In some cases, gestational diabetes mellitus( GDD) occurs in pregnant women. This form of the disease can appear only during pregnancy, and disappear after some time after childbirth. But if you do not make timely treatment, then the disease can develop into type 2 diabetes, which has complex consequences.
When pregnancy comes, every woman should be registered, where under the supervision of specialists, there will be control over the well-being of the future mother and development of the fetus.

Regularly monitor the sugar, handing out tests of urine and blood, should every pregnant woman. Single cases of increasing the level of glucose in the analyzes should not panic, since such jumps are considered normal physiological process. But, if you take the tests, increased sugar is seen in two or more cases, it already signals the presence of gestational diabetes mellitus during pregnancy. It is noteworthy that an elevated level is detected when the material is delivered to an empty stomach( increasing the blood sugar level after a meal is the norm).
The causes of the pathology
At risk, we can refer women, which can apply the following parameters:
- excess body weight or the presence of obesity;
- if previous births occurred with gestosis diabetes;
- hereditary factor( transmitted genetically);
- pathology of the ovaries( polycystosis);
- pregnancy after 30 years of age.
According to statistical data, 10% of women experience complications in carrying a child. The cause of gestational diabetes, can be called, as with type 2 diabetes, the loss of cell sensitivity to insulin. At the same time there is a high blood glucose level because of the high concentration of pregnancy hormones.
Immunity to insulin appears most often at 28-38 weeks of gestation, and is accompanied by weight gain. It is believed that the decrease in physical loads at this time, also affects the appearance of GDD.
Symptoms of
Symptoms in GDD differ little from those of type 2 diabetes:
- a constant thirst, while drinking does not bring relief;
- frequent urination causing discomfort;
- may cause a decrease in appetite or a feeling of constant hunger;
- appear jumps in blood pressure;
- suffers from vision, there is turbidity in the eyes.
Diagnostics
If at least one of the above signs is present, then an obligatory visit to the gynecologist and delivery of tests to the sugar level is required. This analysis is called a glucose tolerance test( GTT).The test helps to determine glucose uptake by the cells of the body of a pregnant woman and possible violations of this process.
For the test, venous blood is taken from the patient( on an empty stomach).If the result shows an increased sugar content, then a diagnosis of "gestational diabetes" is made. Underestimated indicators, GTT is carried out. To do this, glucose in the amount of 75 grams, diluted in a glass( 250 ml) of slightly warmed water, and given to a woman to drink. An hour later, a second blood sample is taken from the vein. If the indices are normal, then for the control the test can be repeated after 2 hours.
Danger of HSD for fetus
What is the risk of histological diabetes to the developing fetus? Since this pathology does not directly endanger the life of the future mother, and can be dangerous only for the baby, the treatment is directed to the prevention of perinatal complications, as well as complications during childbirth.
Consequences for the child, with diabetes of pregnant women, are expressed in a negative effect on the microcirculation of the blood in the tissues of the pregnant woman. All the complex processes caused by the disturbance of microcirculation ultimately lead to hypoxic effects on the fetus.
Also, can not be called innocuous receipt of a large amount of glucose to the baby. After all, insulin, developed by the mother, can not penetrate the placental barrier, and the pancreas of the baby is not yet able to produce the required amount of the hormone.
As a result of the effect of diabetes mellitus, metabolic processes in the fetus are disrupted, and it begins to gain weight due to the growth of adipose tissue. Further, the baby has the following changes:
- , there is an increase in the shoulder girdle;
- significantly enlarges the abdomen;
- increases in size of the liver and heart;
All these changes take place against the backdrop of the fact that the head and limbs remain the same( normal) sizes. All this can affect the development of the situation in the future, and cause the following consequences:
- due to an increase in the fetal shoulder girdle, it is difficult to pass it during childbirth through the birth canal;
- during childbirth, injuries to the baby and the mother's organs are possible;
- can begin premature delivery, due to the large mass of the fetus, which has not yet fully developed;
- in the lungs of a baby in the womb of the mother, the production of a surfactant that does not allow them to stick together decreases. As a result, after giving birth, the baby may have trouble breathing. In this case, the child is rescued with the help of an artificial respiration apparatus, and then placed in a special incubator( kuvez), where he will stay for some time under the close supervision of doctors.
Also, one can not help mentioning the consequences of gestational diabetes mellitus: children born to a mother with a GDD can have congenital malformations of organs, and some may develop diabetes of the second degree in adulthood.
The placenta also has the property of increasing with GDD, it begins to fail to perform its functions, it can become swollen. As a result, the fetus does not receive the right amount of oxygen, hypoxia occurs. It is at the end of pregnancy( third trimester) that there is a risk of fetal death.
Treatment of
Because the disease is caused by an increased sugar content, it is logical to assume that for the treatment and prevention of pathology, it is required to control that this index is within the normal range.

The main factor influencing the course of diabetes treatment during pregnancy is strict adherence to dietary rules:
- excludes baking and confectionery products from the diet, which can affect the increase in sugar levels. But it's not worth giving up carbohydrates, because they serve as a source of energy. It is only necessary to limit their number throughout the day;
- to limit the consumption of very sweet fruits with a high carbohydrate content;
- exclude noodles, mashed potatoes and instant cereals, as well as various semi-finished products;
- remove smoked and fats( oil, margarine, mayonnaise, lard) from the ration;
- should be eaten with protein foods, it is important for the mother and baby;
- for cooking, it is recommended to use: stewing, cooking, steaming, baking in the oven;
- should be taken every 3 hours, but in small portions.
In addition, a positive effect on the health of the expectant mother is proved:
- is a complex of physical exercises designed for pregnant women. During exercise, there is a decrease in the concentration of sugar in the blood, improving metabolic processes in the body and overall well-being of the pregnant woman;
- regular walks on foot away from highways.
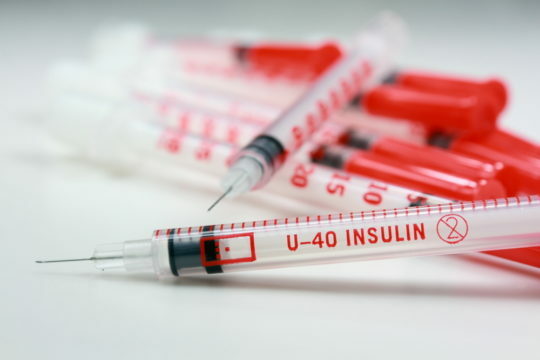
In case of severe disease, a doctor may prescribe insulin preparations. Other medications that reduce sugar are prohibited.
Insulin preparations are divided into 2 categories, according to FDA recommendations:
- B - category. It includes the means, in the description to which it is written that when tested on animals, no harmful effect on the fetus was observed. The effect of the drug on pregnancy was not tested.
- C - category. Enter drugs that, when tested, have been shown to affect the development of the fetus in animals. At pregnant women, also tests were not spent.
Therefore, all drugs should be prescribed only by a qualified doctor, with the obligatory indication of the trade name of the medicine.
Hospitalization with GDS, is relevant only if there is a suspicion of complicated obstetric complications.
GDD is not an excuse to stimulate preterm delivery or cesarean section surgery.
Post-partum period
After childbirth, a woman should regularly check for sugar levels, observe the presence of symptoms and their frequency( thirst, urination and others) until they disappear completely. The test is usually prescribed by doctors after 6 and 12 weeks after delivery. By this time the level of sugar in the blood of a woman should be normalized.
But, according to statistics, 5-10% of women giving birth normalize their sugar levels. In this case, medical care is needed, which should not be neglected, otherwise simple hormonal disorder can develop into a serious incurable disease.