 Spondylarthrosis of the thoracic spine is a type of osteoarthritis.
Spondylarthrosis of the thoracic spine is a type of osteoarthritis.
This disease affects the structures involved in the formation of the joint, namely:
- cartilage surfaces;
- capsule;
- ligaments surrounding the joint;
- muscles that strengthen it;
- subchondral bone regions located directly under the cartilage.
Spondylarthrosis in the thoracic region can lead to the defeat of both joints between the vertebral bodies and the joints between their arches.
Clinically, these two conditions are not much different, and their treatment does not differ at all.
Article Contents
- Types of localization of the disease
- Causes and risk
- extent of disease
- symptoms with regard to the stage
- deformation Diagnostics
- therapy methods
- treatment goals
- Methods
- Traditional medicine
- What complications fraught with disease
- Prevention
Types of disease localization
Spondylarthrosiscan affect any part of the spine.
In view of this, three main types of this disease are distinguished:
- cervical spondylarthrosis;
- thoracic( dorsartrosis);
- lumbosacral( most often found).
Causes and at-risk groups
People at the age of 55-60 years are at risk for developing this disease. They have it diagnosed with a frequency of 85 to 90%.
However, this does not mean that spondyloarthrosis can not develop in young people. Thus, at the age of 25 to 30 years, initial changes in this disease can be detected, which are not yet clinically apparent.
The risk factors for spondylarthrosis in young are:
- increased joint mobility;
- weighed down by heredity;
- spinal trauma;
- abnormal structure of the spinal column;
- obesity.
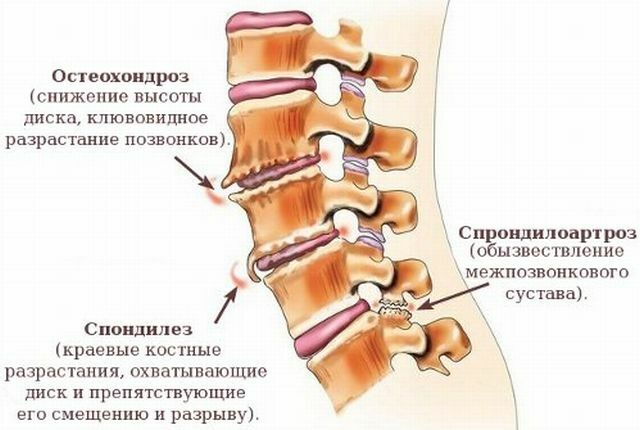
This disease develops degenerative joint damage. They are based not only on permanent trauma, but also on the specific predisposition of connective tissue .
It turns out that for the emergence of this disease requires a combined effect of these two factors. Separately, they can not cause a pathological process.
Various loads lead to depletion of the gelatinous nucleus located between the vertebral bodies and acting as a kind of shock absorber. Therefore, the articular surfaces are much more easily damaged by the influence of insignificant provoking factors.
This leads to reactive inflammatory changes in articular surfaces, which supports the pathological process( this is how the "vicious circle" closes).
In parallel, a ligamentous and muscular apparatus is involved, in which inflammatory changes also develop. Against this background, the muscles are spasmodic, which leads to a curvature of the spine.
 Kifoscoliosis is a dangerous deformity that is fraught with many complications and disability. Details in the article.
Kifoscoliosis is a dangerous deformity that is fraught with many complications and disability. Details in the article. Water gymnastics for health and body tone - hydrokinesotherapy is used to prevent and treat many diseases of the joints and spine.
Degrees of disease
Degrees of disease are a sign of disease progression. They can be determined both morphologically and radiological.
The first degree is characterized by the following features:
- insignificant narrowing of the joint slit;
- minimal destruction of cartilaginous tissue;
- reduction of the gelatinous nucleus;
- erasing intervertebral discs and cartilage.
In the second degree of the disease, the destruction of the cartilage becomes more pronounced. This leads to an even greater narrowing of the space between the articular surfaces.
The fourth degree is a complete fusion of articular surfaces, therefore the following signs are determined on the roentgenogram:
- disappearance of the gap between the joints;
- presence of osteophytes;
- blurs the contours of the vertebrae due to inflammatory changes.
