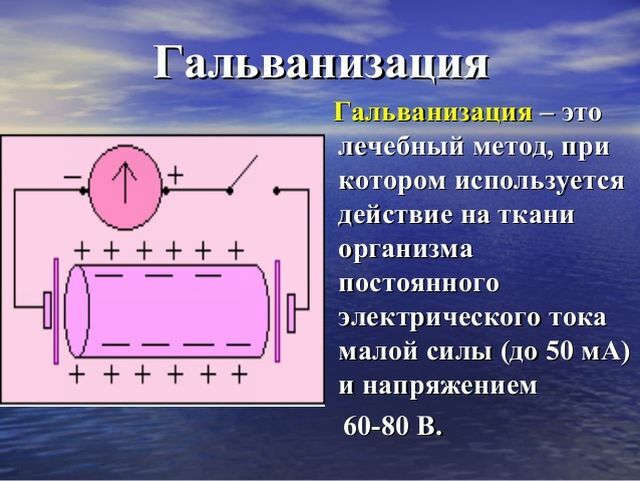
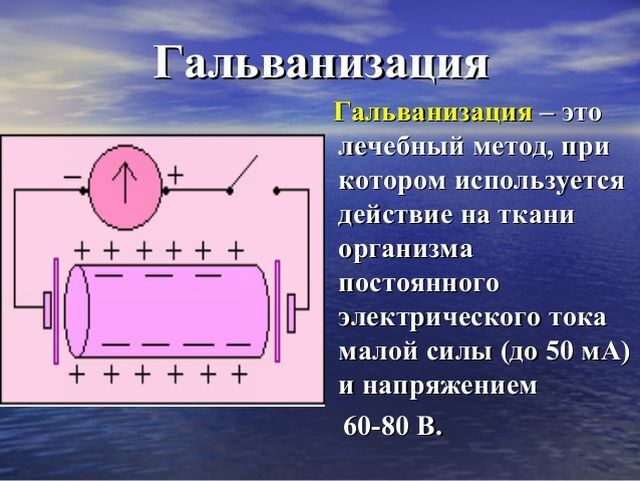
 Galvanization is a physiotherapeutic method in which the patient's body is exposed to a continuous electric current of low strength and tension.
Galvanization is a physiotherapeutic method in which the patient's body is exposed to a continuous electric current of low strength and tension.
Galvanic current penetrates into the organs and tissues of the human body, stimulating the appearance of complex physico-chemical processes.
Contents
- Therapeutic effect
- The main parameters of the procedure
- The main parameters of the procedure
- The place in the neurological and general medical practice
- Techniques and methods of the procedure
- Electrophoresis as an improved galvanization method
- Applied devices
- Contraindications to the application of physiotherapy
The therapeutic effect of
The mechanism of galvanization is the continuous action of electric currentsmall strength and tension on individual parts of the body and skin of the patient. When the current is applied to the human body in the cells, the ion balance changes, and physical and chemical transformations take place.
Application of galvanization leads to such effects:
- improvement of blood circulation and lymph circulation;
- increases the level of biologically active substances;
- stimulates metabolic and trophic processes;
- is enhanced by trophic and regulatory function of the nervous system;
- improves blood flow to the brain;
- normalizes the metabolism in the brain;
- is anesthetic;
- has a sedative effect;
- muscle relaxant effect;
- secretory function of glands is activated;
- prolongation of exposure to psychotropic drugs( Seduxen, Haloperidol, Amisil);
- increase in the overall level of immunity;
- improved tissue regeneration.
Basic parameters of procedure
The procedure for galvanization in physiotherapy can be carried out with a different dosage of density, current intensity and duration of exposure. For a given physiotherapeutic method, low-voltage current( up to 80 V) and insignificant force( up to 50 mA) is used. The current density varies from 0.01 mA / cm2 to 0.08 mA / cm2.
The strongest current is used for therapeutic treatment of the trunk and limbs( from 15 mA to 30 mA).When applying electrodes on the head, face, mucous membranes, the current does not exceed 5 mA.
