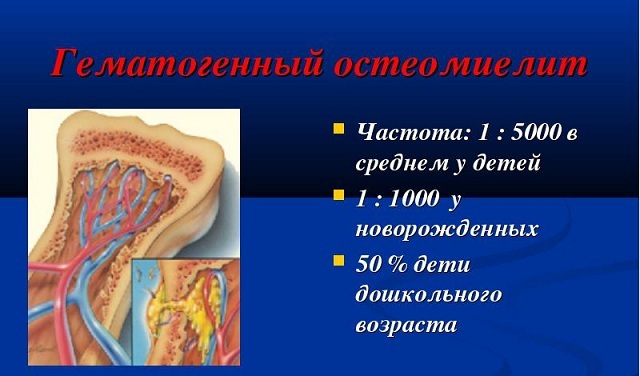
 Hematogenous osteomyelitis is a disease that is characterized by inflammation of the bone marrow and destruction of bone.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis is a disease that is characterized by inflammation of the bone marrow and destruction of bone.
This condition can arise if there are any infectious pathogens, a tumor process and a conditionally pathogenic microflora in the body in the presence of a decrease in the response of the immune system.
Contents of the article
- Risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Stages of the disease development
- Clinical picture
- Modern approach to the diagnosis
- Therapy of the disorder
- What complications is fraught with the disease?
- Prevention of the disease
Risk factors
There are risk groups, which include people with imperfect immune system formation.
These are:
- children under 7 years of age due to unformed bone marrow and bone tissue;
- people with congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies;
- people of advanced age;
- patients with sepsis;
- people with chronic infection;
- patients with neoplastic diseases.
In children of the first year of life, the entrance gates for infection are microcracks and injuries to the mucous membrane of the mouth and nose.
An important factor in the development of the disease is the mucosal infection of respiratory infections.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis can occur in children and adults of any age in the presence of tuberculosis in the body.
To prevent the causative agent of tuberculosis from the lungs into the bone marrow, it is necessary to adhere to the prescribed treatment schedule by the doctor, without missing medication.
Hematogenous bone osteomyelitis of the skull bones, can often be associated with such diseases as:
- otitis media;
- etmoiditis;
- sinusitis;
- front;
- dacryocystitis;
- purulent periodontitis.
Forms of the disease
There are two forms of hematogenous osteomyelitis:
- The acute form of is most often observed in children, adolescents and middle-aged people. In people with the presence of immunodeficiency states, in most cases, a chronic form is observed.
- Chronic , hematogenous osteomyelitis can also occur in elderly people. This form is also characteristic of people with the presence of chronic diseases of the body.
Stages of the development of the disease
Development of hematogenous osteomyelitis begins with an inflammatory process in the bone marrow and can result in the breakthrough of inflammation products through the skin.
Depending on the damage to organs and tissues, several stages of the development of the disease are distinguished:
- development of bone marrow inflammation;
- formation of bone abscess;
- inflammation of periosteal tissues and development of abscess;
- formation of phlegmon in intermuscular cases;
- development of the fistula and the breakthrough of purulent contents.
During the first stage, pathogenic microorganisms and altered body cells enter the bone marrow with blood flow. It is there that they find their own cells of the immune system and attack them.
In this case, an inflammatory process develops, which seizes more and more bone cells.
In the next stage of the disease, the inflammatory process is transformed into melting of bone and bone marrow cells. In place of the cavity in which the bone marrow is located, a purulent abscess forms.
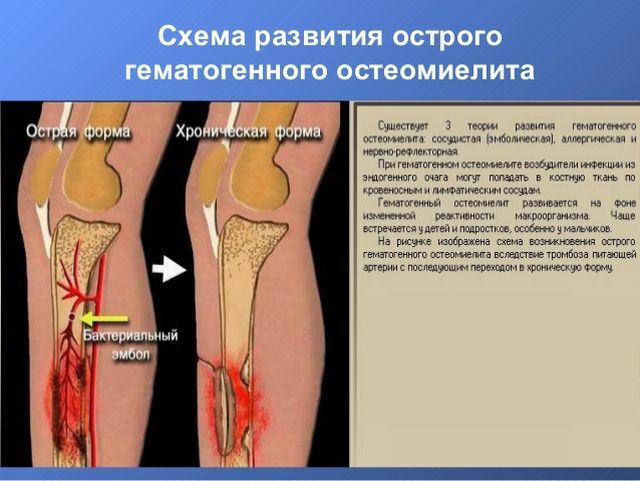
Continuing to spread bony cells, hematogenous osteomyelitis extends to the periosteum and cartilage, forming inflammation and periosteal abscesses in them.
After the pus has finally melted the periosteum, it breaks through into soft tissues, lingering in muscle cases and forming a phlegmon.
