Hormones participate in the processes that control the activity of the whole organism. But men often have hormonal changes for various reasons. Sometimes this is considered normal, and in other cases - pathology. One such condition is hyperprolactinemia in men . This condition is the increased content of the hormone prolactin. This condition occurs mainly in 25-45-year-old men and causes a lot of violations in reproductive and sexual activity.

Causes of hyperprolactinemia development
Hyperprolactinemia occurs in men of two aetiological varieties:
Pathological pathology developed against a background of any tumor or pathological process:
- Due to pituitary or hypothalamic tumor processes( meningioma, germinoma, glioma, adenoma, prolactinoma, etc.);
- Due to pathologies of an infectious origin like meningitis, encephalitis;
- As a result of granulomatous or infiltrative processes such as sarcoidosis, histiocytosis, tuberculosis, etc.;
- Because of primary hypothyroidism;
- Because of cirrhosis of the liver;
- Against the background of chronic kidney failure;
- Idiopathic form, when the reasons for revealing it is not possible;
- Due to prostatitis of chronic course;
- Caused by systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Due to abnormalities of the activity or pathological conditions of the adrenal glands;
Physiological hyperprolactinemia has nothing to do with pathological disorders and arises from natural processes in the male body:
- Due to the abuse of protein foods;
- Against the backdrop of stress;
- After sexual intercourse;
- After sleep;
- Due to reduced glucose content;
- After physical activity;Surgical or medical interventions;
The drug form of an increased level of prolactin arises from the use of medications:
- Narcotic action( amphetamines, morphine, cocaine, etc.);
- From the group of antidepressants( Doxepin, Amitriptyline, etc.);
- Based on estrogen;
- Hypotensive action( methyldofa or reserpine);Calcium antagonists like Verapamil;
- Histamine receptor antagonists( famotidine or cimetidine).
The importance of prolactin for the male body
According to accepted standards, the concentration of prolactin should be around 400 mU / l or 15-20 ng / ml. Prolactin plays a crucial role. This hormone, at its normal level, enhances the effect of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones that support and control the processes of sperm formation and maturation( spermatogenesis).In addition, prolactin helps to enhance the processes of material exchange and increase the mass of male testes, increases the seminiferous tubule.
Attention! The increased level of prolactin hormone has a very negative effect on spermatogenesis - it contributes to impaired motor activity of spermatozoa, reduces their quality, provokes an increase in pathological spermatozoon forms or dead spermatozoa. All this invariably leads to male infertility.
No less important functions of prolactin are to stimulate the secretory abilities of the prostate, to regulate spermatozoa mobility. Prolactin actively participates in the metabolism of carbohydrates in spermatozoa and enhances the testosterone effect on the testes and the prostate. In addition, prolactin is involved in the initiation of metabolic processes and promotes an increase in sperm motility after orgasm.
Clinical picture of the disease
The pathologically elevated level of prolactin in men is manifested, first of all, by a marked decrease in erectile function and sexual desire. Since such manifestations can develop due to psychological reasons, the specialist simply must differentiate such conditions for hormonal imbalance. This is important, because often such patients are mistakenly diagnosed with psychogenic impotence, whereas the cause lies in another disease.
So, practically in all men, hyperprolactinaemia causes significant violations of sexual desire and potency, up to their absence. In addition, the pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Metabolic disorders such as pathologically high cholesterol or obesity, often accompanied by insulin resistance;
- Oligospermia is a pathological condition in which the amount of sperm released during orgasm is significantly below normal;
- Infertility due to oligospermia;
- Osteoporosis or a decrease in bone mass and mineral density, tenderness in the bones;
- Male sexual characteristics of a secondary nature decrease;
- Problems with vision - most often associated with the limitation of visual fields or with a sharp decrease in visual acuity. Such a symptom often indicates extensive pathological processes in the pituitary region;
- Violations of psychoemotional origin, such as memory impairment, excessive fatigue, headaches, sleep disorders or depressive conditions;
- Gynecomastia is a pathological condition associated with an increase in the masculine mammary glands, accompanied by hypertrophic changes in the gland itself and nearby fatty tissues. The male breast can increase by as much as 10 cm.
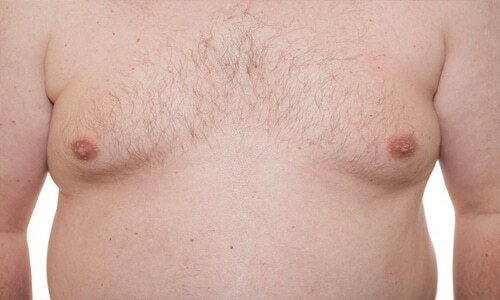
In addition, hyperprolactinemia causes a pathological decrease in testosterone secretion, which explains the decrease in sexual possibilities and the decline of sexual desire. Sometimes, hyperprolactinaemia is accompanied by symptomatic signs of hypogonadism( a pathological condition caused by a low androgenic level and underdevelopment of the genital organs).
