Tetraparesis is a pathological disorder characterized by a decrease in the motor activity of the hands and feet. Long-term course of this pathology leads to a change in the state of the limbs, the emergence of contractures, muscle atrophy, severe pain or complete loss of motor functions.
Tetraparesis is a pathological disorder characterized by a decrease in the motor activity of the hands and feet. Long-term course of this pathology leads to a change in the state of the limbs, the emergence of contractures, muscle atrophy, severe pain or complete loss of motor functions.
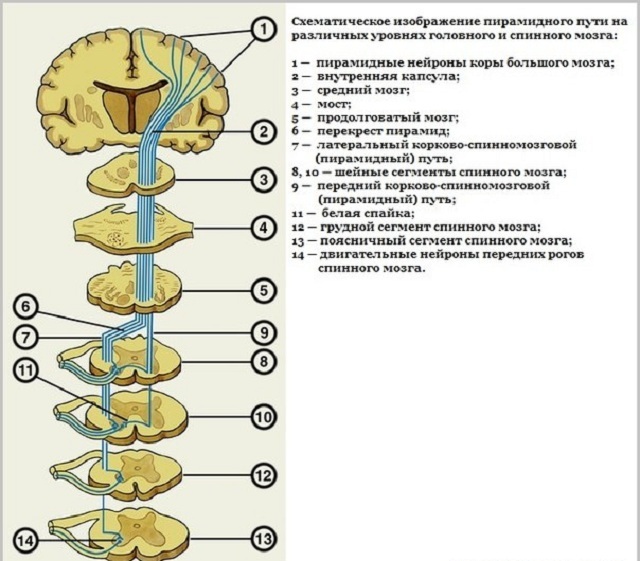
The mechanism of the development of the disease, as a rule, is formed as a result of the defeat of the central and peripheral nervous system.
Tetraparesis occurs due to pathological processes in the trunk, hemispheres of the brain or in the cervical spine. In a more acute form, it occurs with a spinal injury, after an internal cerebral hemorrhage, for example, after a stroke or with abnormal metabolic processes in the brain.
Because of damage to the upper cervical vertebrae in an acute period of the trauma, flaccid paralysis of the limbs, violation of the respiratory and pelvic functions occurs. In the event of an injury in the cervical spine, death may occur, because vital body structures are violated.
Content
- factors causing paresis
- Varieties symptom
- clinical picture
- Spasticity - as a special form of paresis
- diagnosis in a medical institution
- complex therapeutic measures
- Surgery
- rehabilitation period
- Forecast and complications
factors causing paresis
tetrapareses should be classified in twogroups:
- acquired - occurs as a result of spine trauma, after cerebral hemorrhage, with development of an evilquality or benign education, encephalitis, polyneuritis;
- congenital - occurs as a result of complications during pregnancy.
Violation of the central or peripheral nervous system, which leads to the development of this symptom, develops under the influence of such factors:
- Cerebral Palsy;

- trauma of the cervical spine;
- polyneuropathy;
- Landry-Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- Krabbe disease;
- occlusion of cerebral arteries;
- myasthenia gravis;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- hydropathy of the brain;
- complications of surgical intervention on the brain or spine.
Variation of the symptom
Tetraparesis is:
- Spastic .It manifests an increased muscle tone in the hands and feet, which leads to stiffness of movements. Such a mechanism can occur due to increased intracranial pressure, for example, in cerebral palsy or encephalopathy. As a consequence, depletion of the cerebral cortex may develop, which contributes to mental underdevelopment.
- Central .Occurs when both hemispheres, brainstem or upper spinal cord are damaged.
- Reflective .It is characterized by hypertonicity and hyperreflexia in the limbs when normal muscular force is present in them. Such a condition, as a rule, is accompanied by pathological reflexes.
- Mixed .There is a different intensity of muscle tone in the hands and feet. In other words, hypotonicity and hypertonicity can occur simultaneously.
- Sluggish .There is weakness and marked partial loss of sensitivity in the limbs.
Clinical picture
 In cerebral palsy, which is most often accompanied by spastic tetraparesis, the child suffers from a cerebellum.
In cerebral palsy, which is most often accompanied by spastic tetraparesis, the child suffers from a cerebellum.
Because of this, the child can not hold the head, sit down, stand, and generally move without help.
Also, depending on the localization of brain damage, a delay in mental development and a decrease in intelligence is detected.
Very often tetraparesis is accompanied by other diseases of a congenital nature - dropsy of the brain and underdevelopment of the skull's skull structure.
Common signs of pathology include:
- marked decrease in motor function of the limbs;
- respiratory function disorder;
- change in the shape of the limbs;
- dysfunction of the pelvis;
- spasticity in muscles;
- muscle pain;
- complete loss of activity of hands and feet after a while;
- irritation of the spinal part of the diaphragm, and as a result - hiccough, shortness of breath, cough.
Spasticity - as a special form of the
paresis The most common form of this condition is spastic tetraparesis. It is characterized by a decrease in motor activity. 
In this case, there is an increase in muscle tone, and it is because of this that the stiffness and "disobedience" of the hands and feet, as well as severe pain, appear.
After a while spasticity leads to pathological changes in the joints, deformities of the limbs, and in some cases even the trunk.
