 Neurocysticercosis( cysticercosis of the brain) is a parasitic disease that affects the central nervous system.
Neurocysticercosis( cysticercosis of the brain) is a parasitic disease that affects the central nervous system.
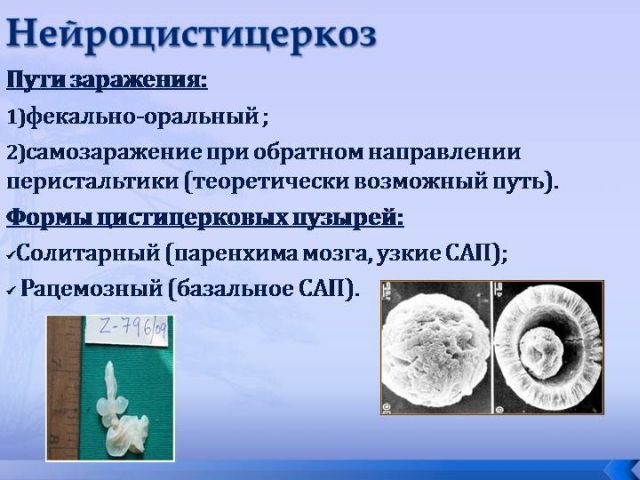
It is called by the encapsulated larvae of the pork chain. Infection occurs when the ribbonworm eggs enter the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of this type of helminthiosis may not appear immediately, but only after several years or more after the invasion.
Causes and stages of development of
The cause of the disease is the ingestion of parasite eggs in the digestive tract. The life cycle of the parasite is divided into 3 stages:
- egg;
- larva;
- adult individual.
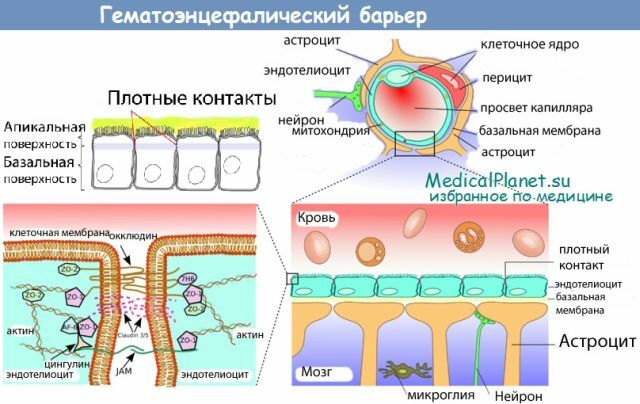
Often, the intermediate owner is a pig or a man who swallowed the egg of a pork chain. In the gastrointestinal tract, under the influence of gastric juice, the egg shell dissolves, and they migrate through the intestinal wall, settle in the soft tissues of the muscles and the brain. Individual larvae penetrate the brain and its membranes, causing symptoms of CNS infection.
An adult helminth specimen lives in the intestinal region, without manifesting at all. The infected person, along with the feces, allocates a lot of parasite eggs to the
 environment. They can fall on household objects, clothing and food, which become sources of invasion of healthy people. Very often self-infection occurs.
environment. They can fall on household objects, clothing and food, which become sources of invasion of healthy people. Very often self-infection occurs. After entering the brain, the embryos take the form of larvae. The larva is a 10 mm capsule with a liquid inside. A cyst can be a few pieces, or several hundred. In the place of their localization, a focus of inflammation is formed, and subsequently - a fibrous capsule, which clearly delimits brain tissue from the larva.
After a long time( more than a year) parasites can die, and the remaining capsules undergo calcification, ie, cysts with calcium deposition are formed. Thus, the inflammation continues and takes on a chronic form.
In the brain, cysts are localized on the surface of the cortex of the cerebral hemispheres, at the base of the brain, in the soft callous membranes, inside the ventricles. In addition to provoking inflammation, they also interfere with the natural circulation of the liquor fluid, irritate and exert pressure on the brain tissue.
Forms of the disease and clinical picture
The manifestations of cysticercosis of the brain are diverse and can vary depending on the location of the worms, their number, the stage of their development and the physiological characteristics of the organism of the individual.
There are 6 forms of neurocysticiosis, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms.
Parenchymal( larvae localized between gray and white matter of the brain):
- convulsions - epileptic syndrome develops;
- paresis - reduction of muscle tone in the limbs;
- sensitivity disorder in the hands and feet;
- speech disorders - patients may speak poorly and do not understand the speech of others, often a partial violation of speech( for example, rearrangement of sounds and letters in places);
- lesion of cranial nerves;
- falling out of the field of view( for example, part of the image is not perceived);
- impaired gait, instability;
- dizziness;
- involuntary movements and tremor of the limbs;
- a violation of intelligence up to complete dementia( with extensive lesion);
- changes in the psycho-emotional sphere - a delusional state, accompanied by hallucinations, nervous excitement.
Subarchnoidal( accompanied by meningeal symptoms):
- increased susceptibility to light;
- severe headaches;
- nausea with vomiting;
- increased neck muscle tone;
- vision impairment;
- pain during eye movement;
- high intracranial pressure.
Symptoms will be all the more pronounced, the more the number and size of parasites will be.
Intraventricular( cerebral ventricles, mainly IV) are affected:
- high intracranial pressure( paroxysmal nature);
- severe dizziness until loss of consciousness;
- sharp headache;
- nausea with vomiting;
- impaired consciousness;
- pallor of the face;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- respiratory function disorder;
- severe sweating.
Spinal( the rarest form, characterized by lesion of the cervical and thoracic spinal cord):
- partial paralysis of hands and feet;
- impaired sensitivity;
- pain in the limbs;
- tinea in the body;
- involuntary urination and defecation.