A large amount of pus in the bones and soft tissues can lead to the formation of a fistula through which pus and necrotic bone masses go out through the hole in the skin.
The formation of the fistula and the release of pus outward often results in an acute period of the disease. In the chronic form of the disease, small phlegmon forms which do not lead to the development of the fistula, but remain in the soft tissues.
Clinical picture of
Manifestations of hematogenous osteomyelitis may be different, depending on the form, stage of the disease and the state of the human body.
The acute form in the inflammation stage is manifested by the common symptoms of intoxication:
- high temperature;
- profuse sweating;
- weakness.
With further development of the disease, there is weakness during movement( localization depends on the affected bone), fast 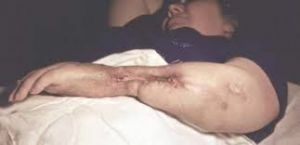 fatigue, high temperature persists.
fatigue, high temperature persists.
If the bones of the lower limb are affected, it becomes difficult for a person to move around. If the lower jaw is affected, the masticatory function is impaired. With a large area of damage to the bone can be observed pathological fractures.
In the acute phase of the disease it is possible to form a fistula through which pus comes out. After the release of necrotic masses and the remains of pus, there is a sharp drop in temperature, a feeling of discomfort disappears.
In case of insufficient treatment of the acute phase of the disease, hematogenous osteomyelitis changes into a chronic form.
Chronic course of hematogenous osteomyelitis is characterized by a constant slight increase in temperature to subfebrile digits.
Also in the chronic form of the disease there is a constant weakness, a slow but noticeable muscle fatigue, discomfort during movements.
If the chronic form is observed in infants or in older people, it is difficult to diagnose.
Modern approach to diagnosis of
An important diagnostic criterion of purulent osteomyelitis is an increase in temperature. In a person with purulent osteomyelitis, the temperature can reach 38.5 ° C - 40 ° C.
However, the disease can occur almost asymptomatically - in people with immunodeficiencies, body temperature can either remain at normal level or decrease due to the depletion of the body's immune system.
Chronic form also occurs with a slight increase in body temperature.
A feature of the diagnosis of hematogenous osteomyelitis is the difficulty in recognizing this process. In the presence of purulent lesions on the skin, it is difficult to understand where this formation came from and what depth it reaches.
It is possible to suspect purulent osteomyelitis in the presence of the following formations:
- phlegmon;
- abscess;
- periostitis;
- breakthrough of the abscess and prolonged excretion of pus.
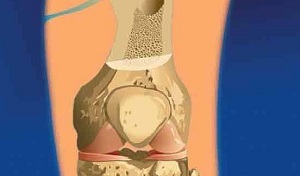 In addition to the clinical picture, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are of no small importance.
In addition to the clinical picture, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are of no small importance.
So, laboratory tests will help to detect inflammation in the body. A blood test for a specific flora will help identify the pathogen and prescribe the necessary antibiotics.
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, X-ray and CT are the most informative. X-ray examination will allow to see the pathological process. By measuring bone density, one can know the degree of its destruction.
CT will allow doctors to know the degree of damage to the bone and surrounding tissues. This will determine the amount of necessary surgical intervention.
The timely diagnosis of the disease depends on the success of osteomyelitis treatment.
Therapy of violation of
The main tasks of treatment of hematogenous osteomyelitis are:
- elimination of the causative agent of the disease;
- stop the inflammatory process;
- removal of necrotic tissue;
- recovery of lost function.
For effective treatment, pharmacotherapy, surgical treatment and a combination of these options can be used.
Exclusively drug therapy is assigned to patients in the initial stages.
As medicines are used:
- specific and nonspecific antibiotics;
- steroid and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectors;
- vitamins;
- mineral complexes.
Surgical treatment aimed at eliminating pus, necrotic masses and eliminating non-viable tissues. 
Also used prosthetics, which allows you to install special pins in place of damaged bone and make the plastic of the removed muscles.
In the presence of a fistula, the fistulous course is washed with antibacterial solutions and puts drains, due to which the purulent contents come out.
What complications is fraught with the disease?
Individual sensitivity to antibiotics does not always allow you to select adequate antibiotic therapy for a particular patient.
Insufficient revision of the fistula, bone and adjacent soft tissues, can promote the propagation of pathogenic microflora in the inflammatory focus. All this leads to the fact that the disease continues to develop in chronic form.
After performing a surgical procedure, it is not always possible to restore the function of bone and soft tissue. This creates a predisposition to frequent fractures, impaired function( chewing, supporting, motor).
Prevention of the disease
Prevention of the disease consists in the implementation of simple rules for monitoring health status.
These include:
- timely treatment of infectious diseases;
- complete treatment of chronic diseases;
- health status check every six months.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis is a nonspecific disease that can develop at any age.
To prevent its development, you must carefully monitor your health and regularly visit the therapist for preventive examinations.