A number of diseases can not be diagnosed only by blood tests or complaints of the patient. Some cases require careful examination to identify or rule out a possible pathology. A biopsy of the prostate gland is indicated in those complex cases when the doctor has a suspicion of developing a cancer in his or her patient. This procedure is final when making a diagnosis, allows you to choose a treatment technique that, in prostate cancer, involves surgical intervention.
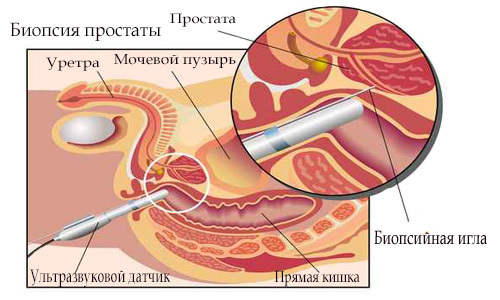
What are the cases of a biopsy procedure?
The prostate biopsy process is today the most common, successfully applied by specialists from all over the world. The most serious indication for a biopsy is the accurate diagnosis of cancer in men. The main purpose of the examination is to provide a histological check of the diagnosis aimed at studying the structure, vital activity, development of tissues or cells. Thanks to a biopsy, it becomes possible to estimate the prevalence of the neoplasm, by studying its nature, growth and stage. All this allows us to develop an adequate treatment regimen aimed at complete or maximum elimination of the tumor or prevention of its spread.
Prostate cancer
The adult part of the male population is exposed to prostate cancer. Unfortunately, the disease is diagnosed in most men at a late stage of its development, which complicates the treatment process. Only in a few, the disease is detected at random, as a result of a prophylactic examination of the patient. Often the symptoms are deceptive because of their similarity to those caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia, and are characterized by:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- by difficulty of the process of urination;
- spastic or painful sensations in the perineum;
- with a delay in urine.
Risk factors due to:
- elderly age - it is noted that a greater percentage of the disease falls on men over 65 years of age;
- with severe hormonal disorders;
- eating habits - that category of men who prefers fatty foods, is exposed to prostate cancer 2 times more, as animal fats contribute to the development of malignant tumors;
- hereditary predisposition;
- negative environmental factors, such may be ultraviolet rays;
- by viral infections;
- harmful working conditions.
Prostate biopsy is performed often after the patient has been subjected to a thorough examination, that is:
- by rectal palpation;
- to transrectal ultrasound examination;
- study related to the evaluation of the prostate-specific antigenic level.
By means of the obtained results of prostate biopsy, there is a unique opportunity to choose the most competent method of treatment for a particular patient. The results are based on the use of several methods of performing a biopsy, but the majority of specialists chose the transrectal as it is recognized as the most painless. The transrectal method of examination is carried out with the help of a "biopsy gun" and disposable needles designed specifically for carrying out such manipulations.
How is biopsy performed?
Prostate biopsy is performed in several ways, depending on which part of the organ has been damaged by neoplasm. Medical practice distinguishes its following types:
- transrectal;
- transperineal;
- sextant;
- advanced;
- saturation.
The method of transrectal biopsy is the least painful, carried out through the rectum. The transperineal method( it is also called the perineal method) is used when the patient has signs of anus stenosis or rectal resection, and there is no way to insert the instrument. The sextant method of biopsy is carried out in such a way that provides the possibility of taking tissue samples from 6 different sites. That is, several tissue samples affect completely different areas of the prostate gland.
Thanks to the use of an extended biopsy method, the possibility of detecting prostate cancer increases, since samples are taken from 10-18.The remaining positive aspects of the extended biopsy method rest on the high possibility of a coincidence of the sum on the Gleason scale( this scale allows histological evaluation of differentiation of prostate cancer, with a high sum judged of a serious prognosis of the disease) and the ability to identify one- or two-sided neoplasm.
No less effective is the implementation of biopsy by the carbonation method, in which the samples are taken from 24 points.
