Lung abscess most often develops against the background of infectious inflammatory diseases, acting as their complication. Without proper diagnosis and timely treatment, pathology leads to serious consequences and even death.
Contents of
- 1 Abscess of the lung - What is it?
- 2 Pathogenesis of the disease
- 3 Classification
- 4 Signs and symptoms of lung abscess
- 5 Diagnosis of lung abscess
- 6 Treatment of lung abscess
Abscess of the lung - What is it?
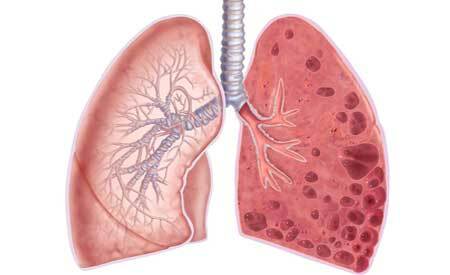
Lung abscess is a disease in which pulmonary tissue becomes inflamed and necrotic. As a result, cavities with purulent-necrotic contents are formed, resulting from infection. When there are several such foci in the lungs, one speaks of necrotic pneumonia or gangrene.
The most common cause of abscesses are pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, aerobic gram-negative bacteria and anaerobic non-spore-forming microorganisms.
In light microbes penetrate through the bronchi, and the triggering mechanism of infection and inflammation can serve not only sore throat, pneumonia, bronchitis and other pathologies of the respiratory system, but also the oral cavity - for example: tonsillitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis, caries.
Rarely bacteria are entered into lung tissue with blood, that is, hematogenous way - from other inflamed organs - for example, with purulent appendicitis.
Pathogenesis of the disease
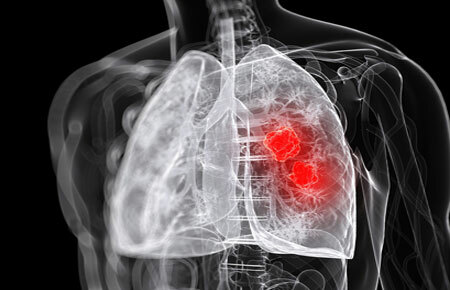
Lung abscess occurs in the airless area of the tissue, which can be caused by various factors. In most cases, there is a combination of lung abscess and pneumonia. Also purulent-necrotic cavities appear due to ingress of a foreign body into the lung with an infection - a small fragment of a carious tooth, vomit.
Alien bodies clog the smallest branches of the bronchi, and block the flow of air in this place. Such a site is called atelectatic or airless, and an abscess is formed here.
Abscess in the lung tissue can occur with bronchoectatic disease, provoking factors also serve as elderly and advanced age, exhaustion and weakened immunity.
The pathogenesis of lung abscess in the purulent cavity occurs as follows:
- in the lung tissue, a restricted area with an inflammatory infiltrate is formed;The
- ulcer melts the tissue from the center to the edges, forming a cavity;
- occurs lining the cavity granulation tissue, and infiltration around it disappears;
- further obliteration of the cavity is observed and a section of pneumosclerosis is formed - in acute course;
- but if the cavity walls are formed by a fibrous tissue, the suppuration can last for a long time, and the lung abscess takes on a chronic character.
The risk group includes not only people with inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, respiratory or other organs, but also people with such problems:
- diabetes mellitus, when the probability of development of purulent inflammation is increased at times;
- chronic alcoholism, in which there is a risk of ingress of vomit into the bronchi;
- bronchiectatic disease - aspiration with sputum containing an infection is possible.
Classification
The duration of the course of the disease lung abscess is acute and chronic. In the first case, abscesses appear only 3-6 weeks after the onset of the disease. With a chronic abscess, foci of necrosis form slowly.
By origin, the disease is classified into groups:
- along the path of infection - hematogenous, traumatic, bronchogenic;
- for the causative agent - staphylococcal, pneumococcal and others.
By localization in tissues, the pathological process must be single or multiple, one-sided( abscess of the right lung or left) or bilateral, central and peripheral.
Signs and symptoms of lung abscess
 Signs of acute lung abscess are manifested by a strong cough with the release of purulent sputum, often with impurities of blood, pains are felt in the chest. In a chronic abscess, the states of remission and exacerbation alternate.
Signs of acute lung abscess are manifested by a strong cough with the release of purulent sputum, often with impurities of blood, pains are felt in the chest. In a chronic abscess, the states of remission and exacerbation alternate.
During relapse, the above symptoms are observed. At the onset of remission, pain in the chest becomes less pronounced, but more sputum is produced with pus, fatigue, sweating at night and coughing occur.