Ophthalmic:
- omission of the eyelid;
- conjunctivitis;
- the shift of the eyeball to the side;
- eye movement disorder;
- sensation of foreign body inside the eye;
- edema;
- loss of visual fields;
- atrophy of the optic nerve( with the death of the larva);
- complete loss of vision( in rare cases).
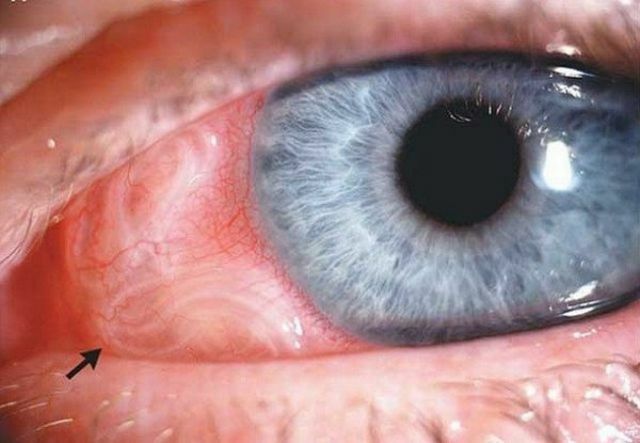
In the photo, the eye form of neurocysticercosis - cystodes in the eye
How to diagnose correctly
To diagnose this disease is very difficult, because the symptomatology in this case is nonspecific, and all manifestations can be mistaken for another disease. For the accurate diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Blood test for the level of eosonophils - with neurocysticercosis, a high level of eosinophil content will be detected.
- Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid - reveals high protein content, low glucose level, high lymphocyte count.
- Serological examination of is the detection of antibodies in CSF, ie, the complement fixation reaction is observed. The reliability of this procedure is 85-90%.
- X-ray of the head - shows calcified formations in the brain and increased intracranial pressure.
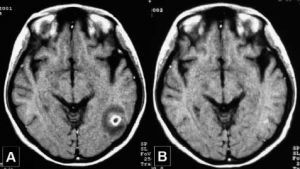
- CT and MRI - can detect granulomas, edema, cysts and other lesions.
- Ophthalmic examination - examination of the fundus. In this case, you can often see the eyes floating in the anterior chamber and the vitreous body of cysts.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Therapy of this type of helminthic disease is carried out in two directions - medicamental and surgical. The choice of method will be carried out depending on the form of the disease.
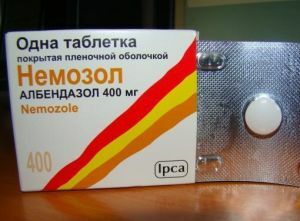
The drug treatment of neurocysticercosis is the use of antiparasitic drugs, such as:
- Azinox;
- Cestoks;
- Nemosol;
- Parasiquantel;
- Albendazole;
- Sanoxal.
 The action of these funds is aimed at the destruction of parasites. After helminths die, decay products form, toxic substances enter the bloodstream, which poison the body.
The action of these funds is aimed at the destruction of parasites. After helminths die, decay products form, toxic substances enter the bloodstream, which poison the body.
As a result, the patient's condition worsens, severe weakness, high fever, nausea, various allergies, inflammations, convulsive seizures, and in some cases a cerebral edema.
In order to protect a person from these dangerous complications, in combination with antiparasitic medicines such agents are prescribed:
- hormones - Dexamethasone;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen, Diclofenac;
- anticonvulsant preparations - Depakin.
Surgical intervention is required when the disease has a malignant course and with the ocular form of neurocysticercosis.
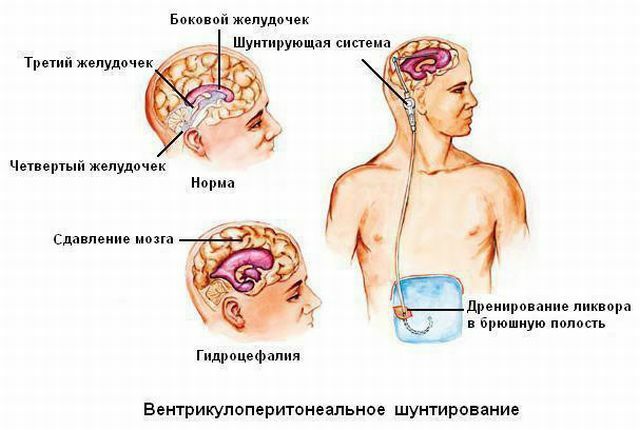
Malignant course of the disease is accompanied by a rapid increase in intracranial pressure, multiple cystic lesions, edema of the brain. To eliminate dropsy and reduce pressure, the shunting of the ventricles of the brain is performed. Cysts are extracted.
In case of damage to the organs of vision, surgical manipulations should be performed prior to the use of medications, because when cyst decays that occurs during the application of drugs, inflammation will occur, and this can lead to irreversible loss of vision.
Prevention measures
Prevention aims to avoid re-invasion and protect people who are in close contact with the patient from infection with  worms. For this it is necessary:
worms. For this it is necessary:
- all family members undergo a comprehensive examination for neurocysticercosis;
- observe personal hygiene, wash hands every time after coming from the street, interacting with animals, before eating;
- do not have unwashed vegetables and fruits, carefully treat them with hot water before use( or better with boiling water);
- pork meat is always cooked and roasted to the end.
Forecast and consequences of
Neurocysticercosis is a very dangerous disease in which invasion occurs imperceptibly and can be latent for a fairly long period.
It is very difficult to make an accurate forecast. It will depend on the extent of the lesion, timely and accurate diagnosis, and on properly selected methods of treatment.
The most severe consequences are a blockage of the IV ventricle with the further development of hydrocephalus. Without the provision of adequate medical care, a fatal outcome may occur.