 Marcus Gunn syndrome( palpebromandibular synkinesia) is a pathology of an innate, sometimes acquired character. It occurs very rarely.
Marcus Gunn syndrome( palpebromandibular synkinesia) is a pathology of an innate, sometimes acquired character. It occurs very rarely.
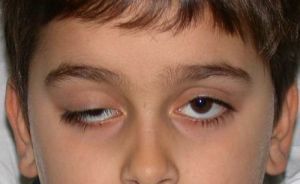
Accompanied by blepharoptosis( lowering) of the upper eyelid, combined with syncopeesis - lifting under jaw movements affected by ptosis eyelids. Diseases are often accompanied by a variety of eye pathologies: strabismus, amblyopia.
Variants of blepharoptosis
The symptom of Marcus Gunn is observed in about 5% of patients with congenital blepharoptosis. The latter can be unilateral( 69% diagnosed cases) and bilateral( 31% of situations).
This is not only a cosmetic defect, giving the face an apathetic expression and provoking a constant position of raised eyebrows. Palpebromandibular syncopeesis mechanically hinders vision, prevents the normal development of the visual analyzer.
In terms of severity, blepharoptosis happens:
- partial - slightly closes third of the pupil;
- incomplete - it is already blocked by 2/3;
- complete - the pupil is not visible at all.
True and false blepharoptosis is different. Pseudoptosis is observed with a significant accumulation of fat under the skin( hernia of the century), a decrease in the elasticity of eyeballs.
Causes of the
Syndrome The pathological process is congenital and acquired.
The first is often inherited due to disruption of normal muscle development, regulating the rise of the upper eyelid. Synkinetic palpebromandibular syndrome may also result from birth trauma.
Acquired Hunn Syndrome also occurs with:
- muscle relaxation, regulating the eyelid lift, due to the natural aging process;
- for diabetic neuropathy;
- as a complication after the Botox procedure;
- Multiple Sclerosis;
- Horner's syndrome;
- chronic circulatory failure of the brain;
- of ophthalmoplegic migraine;
- craniocerebral trauma;
- stroke;
- encephalitis.
The pathogenesis of the syndrome is not established, but some authors explain the development of the syndrome by the pathological relationship between the oculomotor and the mandibular nerves or between their nuclei.
Symptomatic
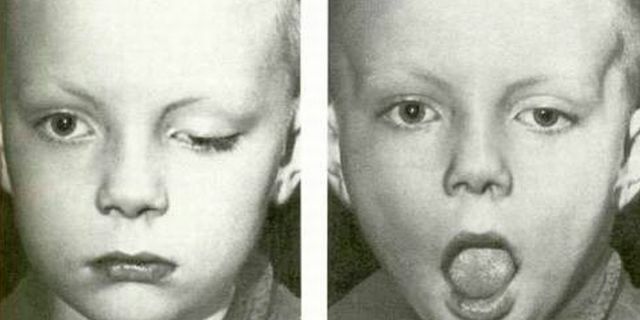
In a calm state, one or both eyes do not open completely due to blepharoptosis. There is synkinesia - reflex 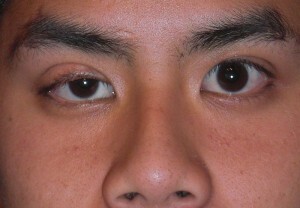 lifting of the eyelid during jaw movements( during a conversation, chewing food).
lifting of the eyelid during jaw movements( during a conversation, chewing food).
The severity of the descent of the ptotic eyelid, as well as the magnitude of its dependence on the movements of the mouth may be different.
To close eyes, you have to put some effort. As a result - they quickly get tired, there is increased tear.
Diagnostic measures
The ophthalmologist performs a visual inspection during which he studies the mobility of the eye and eyebrows, the placement of the upper eyelid, and the width of the eye opening. And also collects the patient's anamnesis, specifying the possibility of inheriting the disease, getting it as a result of traumatization or accompanying pathologies. Additionally, consultation with a neurologist is undertaken to identify concomitant neurological abnormalities.
Usually, diagnosis is not difficult, because symptoms are too characteristic. However, for the confirmation of the syndrome and the precise establishment of its cause, the doctor prescribes a variety of procedures. First, visual acuity is assessed, then biomicroscopy is performed - eye examination using a slit lamp. Thus, the condition of the eyelids, the conjunctival cavity and the cornea is checked.