There is also a different symptomatology before and after a breakthrough in lung abscess. Symptoms in the first case are as follows:
- in a certain area of the lung, purulent contents accumulate and the general condition becomes heavy, fast fatigue is observed,
- malaise;
- loss of appetite;
- sweating, especially strong at night;
- dry, painful cough and shortness of breath;
- temperature increase;
- when listening to dry rales, shortened sounds above the place with an abscess;
- on the fingers are often thickened phalanx;
- on the X-ray of the lungs shows a rounded shadow;The
- blood test shows an increase in ESR and leukocytes.
Symptoms of abscess of the lung after a breakthrough of the abscess:
- abundant sputum discharge - up to a liter per day;
- improvement in overall health and normalization of temperature;
- breathe becomes easier, and when you listen wheezing is damp;
- decreased sweating, improved appetite;
- X-ray shows a rounded cavity and in the picture you can see the level of sputum in it.
The pathogenesis of the abscess and its breakthrough are sometimes accompanied by complications:
- pleural empyema when an abscess breaks into the pleural cavity;
- profuse bleeding with severe damage to pulmonary vessels;
- septicopyemia - the formation of purulent metastases in different organs;
- of gangrene of the lung;
- pyopneumothorax, if the abscess communicates with the bronchus and breaks into the pleura;
- disturbed blood circulation and hypoxia with displacement of the mediastinum.
All these consequences are life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of lung abscess
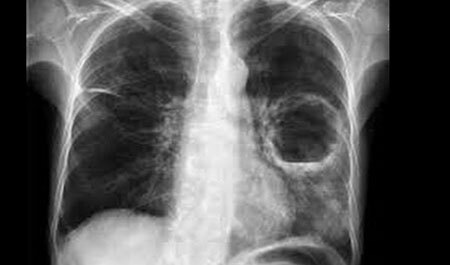
It is more difficult to diagnose the disease in the early stages before the breakthrough of the abscess, in connection with this it is often confused with focal pneumonia. Therefore, the diagnosis of "lung abscess" is based on not only the symptoms, but also other methods of examination:
- Blood test;
- Radiography;
- Listening to the lungs with a stethoscope and phonendoscope( auscultation);
- Percussion( tapping to evaluate the emerging sounds).
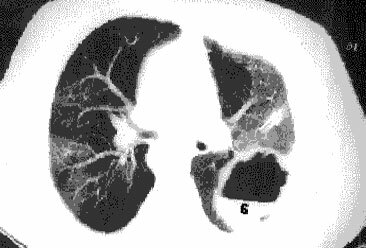
Diagnosis is facilitated after the opening of the abscess, because during this period the disease is easily recognized by the appearance of abundant sputum and a cavity on an X-ray with a certain level of purulent contents.
Puncture of the lung for diagnosis is rarely resorted, as there is a high risk of developing purulent pleurisy.
When diagnosing an abscess of the lung, it is important to exclude the presence of similar symptoms for symptoms, such as cavernous tuberculosis, actinomycosis, pleurisy, focal pneumonia.
Treatment of lung abscess
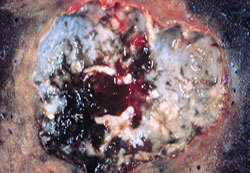
lung abscess, photo
With acute lung abscess, treatment can be surgical or conservative depending on the stage of development of pathology. In the initial phase, when there was an infiltration or no more than 1-1.5 months after the formation of the cavity with purulent contents, antimicrobials of a wide spectrum of action are prescribed.
This may be Streptomycin, Penicillin, Biomycin or other antibiotics - either one drug is used, or a combination of two or more agents. Their effectiveness is observed in the treatment of most patients with acute lung abscess.
In addition, conservative therapy includes:
- high-calorie, balanced nutrition with a high content of proteins and vitamins;
- blood transfusion to enhance immune defense;
- pharmacological immunotherapy;
- anabolic steroid agents;
- parenteral intake of protein preparations - Albumin, Protein;
- pyrimidine derivatives - potassium orotate, methyluracil;Calcium chloride intravenously.
If the abscess is reported with the bronchus, purulent contents are removed from the necrotic cavity by postural drainage or using a bronchoscope, after which antimicrobials are introduced into it.
In most cases( about 70%), conservative therapy produces a positive result, but in a fifth of patients the acute form becomes chronic.
Fatal outcome in the treatment of lung abscess occurs in 5% of cases and the same percentage of patients require surgical intervention.
The operation is performed with severe pulmonary hemorrhage, as well as with intensive development of suppuration against the background of drug therapy.