The Drave syndrome is a severe variant of infantile epilepsy, the symptoms of which occur in one infants of 40,000. The rarity of the disease is phenomenal - only 500 officially recorded cases. Among the patients, 66% of the injured are boys.
The Drave syndrome is a severe variant of infantile epilepsy, the symptoms of which occur in one infants of 40,000. The rarity of the disease is phenomenal - only 500 officially recorded cases. Among the patients, 66% of the injured are boys.
The death rate for the Drave syndrome reaches up to 18% of the cases( mainly as a result of accidents during seizures).
The name derives its name from the French psychiatrist and epileptologist Charlotte Drave, who studied childhood seizures and their consequences for the patient's psyche.
In 1978, she first described the cryptogenic epileptic syndrome, which will bear her name. At that time, the disease was characterized as epilepsy with generalized and focal clinical manifestations. Now pathology is classified as benign myoclonic epilepsy of infancy or epileptic encephalopathy in infants.
Contents of
- What is the basis of the development of the disease
- Variety of the disease
- Clinical picture
- Details of seizures
- Diagnostic approach
- Assignable treatment
- What is the risk of the disease?
What underlies the development of the disease
Doctors are still puzzling over where the legs grow from the disease. According to the observation of experts, the Drava syndrome can be provoked:
- by CNS inflammation;
- impaired brain development;
- is a metabolic disorder.
However, all specialists agree that the main reason for the occurrence of the Drave syndrome is genetic predisposition( mutation of genes in the sodium channel of neurons).It is also noted that any newborn can be a potential carrier of the syndrome.
Syndrome is caused by spontaneous( truncated) mutations in the following genes:
- SCN1A( 80% of cases);
- GABRG2;
- PSDH19.
Species of the disease
By origin, the disease is divided into:
- epileptic;
- is notapeliptical.
The Drava syndrome absorbs several types of epilepsy. On the differentiation of clinical manifestations, the following types of seizures are distinguished:
- myoclonic epilepsy( develops after the first year of the disease);
- febrile seizures;
- tonic-clonic seizures;
- atypical absences( occur after a year of illness);
- focal seizures.
Clinical picture
 Before the debut of the development of the Drave syndrome, the child's development is no different from the development of his healthy peers.
Before the debut of the development of the Drave syndrome, the child's development is no different from the development of his healthy peers.
The first signs of epilepsy in infants are detected already in the first year of life( from 3 to 12 months).
There are cases when the first seizures began at the earliest in the three-month and later - at the age of four. The main symptomatology:
- convulsions;
- seizures;
- tweaking;
- muscle hypotension;
- ataxia;
- photosensitivity;
- autoinduction;
- delayed psychomotor development.
To the textbook signs of the syndrome doctors refer changes in the electroencephalogram of patients. Over time, the symptoms in children only progress: seizures become more frequent, longer. The patient deteriorates motor skills, inhibited mental development.
On the video - the only kid with the Drave syndrome in Russia:
Details of seizures
Seizures in the Drave syndrome fall into the following categories:
- generalized;
- is clonic;
- is tonic;
- one-sided;
- myoclonic;
- atypical absence.
The disease is divided into three stages:
- febrile;
- is catastrophic;
- relative stabilization.
The duration of seizures on average lasts from several minutes to half an hour. Febrile seizures open the way for the disease,  begins the course of the pathology;they can take atypical forms, and their duration does not exceed 20 minutes, appear without precursors.
begins the course of the pathology;they can take atypical forms, and their duration does not exceed 20 minutes, appear without precursors.
However, in 25% of cases, such an attack exceeds this time frame and may take on an epileptic status.
A year later, after the end of the disease, the so-called.myoclonic paroxysms, the intensity of which increases in direct proportion to the course of the course of the syndrome. Paroxysms break up into two groups of seizures:
- massive epileptic;
- segmented.
Seizures can provoke a number of the most varied external and internal factors:
- noise;
- loud music;
- high ambient temperature;
- highlights;
- flickering the TV;
- reflection in the mirror;
- increased excited state;
- stress;
- febrile state;
- hyperventilation.
Localization of seizures in the brain is not determined by any pattern. A seizure can be triggered by an impulse originating in the frontal, temporal or occipital areas.
Diagnostic approach
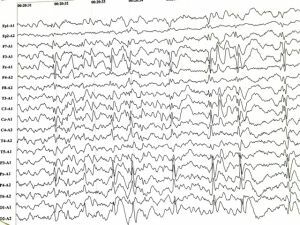 Diagnosis of benign myoclonic epilepsy in infancy is based on a genetic test. An electroencephalogram also fixes pathological changes.
Diagnosis of benign myoclonic epilepsy in infancy is based on a genetic test. An electroencephalogram also fixes pathological changes.
The printouts show a decrease in the bioelectrical activity of the brain with an increased frequency of theta rhythms( 4-5 Hz).It is against the background of a decreased activity that the functioning of cognitive functions is disrupted.
Records of patients in the catastrophic phase of the course of the disease reflect an increase in epileptiform activity( secondary convulsive seizures).It is recorded as the following differentiation:
- generalized peak-polypic;
- generalized + regional;
- generalized with subsequent accession to the regional;
- generalized with substitution regional;
- regional.
Assignable treatment
Therapy of the disease is complicated by the fact that at the moment the disease is resistant to all known medical products. Doctors can only pharmacologically alleviate the manifestations of the disease by prescribing anticonvulsants( alone or in combination) that stabilize the patient's condition:
- Stiripentol;

- Valproic acid( 30-70 mg / kg / day);
- Topiromate( 2-10 mg / kg / day);
- Clonazepam;
- Depakin;
- Urbanil;
- , etc.
Along with drugs, rehabilitation therapy is provided. Dolphin therapy is also practiced.
From a somewhat unconventional point of view, Israeli scientists approached the solution of the issue of treatment. They started the  in the last century with a cannabis plant against epileptic seizures and other diseases.
in the last century with a cannabis plant against epileptic seizures and other diseases.
The results of these studies have shown that treating seizures with oil extracted from a variety of cannabis has a facilitating effect. This oil contains a high content of cannabidiol. This substance, which reduces the electrical activity of the brain. Taking this medicine with food, children became less prone to attacks.
What is the danger of the disease?
Of the complications, developing as a consequence, problems with the psyche:
- hyperactivity,
- attention deficit disorder;
- problem behavior;
- conscious attempts to harm yourself;
- development of psychosis.
During the acute course of the syndrome, the patient experiences an intellectual decline, a retardation in development. However, by the school age, according to the statistics of doctors, patients restore their mental abilities.
Another category of complications is formed by a number of consequences, developing on the basis of intoxication from the constant reception of anticonvulsants:
- asphyxia;
- cardiac arrest.
 With age, the syndrome does not go away, it only modifies and takes a lighter course with a reduction in the number of seizures( mainly at night).Significantly reduced the threshold of photosensitivity and other triggers of an attack of factors.
With age, the syndrome does not go away, it only modifies and takes a lighter course with a reduction in the number of seizures( mainly at night).Significantly reduced the threshold of photosensitivity and other triggers of an attack of factors.
Early diagnostics of the disease falls into the category of preventive measures. Rapid diagnosis of the diagnosis makes it possible to reduce the number of unnecessary interactions with the child, such as visiting a multitude of specialists, conducting tests, taking medications.
Seizures occur in conjunction with infectious diseases. Therefore, the use of immunoglobulins is recommended.
To reduce photosensitivity provoking convulsions, doctors prescribe wearing special glasses with blue lenses.