Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs( NSAIDs) are one of the main drugs used to treat inflammatory joint diseases.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs( NSAIDs) are one of the main drugs used to treat inflammatory joint diseases.
They are prescribed by periodic courses in chronic processes, if necessary - with exacerbations of diseases and acute inflammatory processes. NSAIDs exist in various dosage forms - tablets, ointments, solutions for injections. The choice of the necessary agent, dosage and frequency of its use, should be performed by a doctor.
Contents of the article
- NSAIDs - what is this group of drugs?
- History of the discovery and formation of
- Pharmacological properties and mechanism of action
- Indications for use - the scope of application
- The most famous preparations of the
- group Side effects of
- Classification of NSAIDs
- Chemical structure of
- On the effects on COX-1 and COX-2
- Selective and non-selective NSAIDs
- what is this group of drugs?
The NSAID group is quite extensive, and includes various chemical preparations. The name "nonsteroidal" shows their difference from another large group of anti-inflammatory drugs - corticosteroid hormones.
The general properties of all drugs of this group are three of their main effects - anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic.
This is due to another name for this group - non-narcotic analgesics, as well as the enormous breadth of their use. These three effects are differently expressed in each drug, so they can not be completely interchangeable. 
Unfortunately, all drugs of the NSAID group have similar side effects. The most famous of them is a provocation of peptic ulcer of the stomach, toxicity for the liver and suppression of hemopoiesis. For this reason, do not exceed the dosage indicated in the instructions, and also take these drugs if they are suspected.
To treat with such medications, pain in the abdomen is impossible - there is always a risk to worsen your condition. Various dosage forms of NSAIDs have been invented to improve their effectiveness in each particular situation and reduce potential health hazards.
The history of the discovery and formation of
The use of herbal remedies with anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effect is described in the works of Hippocrates. But the first accurate description of the effect of NSAIDs dates back to the 18th century.
In 1763 an English physician and priest Edward Stone reported in a letter to the chairman of the Royal Society of London that the infusion of the willow bark growing in England had antipyretic properties, described the formulation of its preparation and the way it was used in feverish conditions.
Almost half a century later in France, I.Lir singled out the substance from the bark of the willow, which determined its medicinal properties. By analogy with the  Latin name of the willow-salix, he called this substance salicin. This was the prototype of modern acetylsalicylic acid, which they learned to receive chemically in 1839.
Latin name of the willow-salix, he called this substance salicin. This was the prototype of modern acetylsalicylic acid, which they learned to receive chemically in 1839.
The industrial release of NSAIDs was established in 1888, the first drug released on drugstores was acetylsalicylic acid under the trade name Aspirin, manufactured by Bayer, Germany. She still owns the rights to the trademark Aspirin, so the rest of the producers release acetylsalicylic acid under an international non-proprietary name or create their own( for example, Upsarin).
More recent developments have led to the emergence of a number of new drugs. Studies continue to this day, creating more and more safe and effective means. Strangely enough, the first hypothesis about the mechanism of action of NSAIDs was formulated only in the 1920s. Prior to this, the drugs were applied empirically, their dosages were determined by the patient's well-being, and the side effects were not sufficiently investigated.
Pharmacological properties and mechanism of action
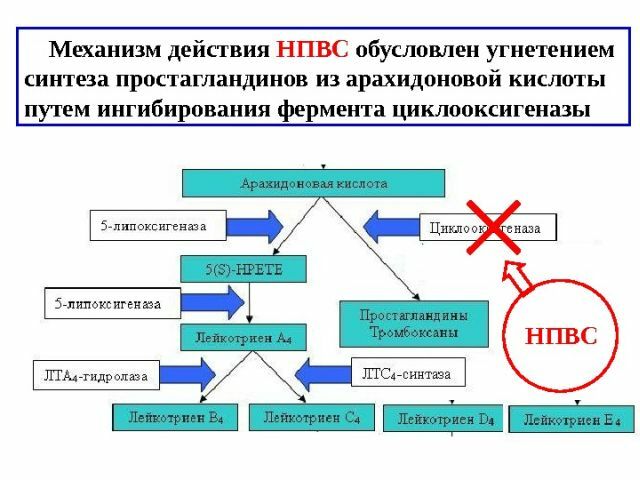
The mechanism of development of the inflammatory reaction in the body is quite complicated, and includes a chain of chemical reactions that trigger each other. One of the groups of substances taking part in the development of inflammation is prostaglandins( they were first isolated from prostate tissue, hence the name).These substances have a dual function - they are involved in the formation of protective factors in the gastric mucosa and in the inflammatory process.
