 The penetration of the intracellular parasite Clamidia into the human body causes the development of chlamydosis, one of the most common venereal diseases.
The penetration of the intracellular parasite Clamidia into the human body causes the development of chlamydosis, one of the most common venereal diseases.
Infection with chlamydia can occur not only sexually, but also occasionally by domestic routes within the family, from animals, through the pool water. Children can get infected from a sick mother during the intrauterine period, become infected during passage through the birth canal.
Chlamydial infection in the initial stages in most cases is asymptomatic, latent, which makes it extremely difficult to diagnose it.
But without treatment, it takes a chronic form, leads to complications, lesions of  internal organs and systems.
internal organs and systems.
After infection with Clamidia trachomatis, chlamydial arthritis may occur, which is attributed to acute autoimmune lesions of peripheral joints.
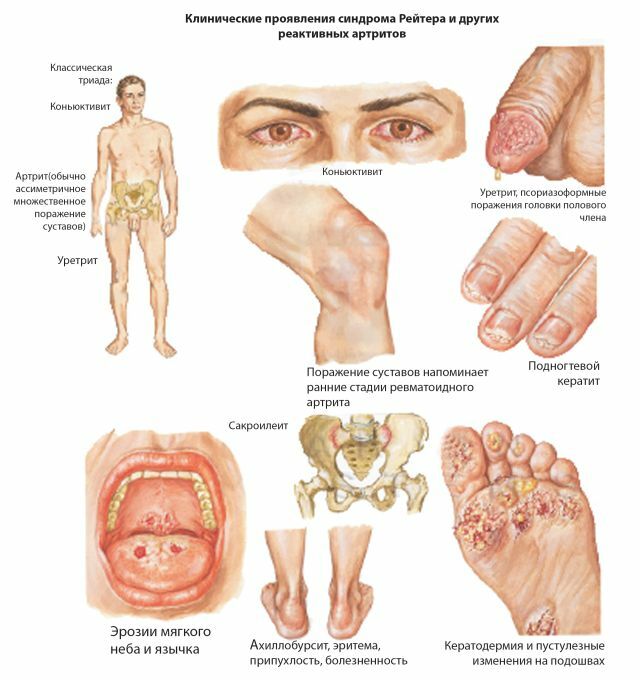
This disease is a manifestation of Reiter's syndrome, which simultaneously or sequentially affects the genitourinary system, the mucosa of the eyes and joints.
Contents of the article
- Mechanism and causes of inflammation
- Classification of the disease
- Symptoms of chlamydial arthritis
- Diagnostic approach
- Medication
- Antibiotic therapy
- Anti-inflammatory therapy
- Immunosuppressors
- What is the danger?
- Prevention of lesions - everything is simple
Mechanism and causes of inflammation
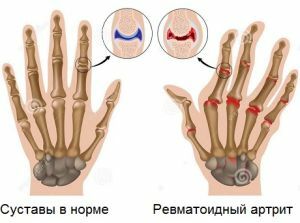
The inflammatory process with reactive postinfectious arthritis is caused by the activity of the body's own immune system.
Joints are affected by antibodies produced in response to infection, attacking connective tissue cells by mistake due to the similarity of their structural proteins to pathogens.
In this case, antibodies do not affect pathogenic bacteria, and immunity does not prevent the destruction of healthy tissues. The risk of developing arthritis after infection has increased the presence of specific genes in humans.
 At the initial infectious-toxic stage of the disease, the immune cells get acquainted with chlamydia, it is clinically manifested by urethritis. At the next autoimmune stage, autoantibodies are formed, which damage the synovial membrane of the joints.
At the initial infectious-toxic stage of the disease, the immune cells get acquainted with chlamydia, it is clinically manifested by urethritis. At the next autoimmune stage, autoantibodies are formed, which damage the synovial membrane of the joints.
The first symptoms of joint damage are noted in 2-10 weeks from the onset of the infectious disease, as the immune system takes time to recognize foreign antigens and develop antibodies to them.
Chlamydial arthritis is more common in men aged 20-40 years, the immune system of women is more resistant to pathogenic infections, which can cause the development of the inflammatory process in the joint bag.
Joint pathology is observed in 5-15% of patients with chlamydosis, Reiter syndrome accounts for about 60% of cases of development of urogenital arthritis.
Classification of the disease
The number of affected joints is as follows:
- monoarthritis - one joint is affected;
- oligoarthritis - 2-3 joints are involved in the pathological process;
- polyarthritis - more than 3 joints were affected.
Downstream:
- acute form - active phase duration 1-2 months;
- lingering form - active phase duration up to 1 year;
- chronic form - with periods of exacerbation more than 1 year;
- relapsing form - the immune system is exposed to pathological processes on average once every six months.
According to the degree of activity:
- is low;
- average;
- high;
- propensity to remission.
Symptoms of chlamydial arthritis
Symptoms of this type of arthritis most often occur after the manifestation of such pathologies as urethritis, adnexitis, prostatitis, cerviitis, conjunctivitis caused by damage to tissues of organs by chlamydia.