The current to the patient's body is supplied by means of electrodes( lead plates up to 1 mm thick, with a wet gasket, and a cord attached to the plate).Also, the electrodes can be built into the tank( "bathtub"), used to immerse a part of the body that requires therapy. The hydrophilic gasket and water in the reservoir are necessary to prevent burns of the skin of the patient with electrolysis products.
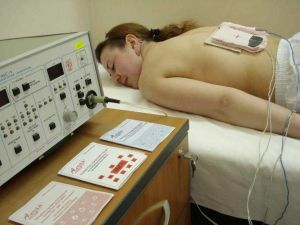 Electrodes can have a rectangular shape, be in the form of a half mask( application on the face), in the form of a "collar"( for impact on the upper back and shoulder), in the form of a funnel( for use in the ears), "bath".Also, cavity electrodes are available for intravaginal and rectal administration.
Electrodes can have a rectangular shape, be in the form of a half mask( application on the face), in the form of a "collar"( for impact on the upper back and shoulder), in the form of a funnel( for use in the ears), "bath".Also, cavity electrodes are available for intravaginal and rectal administration.
After the electrodes are fixed on the patient's body, or the body part is placed in the "bathtub", a current is started, and gradually increases until the necessary parameters are reached. The procedure ends with a gradual reduction of the current before it turns off.
Electrodes can be applied transversely or longitudinally. Transverse overlap contributes to a more effective effect on deep tissue. The electrodes are located on opposite sides of the body, opposite each other. Longitudinal arrangement provides an impact on the surface areas of tissues. Electrodes are superimposed on one side of the body.
After a 5-7 galvanization session, the patient's condition may worsen. This effect indicates a positive effect of the procedures performed.
The duration of the procedure is from 15 minutes( under general exposure) to 40 minutes( with local exposure).The therapeutic course consists of 10-20 sessions of galvanization. It is recommended that the procedure be performed every day or every other day. Passing a second course is possible in a month.
A place in the neurological and general medical practice
Galvanization is an effective method of therapy for such neurological diseases:
- lesions of the peripheral and central nervous systems as a result of traumatic, toxic and infectious effects;
- neuroses;
- consequences of spinal cord and brain injury;

- neuritis;
- circulatory disorders in the spinal cord and brain;
- Multiple Sclerosis;
- paralysis, paresis;
- encephalopathy;
- osteochondrosis.
Also galvanizing is widely used in such fields of medicine:
- cardiology;
- gastroenterology;
- Urology;
- pulmonology;
- dentistry;
- ENT;
- surgery;
- endocrinology;
- orthopedics;
- gynecology;
- cosmetology;
- dermatology;
- ophthalmology.
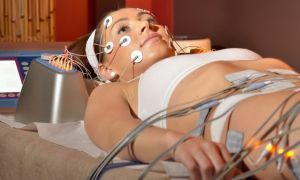
Techniques and methods of procedure
Before the procedure begins, the patient's skin must be cleaned. In the presence of damage to the skin, these areas must be treated with petroleum jelly, and covered with cotton, rubber or oilcloth.
Electrodes are applied longitudinally( affecting surface tissues) and transversely( affecting deep tissues and organs).The arrangement is cross-diagonal.
During the procedure the patient occupies a sitting or lying position. Electrodes are fastened with a plaster, bandage, or small containers with sand.
There are various methods of applying galvanization:
- General .A hydro-galvanic bath is used, consisting of four separate baths with water, into which the limbs of the patient's
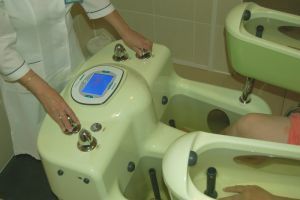 are immersed. Current strength does not exceed 30 mA.
are immersed. Current strength does not exceed 30 mA. - Local .2-4 lead electrodes are applied, which are superimposed on the patient's body.
- Processing of reflex segmental areas .Influence on the paravertebral parts of the spine. Electrodes for the collar zone and electrode "cowards" are used. The current strength starts from 6 mA and increases gradually to 16 mA( for several sessions).
- Longitudinal galvanizing of the head .Two electrodes are used: one on the forehead, the other in the back of the neck and neck.