Diagnosis of
In the content of prolactin blood, a specialist will be able to assume the possible causes of hyperprolactinaemia:
- At a level of less than 200 ng / ml, it can be assumed that the cause of hyperprolactinemia was the pituitary micro-tumor or idiopathic hyperprolactinemia;
- If the level of prolactin is more than 200 ng / ml, hyperprolactinaemia is most likely caused by the tumor of the pituitary gland, although such a prolactin content may not depend on the pituitary gland, but be caused by several provoking factors( for example, some disease and simultaneous use of drugs).
In general, MRI or CT of the brain is used to detect pituitary-hypothalamic tumor processes, or a radiographic examination of the cranium is performed. To exclude hypothyroidism, tests for the content of hormones secreted by the thyroid gland are prescribed. Also, various tests and pharmacodynamic tests with metoclopramide or tyroliberin are prescribed.
Methods of elimination of hormonal disorder
The treatment process involves the use of conservative techniques aimed at normalizing the concentration of prolactin. If hormonal disorders are caused by drug etiology, then the withdrawal of the drugs taken is indicated. Then, after 3 days after cancellation, a laboratory test is again performed on the level of prolactin.
Usually the basis of therapy is the intake of certain medications that help normalize the level of prolactin and reduce the size of prolactinoma, up to its full resorption, which is also quite possible.
Medication correction
The basis of conservative therapy is the use of ergoline and neergolinovyh drugs. A common group among such drugs are drugs based on bromocriptine like Lactoodel, Bromocriptine, Parlodel, Bromergon or Apo-Bromocriptine. At one time, these drugs were considered to be the only effective in the treatment of hyperprolactinemia. Among all these drugs Parlodel is considered the drug of choice.
Important! Bromocriptine preparations have very pronounced undesirable reactions and a short elimination period. In addition, about a third of patients have resistance to such drugs.
Often, patients with hyperprolactinemia are prescribed Abergin. This drug oppresses the secretion of prolactin, but does not affect other hormonal substances produced by the pituitary gland. This remedy acts longer and has less pronounced adverse reactions.
Most often men with hyperprolactinemia are prescribed Dostinex today on the basis of cabergoline. This medication provides the greatest therapeutic effect, and it should be taken only twice a week, and not every day. The undoubted advantage is considered to be a minimum of adverse reactions.
Among non-ergoline preparations, Norprolac is most commonly prescribed. This drug is different in patients better tolerability, take it once a day. Conservative therapy with the above means helps to normalize the prolactin concentration in the blood. But in some cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
Surgical treatment of
If a patient has a large tumor that has a destructive effect on the Turkish saddle, or if there is a fast-growing formation that compresses the optic nerves, or is not subject to prolactinoma therapy, then the intervention of the surgeons is indicated. The operation is carried out through the nose.
Warning! After surgery for the first six years, half of the patients undergoing surgery had a relapse of prolactinoma. Of course, successful removal is remarkable, as a one-step procedure. But nevertheless this intervention is of a surgical nature, having its own specific risks and complications.
The effectiveness of this treatment is 65-90% in men who have a pituitary microscope. In persons with macro-forming, the effectiveness of hypophysectomy is much lower - 3-40%.Often, as an additional therapeutic method resorted to radiotherapy procedures, involving the irradiation of the patient with gamma rays.
Medical and surgical tactics of treatment of hyperprolactinemia can be successfully used in complex treatment, mutually complementing each other.
Possible complications of hyperprolactinaemia
Increased concentration of prolactin is fraught with a mass of complications:
- Pituitary deficiency resulting in endocrine system failure - in such situations, hormonal treatment is indicated, the purpose of which is to restore the inadequate activity of the affected organ;
- Malignancy of pituitary benign formations, for the elimination of which immediate intervention of the oncologist is necessary;
- Osteoporosis or a decrease in bone density develops due to a prolonged absence of therapeutic effects on hyperprolactinemia;
- The constriction of the optic nerve leads to a noticeable narrowing of the visual field and visual acuity, up to blindness. Vision is restored usually after the elimination of compression.
Summing up
Hyperprolactinaemia requires immediate medical attention. Self-treatment here is absolutely not permissible, since an increased concentration of prolactin often indicates dangerous pathological processes. Therefore, it is undesirable to delay a visit to a specialist.
Modern medicine has all the possibilities for reliable diagnosis and effective treatment of hyperprolactinemia, therefore, on the whole, the prognosis is favorable. To avoid complications, people who have pituitary prolaktinomy, it is recommended to periodically see a specialist, undergo a CT scan and at least every six months to test for prolactin. Such preventive measures will help to avoid a lot of health problems.