Synthesis of prostaglandins is carried out by two types of cyclooxygenase enzyme. COX-1 synthesizes "gastric" prostaglandins, and COX-2 - "inflammatory", and is normally inactive. It is in the activity of COX that the NSAIDs interfere. Their main effect - anti-inflammatory - is due to oppression of COX-2, and the side effect - violation of the protective barrier of the stomach - oppression of COX-1.
In addition, NSAIDs interfere quite strongly in the cellular metabolism, what causes their analgesic effect - they disrupt the conduct of nerve impulses. This is also the cause of retardation, as a side effect of taking NSAIDs. There is evidence that these drugs stabilize the membranes of lysosomes, slowing the release of lytic enzymes.
When entering the human body, these drugs are absorbed for the most part in the stomach, in a small amount - from the intestine.
Absorption is different, in new drugs bioavailability can reach 96%.Preparations in the enteric membrane( Aspirin-cardio) are absorbed significantly worse. The presence of food does not affect the absorption of drugs, but since they increase acidity, it is advisable to take them after eating.
Metabolism of NSAIDs occurs in the liver, this is associated with their toxicity for this organ and the inability to use in various liver diseases. Through the kidneys, an insignificant part of the dose of the drug is taken out. Modern developments in the field of NSAIDs are aimed at reducing their effect on COX-1 and hepatotoxicity.
Indications for use - scope of application
Diseases and pathological conditions in which NSAIDs are prescribed are diverse. Tablets are prescribed as an antipyretic agent for infectious and non-infectious diseases, and also as a remedy for headache, dental, joint, menstrual and other types of pain( except for abdominal pain, if its cause is not clear).Children use suppositories with NSAIDs to relieve heat. 
Intramuscular injections of NSAIDs are prescribed as an analgesic and antipyretic agent in case of a severe condition of the patient. They are necessarily included in the composition of the lytic mixture - a combination of drugs that can quickly bring down a dangerous temperature. Intraarticular injections are treated with severe joint damage caused by inflammatory diseases.
Ointments are used for local effects on inflamed joints, as well as spine diseases, muscle injuries to relieve pain, swelling and inflammation. Ointments can be applied only to healthy skin. In diseases of the joints, all three dosage forms can be combined.
The most famous drugs of the
group The very first NSAIDs that went on sale was acetylsalicylic acid under the trade name Aspirin. This name, despite being commercial, is strongly associated with the drug. It is prescribed for lowering the temperature, relieving the headache, in  with small doses - to improve the rheological properties of the blood. It is rarely used in diseases of the joints.
with small doses - to improve the rheological properties of the blood. It is rarely used in diseases of the joints.
Metamizole( Analgin) - no less popular than aspirin. Used to relieve pain of various origins, including articular. It is forbidden in many countries of Europe, as it has a strong oppressive effect on the blood.
Diclofenac is one of the popular drugs for the treatment of joints. Included in many ointments, is available in tablets and injections. Has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, with local application almost does not cause a systemic effect.
Side effects of
As with any other means, numerous side effects occur when taking NSAIDs. The most famous among them is ulcerogenic, ie provoking ulcer. It is caused by oppression of COX-1 and is almost completely absent in selective NSAIDs.
Acid derivatives have an additional ulcerogenic effect due to increased acidity of gastric juice. Most NSAIDs are contraindicated in gastritis with high acidity, peptic ulcer of stomach and duodenum, GERD.
Another common effect is hepatotoxicity. It can manifest pain and heaviness in the abdomen, digestive disorders, sometimes - short-term icterus syndrome, skin itching, other manifestations of liver damage. When hepatitis, cirrhosis and  liver failure, NSAIDs are contraindicated.
liver failure, NSAIDs are contraindicated.
Inhibition of hematopoiesis, which, if the dosage is constantly exceeded, leads to the development of anemia, in some cases - pancytopenia( lack of all blood cells), impaired immunity, bleeding. NSAIDs are not prescribed for severe bone marrow diseases and after its transplantation.
Effects associated with impaired well-being - nausea, weakness, inhibition of reaction, decreased attention, fatigue, allergic reactions up to asthmatic attacks - arise individually.
Classification of NSAIDs
To date, there are many preparations of the NSAID group, and their classification should help the doctor choose the most appropriate drug. Only international non-proprietary names are listed in this classification.
Chemical structure
By chemical structure, such non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents are isolated.
Acids( absorbed in the stomach, increase acidity):
- salicylates:
- pyrazolidines:
- derivatives of indoleacetic acid:
- derivatives of phenylacetic acid:
- oxicamides:
- derivatives of propionic acid:
Non-acid derivatives( do not affect the acidity of gastric juice, absorbed in the intestine):
- alkanones:
- sulfonamide derivatives:
On effects on COX-1 and COG-2
Non-selective - inhibit both types of enzyme, they include most of the NSAIDs.