There is a breakdown of the functions of not only skeletal muscles, but also smooth muscles, which in turn leads to a violation of respiratory and pelvic functions.
Spastic tetraparesis is accompanied by other signs of damage to the nervous system. Violations of the intellect of different degrees are noted in almost 90% of all cases.
In addition to these symptoms, there are signs of lesion of the cranial nerves, against which there are disorders of hearing, vision, strabismus. In rare cases, epileptic activity accompanied by attacks can be diagnosed.
For spastic tetraparesis with double hemiplegia, such signs are characteristic:
- impairment of motor function of hands and feet;
- asymmetry of muscle tone;
- delayed speech and mental development;
- severe damage to the musculature of the face and the muscular girdle of the upper half of the trunk.
In some cases, a disease such as triparesis may develop, i.e., one limb remains completely healthy and the  functions normally.
functions normally.
In cerebral palsy, spastic tetraparesis is diagnosed in two forms: lower paraparesis and tetraparesis in the greater half of the cases. The spastic syndrome develops against the background of destruction of extrapyramidal fibers in the brain.
Due to this, there is a sharp weakening of the braking control over the segmental apparatus of the spinal cord. This accompanies the activation of the pathological stretch reflex. It provokes an increase in muscle tone, because in response to stretching, the muscles begin to contract.
Diagnostics in a medical institution
Diagnostics includes methods of collecting anamnesis, full medical examination, CT, MRI, ultrasound examination, X-ray, EMG.
Differentiate tetraparesis from these diseases:
- Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- botulism;
- idiopathic transverse myelitis;
- Multiple Sclerosis;
- poliomyelitis;
- tumor of the spinal cord and brain.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Treatment of tetraparesis should be complex and conducted in a hospital. Apply conservative, neurosurgical, orthopedic methods and rehabilitation.
Therapy is performed to achieve the following goals:
- reduction in spasticity;
- prevention of malfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- formation of the correct motor stereotype.
Conservative treatment, first of all, includes two main aspects:
- Drug therapy - prescription drugs such as Baclofen and Botulotoxin help reduce the
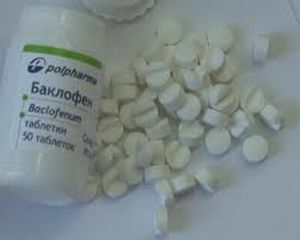 spasticity, resulting in increased impulse conductivity, and improve metabolic processes in the brain, while increasing the number of passive limb movements.
spasticity, resulting in increased impulse conductivity, and improve metabolic processes in the brain, while increasing the number of passive limb movements. - Physiotherapy - is aimed at performing movements, exercises and postures that strengthen the muscles.
Also in the treatment package are:
- reflexotherapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- gymnastics on special simulators;
- kinesitherapy.
Surgical treatment of
For more effective correction of spastic tetraparesis, surgical treatment is required. The operation is performed to restore the functions of a particular damaged zone.
Thanks to the orthopedic procedure, contractures are corrected and muscles are stretched out. Plasticity of muscles and tendons is also carried out. This corrective method brings very good results.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation measures are of great importance in the treatment of spastic tetraparesis, in particular in cerebral palsy, whose task is to improve the physical condition of the child and adapt it as much as possible to the conditions of life. Rehabilitation includes the following methods:
- Occupational therapy - develops motor skills and tactility, regulates movement and orientation. Also, small motor skills develop separately. In occupational therapy, play methods, methods of physical contact, retention, copying are used.
- Logopedic exercises .The purpose of the classes is to develop the correct pronunciation. Special methods allow to eliminate the problem of non-verbal communication and disorder of the swallowing reflex. Also, thanks to these programs, coordination and hearing are improved, previously formed speech disorders are eliminated.
- Aquatherapy .Helps to alleviate pain symptoms by relaxing the spastic parts, and to strengthen the muscles. This
 treatment has a beneficial effect on the emotional state of the child. The procedure is carried out by lowering the child into the water, by means of special seats. The water temperature should be approximately 35 degrees.
treatment has a beneficial effect on the emotional state of the child. The procedure is carried out by lowering the child into the water, by means of special seats. The water temperature should be approximately 35 degrees. - Hippotherapy .A very effective method in which a therapeutic tool is a horse. This procedure stimulates motor reflexes and increases activity. Sometimes therapy gives very good results when the child gradually learns to sit on the saddle and manage the horse.
Forecast and complications of
If the spastic syndrome is due to head trauma or stroke, treatment should be started immediately, in time to restore the functions of damaged nervous tissue and motor activity of the hands and feet.
In the absence of necessary treatment in elderly people, deformation of the spine occurs and the overall physical condition is significantly deteriorating.
Therapy in this case must be performed within the first 1.5 to 2 months after cerebral hemorrhage occurred.
If you miss the right time to start treatment, to restore a normal person's condition will be much more difficult. Therapy and rehabilitation will take much longer. In addition, there is a risk that the patient may simply remain disabled.
With regard to congenital tetraparesis, with severe symptoms of intellectual decline, a child with a severe diagnosis of cerebral palsy is virtually impossible to cure.
If signs of mental retardation are not present, with properly selected and timely treatment can achieve a significant positive effect.