonia is also used:
- out-of-hospital( home) - typical( without reducing immunity) and immunodeficient;
- nosocomial - with hospitalization for more than 2 days, use of artificial ventilation, treatment with cytostatics, transplantation of donor organs;
- associated with medical intervention - often in residents of nursing homes, when carrying out hemodialysis.
Predisposing to the development of pneumonia factors:
- smoking, alcoholism;
- supercooling;
- frequent colds;
- concomitant pathology - heart disease, chronic pulmonary pathology, diabetes mellitus;
- immunodeficiency, including HIV;
- inadequate care for the elderly, lying patients;
- postoperative period;
- adverse living conditions, malnutrition.
Symptoms of pneumonia

First symptoms of pneumonia, photos
Incubation, the period from infection to the appearance of the first signs of pneumonia in an adult with or without a temperature lasts from 1-3 days to 2 weeks.
The long incubation period is typical for atypical inflammation.
Depending on the area of the lungs, pneumonia happens:
- Focal - inflammatory process small area, lesion of several alveoli
- Segmental - inflammation does not go beyond one lung segment
- Share - the whole part of the lung is affected
- Drainage - initially small inflammatory foci expand and unite in larger
- Croup - inflammatory foci in bothlungs.
The course of any pneumonia passes through several stages:
- tide( red surgery) - lasts up to 2 days, exudation in the alveoli leads to an increase in the symptoms of inflammation;
- hepatitis( gray surgery) - an increase in the pulmonary tissue of inflammatory exudate and the beginning of the fight of leukocytes with the pathogen, the period lasts 5-10 days;
- the stage of resolution - the gradual resorption of the inflammatory fluid in the lungs, the restoration of respiratory function and the elimination of symptoms occurs on the 7-11th day.
More on symptoms and treatment of pneumonia in adults
Classical picture of pneumonia:
- intoxication - weakness, sweating, headaches, lack of appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- increase in temperature - at an atypical temperature of up to 37.5 ° C, with a bacterial one - to high figures, temperature jumps in the range of 1.5 ° C are often observed;
- shortness of breath - since the first days of illness;
- cough - from 3-4 days, at first dry, and then with sputum discharge( often rusty), an attempt to take a deep breath leads to a fit of coughing;
- tenderness in the chest - increases with inspiration and with a fit of cough, has an accurate localization, more intense when tilted to the affected side;
- external signs - pallor of the skin, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, often herpes on the lips.
A characteristic sign of pneumonia is the inefficiency of antipyretic agents. Often in adults, pneumonia occurs without coughing.
This development is observed with weak immunity, prolonged inflammatory process due to inadequate antibiotic therapy, with regular suppression of cough reflex.
Symptoms of certain types of pneumonia
- Focal - the symptoms of pneumonia in adults with limited inflammation of a small area often develop without temperature.
- Streptococcal / Staphylococcal - Coughing attacks are not so debilitating. A good effect is provided by expectorants.
- Bacterial - persistent hyperthermia up to 41ºС for more than 3 days.
- Viral - periods of hyperthermia up to 38 ° C are replaced by normal temperature.
- Atypical - rhinitis, bouts of dry cough more often at night / morning, increased axillary lymph nodes, nasal bleeding.
Features of pneumonia and its characteristic symptoms in children

Symptoms of pneumonia in a child, photo
Symptoms of pneumonia in children, especially before the year, differ slightly from the clinical picture of pneumonia in an adult. Distinctive features of pediatric pneumonia:
- often develops against a catarrhal disease - a sharp deterioration in the condition of the baby 2-3 days after the apparent recovery;
- comes to the fore with shortness of breath - up to 50-60 per minute in babies up to a year and up to 40 in mines to 5 years;
- retraction of intercostal and gaps and supraclavicular area;
- the wings of the nose swell, sometimes a thickening of the nasolabial triangle is marked, its cyanosis is pronounced;
- expressed abdominal syndrome - flatulence, pain, diarrhea;
- marked hyperthermia and normal temperature in often ill children;
- adynamia, confusion.
The smaller the baby, the less pronounced are the signs of pneumonia."Raging breath", immobility and swollen wings of the nose are dangerous signs that require urgent medical consultation.
More on the symptoms and treatment of pneumonia in children
Complications of pneumonia
- Pleurisy.
- Acute respiratory failure.
- Lung edema.
- Formation of pulmonary abscess.
- Infectious-toxic shock.
- Myocarditis, meningitis.
Diagnosis of pneumonia
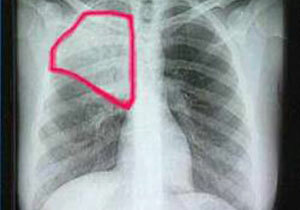
- Auscultation of the lungs - mild respiration in the initial phase of pneumonia, rales in the gray curing stage.
- X-ray - fixing the boundaries of inflammation, re-conducting it helps to track the effectiveness of treatment.
- Sputum analysis( Gram staining) - identification of the pathogen.
- Blood test - leukocytosis, high ESR.
Treatment tactic
Treatment depending on the type of pneumonia includes:
- antibiotic therapy or antiviral drugs( if the temperature persists for 3 days of treatment with antibiotics, replace the drug);
- expectorants;
- detoxification - IV infusion;
- for infectious shock - corticosteroids;
- immunostimulants;
- in severe cases - bronchoscopy, IVL.
Therapeutic tactics are determined individually, conducted with mandatory radiographic monitoring and fixation of blood indicators. Even after a course of effective treatment, mild symptoms( cough, slight shortness of breath) persist for some time.