- Method of Bourguignon .On the patient's closed eyelids, pieces of gauze are placed, covered on top with round metal plates that are connected to the clamp of the galvanizing apparatus. The second electrode is located under the occipital mound. The patient's hair is abundantly moisturized.
- Galvanization of the face area .A half-mask electrode is placed on the patient's face. Adherence should occur in the area of the chin, cheek and forehead. The corner of the mouth and eyes remain free.
- Application of procedure for lesions of the nerves of the upper and lower extremities .When the upper limbs are damaged, the electrodes are placed on the lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae, the region of the forearm. When treating lower extremities, the area of application of electrodes depends on the site of the lesion.
- Chamber baths .Depending on the required number of exposure points( number of limbs), one-, two-, three- and four-chamber baths are used.
Electrophoresis as an improved method of galvanizing
The combination of galvanization with drugs is called electrophoresis. Galvanic current is used for more effective assimilation of medicinal preparations by the body, and makes their impact effective and soft.
Drug solutions are introduced into the body through the mucous membranes and skin under the influence of an electric field. The most effective is the effect on the hair follicles, the ducts of the sebaceous glands, intercellular spaces and sweat glands.
The drugs used in electrophoresis contain ions( charged particles) that are introduced into the body by various electrodes. The choice of electrode depends on the ion charge. During the same procedure, different substances can be introduced from different points of exposure.
The electrophoresis procedure is painless, however, uncomfortable sensations in the form of a slight tingling in the area of application of the electrodes are possible.
Electrophoresis is recommended for such neurological diseases:
- neuroses;
- inflammatory processes;
- is a migraine;
- organic diseases of the central nervous system;
- neurasthenia.
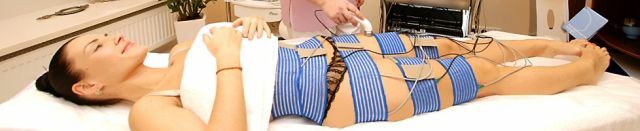
Electrophoresis can be performed in various ways:
- Through the skin - the electrodes are placed on the patient's skin.
- With the help of baths, a solution of medicinal substance is placed in a reservoir with built-in electrodes, and a part of the body that requires action is placed in this "bath".
- Cavity method - the drug solution is injected rectally or into the vagina. The electrode is also inserted inside. From the outside of the body is attached an electrode that has a different polarity( used to treat diseases of the large intestine and pelvic organs).
- The interstitial method - the drug is administered orally, by inhalation, intravenously, the electrodes are applied to the affected organ or area( most effective in respiratory diseases).
As a result of the procedure, medicinal substances accumulate in the skin, and can stay there from 12 hours to 20 days. Due to this, longer-term effects of drugs are provided, and slow elimination of them from the body.
The advantage of the method is that the accumulation of the drug occurs locally, without spreading it to the entire body.
The concentration of the drug in the field of application is several times higher than the concentration for conventional input methods. Electrophoresis allows the introduction of drugs in the area with a violation of microcirculation and circulation, where the penetration of medications is usually difficult. A positive feature of the method is also the low level of allergic and adverse reactions.
Applicable devices
Apparatus for galvanizing and electrophoresis are electronic rectifiers of AC lighting network. For the galvanization procedure, the following devices are used:
- Potok-1, Potok-01M, Potok-Br;
- "GR";
- "AGN-1", "AGN-2";
- "Radius";
- "NET";
- ETER;
- ELFOR, ELFOR-Prof;
- "ESMA".

Apparatus for galvanizing and electrophoresis ELFOR
Contraindications to the use of physiotherapy
The use of galvanization is not recommended in such cases and conditions:
- of individual galvanic current intolerance;
- presence of neoplasms or suspected of them;
- of acute inflammatory diseases;
- cardiovascular disease in severe form;
- of acute purulent diseases;
- systemic blood diseases;
- expressed atherosclerosis;
- eczema, dermatitis;
- febrile states;
- skin diseases;
- skin damage;
- impaired skin sensitivity;
- during pregnancy;
- for cachexia.