If the cause of the syndrome is the result of trauma, then the radiography is assigned. Magnetic resonance tomography is performed if the ailment is a consequence of the CNS lesion. In this case, neurologist consultation is also recommended.
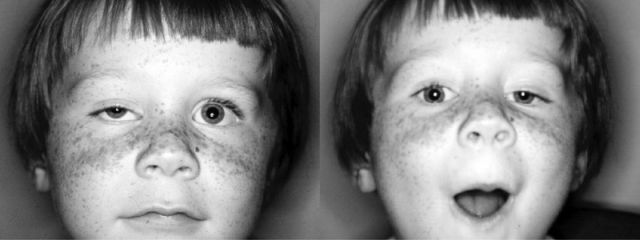
Photo and video for understanding how blepharoptosis looks like in life:
Medical care
In the formation of blepharoptosis due to unsuccessfully performed botulinum therapy, Prozerin, injection of 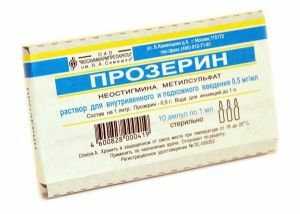 vitamins B1 and B6, physiotherapeutic procedures, facial massage are prescribed. However, all these measures only slightly contribute to the restoration of muscle functions. Usually the pathology disappears on its own for 1-2 months.
vitamins B1 and B6, physiotherapeutic procedures, facial massage are prescribed. However, all these measures only slightly contribute to the restoration of muscle functions. Usually the pathology disappears on its own for 1-2 months.
Non-surgical treatment of Marcus Gunn syndrome is also possible with a false form of the disease or a neurogenic cause of the syndrome.
Correction is performed by the appointment of physiotherapy( electrophoresis with Prozerin solution, Darsonval, microcurrents, galvanotherapy) and massage.
At home, special gymnastics brings increased muscle tonus of the upper part of the face and strengthens them, using a lifting cream, rubbing the face with a tincture made from birch leaves, potato juice, decoction of parsley root, ice cube processing.
Gymnastic exercises for blepharoptosis are as follows:
- circular movement of the eyes( the head is fixed at the same time);
- maximum opening of the eyes in and holding them in this position for about 10 seconds, followed by closure and tension of the muscles at the same time( the procedure is repeated up to 6 times);
- fast blinking for about 30 seconds, with the head tilted back( repeat up to 7 times);
- lowering of eyes with a delay of a sight on a nose about 15 with and the subsequent relaxation( up to 6 times).
Since the formation of the eye gap occurs before 10 years, the children are prescribed fixation of the eyelid with a medical plaster. This method is also used as a short-term care after botulinum therapy or inflammation of the conjunctiva. If blepharoptosis is up to 3 cm, then it is possible to learn how to control the lowering of the eyelid with the help of chewing muscles.
Surgical intervention
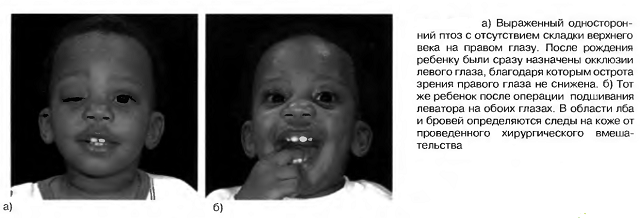
A radical method of treatment is indicated in congenital Marcus Hunn syndrome in children and inefficiency of long-term( more than 6 months) conservative therapy. The procedure is allowed from 5 years. It is performed under general anesthesia. Sutures are usually removed after 2 weeks.
Operations to eliminate blepharoptosis are divided into 3 groups:
- Hess's procedure - is performed if neither the levator nor the upper rectus function. The tightening of the eyelid is due to the use of the frontal muscle work;
- method Mote - with paralysis of the levator with the help of the upper rectus muscle, correction of blepharoptosis is performed;
- BLASKOVICA operation - is aimed at forming the fold of the leftist.
Usually the forecast is quite favorable. In adult and elderly patients, getting used to the pathology and learning to control the chewing muscles, they pay less attention to it, getting used to the defect.
In the case of synchronization of the eyelid and jaw, which worsens the quality of life, a surgical operation is necessary.
Marcus Gunn's syndrome is an unpleasant pathology that forms a cosmetic defect that can worsen vision. However, the disease is successfully treated in an operative way, and in the future nothing reminiscent of itself.