Selective( coxibs) depress COX-2, do not affect COX-1:
- Celecoxib;
- Rofecoxib;
- Valdecoxib;
- Parecoxib;
- Lumiracoxib;
- Etorikoksib.
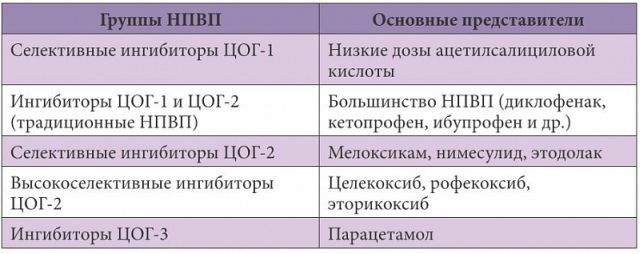
Selective and non-selective NSAIDs
Most NSAIDs are non-selective, because they depress both types of COX.Selective NSAIDs are more modern drugs, affecting mainly COX-2, and minimally affecting COX-1.This reduces the risk of side effects.
Nevertheless, the selectivity of the action of drugs is not yet achieved, and the risk of side effects will always be.
Drugs of the new generation
The new generation includes not only selective, but also some nonselective NSAIDs that have pronounced efficacy, but less toxic for the liver and hematopoietic system. 
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of the new generation:
- Movalis - has an extended period of action;
- Nimesulide - has the strongest analgesic effect;
- Xsefokam - prolonged period of action and pronounced analgesic effect( comparable with morphine);
- Rofecoxib - the most selective drug, is allowed for gastritis patients with peptic ulcer outside of exacerbation.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments
The use of NSAID preparations in the form for topical application( ointments and gels) has a number of advantages, first of all - the lack of a systemic effect and a targeted effect on the inflammation focus. When diseases of the joints are appointed almost always. The most popular ointments:
- Indomethacin;
- Diclofenac;
- Piroxicam;
- Ketoprofen;
- Nimesulide.
NSAIDs in tablets
The most common drug form of NSAIDs is tablets. It is used to treat various pains, including joint pain.
From the advantages - can be prescribed for the treatment of manifestations of the systemic process, which involves several joints. Of the shortcomings - pronounced side effects. The list of NSAID drugs in tablets is quite long, these include:
- Ibuprofen;
- Orthophene;
- Movalis;
- Indomethacin in tablets;
- Analgin;
- Acetylsalicylic acid( rarely prescribed for joint diseases);
- Rofecoxib( DENEBOL).
Injectable forms of
The advantages of this form of NSAIDs are in very high efficiency. Intramuscular injections are used to treat acute conditions associated with high fever or severe pain( Ketorol, Analgin).
Intra-articular injections are prescribed for the treatment of severe exacerbation of joint disease, allow rapid termination of exacerbation, but the injections themselves are very painful. Used drugs:
- Rofecoxib( Denebol);
- Xsefokam;
- Movalis in solutions for injection;
- Indomethacin in solutions for injection;
- Celecoxib( Celebrex).
TOP-3 articular diseases in which NSAIDs are prescribed
The use of NSAIDs is most often justified with the following joint diseases:
- In osteochondrosis, is a disease of the intervertebral discs, most commonly affecting the cervical and lumbar spine. To treat the disease prescribe ointments with NSAIDs in the initial stages during the exacerbation and for preventive purposes, especially in cold weather. Tablets are prescribed for severe course.
- In the case of arthritis, is prescribed NSAID ointments as needed and tablets for the prevention of exacerbations. During an exacerbation ointments and tablets are appointed, in case of severe arthritis - ointments and intraarticular injections in the day hospital, tablets as needed.
- The most common drugs for arthrosis are Xsefoks in the form of tablets and injections, Movalis in the form of injections and tablets( this is all NSAIDs of the new generation), and also do not lose their effectiveness of ointments based on Diclofenac. Since arthrosis, unlike arthritis, rarely worsens, the main emphasis in the treatment is on maintaining the functional state of the joints.
General features of the application
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of joints are prescribed by courses or as needed depending on the course of the disease.
 The main feature of their application is that you do not need to take several drugs of this group at the same time in the same dosage form( especially tablets), as this increases the side effects, and the therapeutic effect remains the same.
The main feature of their application is that you do not need to take several drugs of this group at the same time in the same dosage form( especially tablets), as this increases the side effects, and the therapeutic effect remains the same.
It is possible to apply different dosage forms simultaneously, if necessary. It is important to remember that contraindications to taking NSAIDs are common for most drugs of the group. NSAIDs remain the most important treatment for joints. They are difficult, and sometimes impossible to replace by any other means. Modern pharmacology develops new drugs of this group in order to reduce the danger of their side effects, increase the selectivity of the action.