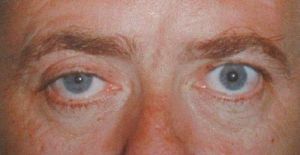
 Associative series: Argyle-Robertson syndrome - pupil - strange - scary leads to an unusual and slightly strange phrase: queen of the pre-dawn phantom.
Associative series: Argyle-Robertson syndrome - pupil - strange - scary leads to an unusual and slightly strange phrase: queen of the pre-dawn phantom.
This epithet, appropriated by the writer I. I. Lazhechnikov to the most ferocious Russian Empress Anna Ioannovna, is quite applicable to another "woman" no less ferocious - to a disease named after the masculine gender - to syphilis.
Far from always satisfying your sexual hunger results in finding the ideal sexual partner - sometimes syphilis can be caught, which has many manifestations and stages. Including in the deeply "absorbed into the body" of the neuroform, it is possible to develop dorsal dry( tabes) with the onset of one of its consequences - the appearance of a symptom involving the eyes. More precisely, their ciliary muscles, which are responsible for the size of the pupils, determine the level of both light transmission and light perception.
It is named after two scientists who discovered it: Robertson and Argyle( in different interpretations it sounds like: Ardzhil, Argyll, Argyll).
The pathology in the reflex motionlessness of the pupils of the eyes is the almost absent reaction to light( the diameter of the pupils is almost unchanged during the day at any level of illumination).While there are no simultaneous parallel disorders of other reactions from the eyes - accommodation and convergence - not observed.
The frustration of both a direct and friendly pupillary reaction is explained by a violation of the innervation of the pupils from the side of the parasympathetic department of the nervous system - either by the disorder of the function of the Yakubovich nuclei themselves, or by damage to their efferent fibers as a structural component of the oculi of the oculomotor nerves.
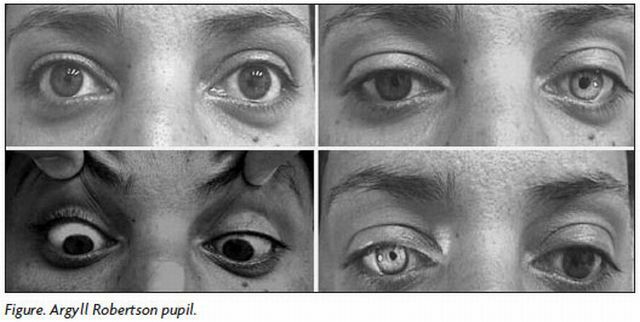
Origins and "tributaries" of the syndrome
Argylle Robertson syndrome is observed not only in the case of syphilis, but also:
- alcoholism;
- syringomyelia( syringobulbia);
- encephalitis;
- craniocerebral trauma;
- of polioencephalitis;
- tumors from the tissues of the upper dichotomy;
- atherosclerosis;
- of diabetic neuropathy.
In addition to the reflexive immobility of the pupils, the appearance of combined signs with it, comprising the symptom complex of Argyll-Robertson, is either complete or incomplete:
- miosis( or mydriasis);
- of varying degrees of anisocoria or pupil deformation;
- pupillary response is more lively than normal, when viewed at close range;
- in the form of a sector of atrophy or smoothed relief of the iris;
- weak response of the pupils to instillation of solutions of Pilocarpine, Atropine and cocaine into the eyes.
Pupillary disorders in the vast majority of cases have a two-sided nature and gradually increasing degree with a greater or 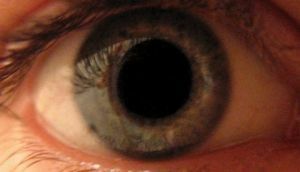 lesser severity of these or other symptoms.
lesser severity of these or other symptoms.
At first, the iris lost its former elasticity and vitality is reduced unevenly due to the difference in the strength of the ciliary muscle in its various sectors, reacting to light by losing the correct concentric character of the narrowing of the pupil. This is expressed by slowing down the time of its narrowing with an elongation of the latent period and a decrease in the amplitude of the narrowing.
After a while, the pupil completely ceases to respond to exposure with light. Or, stalled to a certain level, the decline of the pupillary reaction no longer increases. But even in the case of achieving revitalization of the reaction during a short-term remission, a progressive deterioration of the condition inevitably occurs.
If the development of anisocoria in the earlier stages occurs in almost 100%, then in the later stages it is less than 2/3 of all cases.
Heterochromia is explained by changes in the very fabric of the iris - often sectoral - of its relief, pattern, color. It flattenes and smoothes out, the color changes - it is to a certain extent depigmented due to the thinning of its front leaf and the disappearance of crypts.
The increase in the degree of miosis during the growth of the immobility of the pupillary reflex is a long-noted fact.
In 1/3 of cases, the pupillary opening is less than 2 mm wide, in half the cases - from 2 to 3 mm, the cases of mydriatic pupils are about 8%.
Diagnosis and treatment of
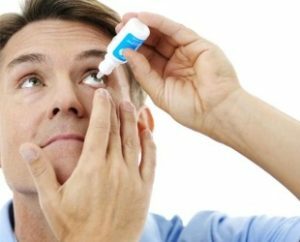 Both in the variant of setting the eyes to a closer distance, and in the case of setting the test with the closing of the eye gap characteristic for the pathological reaction of the pupils to light, there is a large amplitude of constriction and a faster rate of it. This is especially true for patients with one-sided immobility of the reflex.
Both in the variant of setting the eyes to a closer distance, and in the case of setting the test with the closing of the eye gap characteristic for the pathological reaction of the pupils to light, there is a large amplitude of constriction and a faster rate of it. This is especially true for patients with one-sided immobility of the reflex.
No less important diagnostic feature is the low efficiency from the use of Atropine and other mydriatic, as well as the cessation of pupillary dilatation in response to irritation sensitive - sensory, emanating from the senses, or mental, especially when combined with sensitivity disorders of a persistent nature in tabes.
It is necessary to bear in mind the following cases:
- inversion of the Argyll-Robertson syndrome - with the loss of pupillary response when viewed near, but with the preservation of their reaction to light;
- incomplete syndrome - with the pupilless reaction of the pupils to lighting, accommodation and convergence are manifested vividly.
Diagnosis of the condition includes a study for the presence of syphilitic infection, detailed neurological and ophthalmological examination with all necessary eye examinations and determination of the level of vitality of other reflexes and different types of sensitivity.
It is also necessary to exclude general somatic pathology( diabetes and similar endocrine and therapeutic disorders).
Since the Argyll-Robertson syndrome is not an independent disease, the patient needs treatment for the underlying pathology - neuroinfections: syphilis, diphtheria neuropathy and others, or a tumor, chronic intoxication and their consequences.