Symptoms of the disease with regard to stage
Spondylarthrosis is classified into four stages, the first is characterized by such symptoms: 
- movements in the spine are limited;
- ligaments become less elastic;
- periodically develop lumbago in the back( thoracic region).
The second degree of the disease manifests itself more pronounced changes, which include:
- severe pain, which can be either during sleep or during various movements;
- is a feeling of stiffness that occurs only after performing physical exercises( this symptom is related to the observed muscle spasm in the affected department);
- swelling in an inflamed area.
In the third degree of the disease, one of the complications, called spondylolisthesis, appears.
Clinically, it manifests itself following symptoms on the background of even more pronounced destruction of the cartilage:
- persistent pain, becoming burning in nature;
- pronounced muscle spasm;
- pains are localized, but can give into the hand when the nerve roots are compressed.
When the disease progresses to the fourth degree, any movements in the thoracic spine completely cease. The articular surfaces coalesce with each other. This condition is called ankylosis.
The proliferation of bone tissue leads to reactive inflammation and compression of the nerve roots. Therefore, the patient is worried about constant back pain, and also the movement and sensitivity in the hand on the side of the lesion are disturbed.
Diagnosis of deformation
Diagnosis of degenerative lesion of the spinal column implies the following studies:
- objective neurologic examination;
- radiography;
- computed tomography;
- electromyography, which assesses the involvement in the pathological process of a number of located muscles;
- angiography is the study of blood vessels and blood flow in the affected area.
Methods of therapy
Treatment of spinal fusion of the thoracic spine at early stages is carried out by conservative methods, and at later stages requires also surgical intervention.
Conservative therapy involves the appointment of pharmacological agents and manual methods of exposure.
Objectives of treatment
Treatment of degenerative lesions of the spinal column pursues such goals as:
- muscle strengthening;
- correction of existing abnormalities in the structure of the spine;
- fighting with pain;
- increase in cartilage strength;
- cupping of an inflammatory reaction.
Methods
When the disease is in remission, the following treatment methods are shown:
- massage;
- medical gymnastics;
- swimming.
 These all procedures strengthen the muscular framework, which reduces the burden on the spine. Therefore, it retains its normal mobility and prevents compression of the nerve roots.
These all procedures strengthen the muscular framework, which reduces the burden on the spine. Therefore, it retains its normal mobility and prevents compression of the nerve roots.
Strengthen the muscles of the spine and help physiotherapy.
They are widely used in the elderly, who can not perform physical exercises.
Pharmacological therapy is carried out in the following areas:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for pain relief. They also suppress the severity of the inflammatory reaction
- Chondroprotectors , restoring damaged cartilage.
Surgical treatment methods are indicated in the following situations:
- abnormal spinal column structure;
- spondylolisthesis;
- is the second-third stage of the disease.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine in the treatment of arthrosis of the spinal column is just a supplement to the traditional. It allows to strengthen the therapeutic effect of therapy prescribed by a doctor.
There is a huge variety of methods of traditional medicine.
Here are some of them:
- infusion on the basis of birch buds, which are rubbed into the lesions of the thoracic region;
- eucalyptus infusion for external use;
- ointment from mustard and salt;
- is a mixture of olive oil and lemon oil, used for massage, etc.
What complications the disease is fraught with
The main complications of the disease that develop if the patient is not treated in a timely manner are the following:
- spondylolisthesis - slipping of the vertebra;
- ankylosis - fusion of the vertebrae with each other;
- curvature of the spine;
- resistant radicular syndrome.
Prevention
Currently, there are a number of general recommendations that reduce the risk of pathology.
These include the following: 
- regular exercise;
- elimination of curvature of the spine;
- proper nutrition;
- prevention of rickets( long walks in the fresh air, normal duration of sleep, hardening);
- selection of a table and chair for a child, taking into account its growth.
Spondyloarthrosis can develop at any age, affecting both young and old people. This disease is the main cause of back pain. Appearing suddenly, it also suddenly disappears in the early stages of the disease.
When they have already developed, the reserves of treatment for spondylarthrosis are markedly limited.
In this regard, a person can completely lose the ability to make movements in the back, there will be constant pain, as well as violations in the upper limbs( muscle atrophy, pain, weakness, etc.).