The size of the organ and the level of PSA influence the choice of this or that method of research.
- If PSA & lt; 20 ng / ml, prostate volume <50 cm3, samples are taken from 12 points.
- If PSA <20 ng / ml, gland volume> 50 cm3, samples are taken from 18 points.
- If PSA & gt; 20 ng / ml, prostate volume <50 cm3, samples are taken from 8-10 points.
- If PSA & gt; 20 ng / ml, prostate volume> 50 cm3, from 12 points.
Recommendations for biopsy preparation and its implementation
Prostate biopsy requires some preparation, which requires the patient to be sure:
- did not use funds significantly affecting the structure of the blood during the week before the procedure itself( such as "Aspirin", "Heparin ", others);
- stopped preparations with anti-inflammatory effect 3 days prior to the study;
- took antibacterial preparations 3-5 days before the study to prevent inflammation of the prostate;
- in the evening and in the morning before the process applied the measures of the cleansing enema, since the procedure is performed on the empty intestine.
Only after following the recommendations described above, a biopsy procedure can be performed, as the precise assessment depends on the correct approach to the preparation. Examination is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning. Before the examination of the organ in the rectum area, an anesthetic is administered( usually "Lidocaine" is used as such).After a certain time after local anesthesia, an ultrasonic sensor with a nozzle is introduced, specially designed for careful insertion of the needle. By means of this needle samples from certain points of the organ are taken.
Prostate biopsy is performed under a control ultrasound to determine the sampling points. Patients easily undergo the procedure, sometimes unpleasant sensations can occur, lasting for long. Taken samples are transferred to the appropriate laboratory for research, allowing to determine the stage of the disease.
During the day after the procedure, the patient is advised to avoid any heavy workload caused by physical activity in order not to provoke complications. After the completion of the procedure, a tampon is placed on the affected area of the prostate to prevent bleeding. A day after the procedure, the swab is removed.
Risk of Complications
Any process involving the taking of material from a specific tissue site can provoke certain complications. A biopsy of the prostate gland also leads to some complications that can affect any patient. Complications are characterized by:
- hematuria, that is, the presence of blood in the urine;
- with pain in the rectum or perineal region( depends on which biopsy procedure was applied);
- hemospermia, accompanied by detection in the sperm of blood;
symptoms of acute prostatitis; - bleeding from the rectum( if the organ was injured when the needle was inserted);
- inability to urinate caused by acute urinary retention;
- with acute orchiepididymitis( development of the infection process of the testicles or appendage);
- loss of patient's consciousness during the study.
If bleeding lasts more than 2 days and the patient is suffering from fever, a compulsory medical consultation is recommended. The possibility of encountering one of the complications listed above should not be an obstacle to the patient's biopsy procedure. The risk of running the disease in many ways exceeds the risk of possible complications.
What cases require a re-examination?
It happens that there are no cancer cells in the results. However, this is not proof that the patient does not have prostate cancer. With this in mind, specialists recommend an additional examination with biopsy of the prostate, which is performed if:
- during the initial study, a high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia was detected;
- there is a PSA increase of more than 0.75 ng / ml / year;
- there is a suspicion that radiation therapy has proved ineffective;
- palpation reveals questionable areas or some changes in the organ;
- is observed relapse, provoked by radical prostatectomy.
Another biopsy is performed only 3-6 months after the initial. The technique of secondary research differs from the previous one using the extended or saturating methods of sampling. The third and subsequent sampling processes are used in the case of those patients whose indications for the procedure are caused by factors characterized by an increased risk associated with the detection of cancer of the gland. An additional examination is prescribed with:
- the presence of serious signs of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia;
- significant increase in the level of total PSA;
- marked decrease in the ratio of free PSA to the total;
- increased the speed of PSA above the accepted;
- the presence in the previous samples of some changes caused by small-scale proliferation of the atypical form.