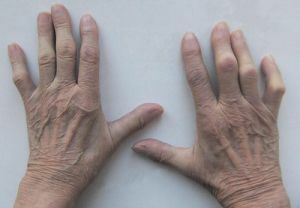
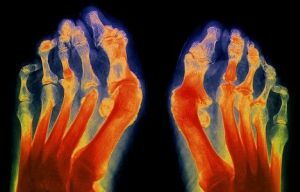
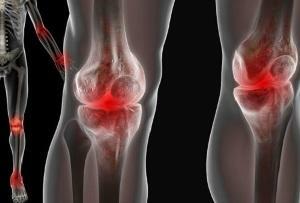
The onset of the disease is marked by the acute development of the inflammatory process in the area of small joints of the feet or hands, the ankle, shoulder, knee, hip joints, spine can be affected. A characteristic symptom is a sausage-like thickening of the toes.
Inflammation is unilateral, in polyarthritis asymmetric joints are affected, the intensity of manifestations of the disease can grow slowly or develop rapidly, per day.
The patient has severe pain and stiffness during movement, asymmetric swelling in the affected area, redness of the skin, accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity, increased body temperature, lymph nodes increase, weakness, fatigue, worsening of appetite.
Over time, soft tissues are located around the joints, joints of the fingers are deformed, contractures appear.
Diagnostic approach
To diagnose the violation, the following research methods are used:
- blood test total - reveals an increase in the number of leukocytes and platelets, increased ESR;
- blood biochemical analysis - Detects acute inflammation phase proteins, absence of rheumatoid factor;
- urine analysis total - shows the appearance of protein, the release of leukocytes and erythrocytes;
- study of synovial fluid - shows low viscosity and fluid turbidity, increased white blood cell count, increased protein content;
- smear from the urethra or cervix - detects the presence of Clamidia trachomatis;
- serological studies of - show high titers of antibodies to Clamidia trachomatis in blood and synovial fluid;
- radiograph of the joint - shows erosive-destructive changes, narrowing of the joint between the joints, reduction of bone density;
- MRI - shows the condition of bones and periarticular soft tissues;
- genetic studies - in 80% of cases, the histocompatibility antigen of the HLA-B27 system is detected.
Medical treatment
The choice of methods of treatment, medicines and their dosage depends on the stage of the pathological process, the severity of symptoms, the general condition and age of the patient.
Treatment should be carried out only in a hospital by a rheumatologist after a complete examination of the patient. Its goal is to eliminate chlamydia and remove the inflammatory process in the joints.
Antibiotic therapy
Uses: 
- antibiotics of the macrolide class of the 2-3rd generation ( Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Macropen, Wilprafen);
- of the tetracycline ( Doxycycline, Tetracycline);
- class fluoroquinolones ( Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin).
The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks. Do not use antibiotics penicillin series and cephalosporins, because they form a resistance in chlamydia.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic effect are used, in the form of tablets, injections, ointments( Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Meloxicam, Naproxen).
Glucocorticoids that are administered intra-articularly or intravenously by
( Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Cortisone, Methylprednisolone) have a more pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
Immunosuppressors
 Drugs that depress the immune system are prescribed only in the most severe cases of reactive arthritis, because they have many side effects( Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide, Ciclosporin, Methotrexate).
Drugs that depress the immune system are prescribed only in the most severe cases of reactive arthritis, because they have many side effects( Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide, Ciclosporin, Methotrexate).
They disrupt the synthesis of antibodies, which leads to the reduction of the inflammatory process in the joints.
In parallel with Reiter's syndrome, treatment of urogenital infection, prescribed by the infectious disease doctor, treatment of the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye, appointed by an ophthalmologist is performed.
It is not uncommon to repeat courses of antibiotic therapy, which is connected with the peculiarities of the structure and vital activity of chlamydia. The final recovery is confirmed by a negative final analysis.
What is the danger?
Without proper treatment, chlamydial arthritis becomes chronic and leads to the following complications: 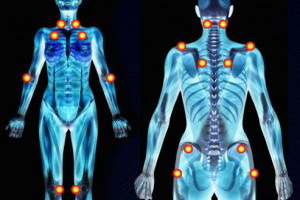
- restricting joint mobility up to human disability, their deformities, the appearance of contractures;
- chronic joint pain due to structural changes;
- chronic diseases of the internal organs - the heart, lungs, kidneys;
- reduced visual acuity, the development of glaucoma, cataracts.
Prevention of defeat - everything is simple
In order not to become infected with chlamydia and to avoid the development of chlamydial arthritis, several simple rules should be observed:
- to avoid accidental sexual intercourse;
- must use condoms;
- each family member have separate towels and washcloths, regularly wash the tub and toilet bowl with disinfectants;
- thoroughly wash after visiting the pool;
- at the slightest suspicion of urogenital infection - the appearance of atypical secretions, itching and pain when urinating, drawing pains in the abdomen immediately seek medical help and undergo examination by specialists.