The Lennox-Gastaut syndrome is a rare and severe form of epilepsy, the symptoms of which begin to manifest in early childhood. Attacks are characterized by a variety of epileptic seizures.
The Lennox-Gastaut syndrome is a rare and severe form of epilepsy, the symptoms of which begin to manifest in early childhood. Attacks are characterized by a variety of epileptic seizures.
This type of epilepsy is very hard to treat, but medicine is developing more and more new techniques for the successful treatment of this disease.
The debut of the disease usually falls on the age of two to eight years, sometimes a little later. Such children are hard to learn, first of all, this is due to the delay in the overall development - they start rather late sitting down on their own, crawling, walking.
Delay in development may be mild or severe, along with cognitive impairment.
Physiological and mental development of each child individually, so it is difficult to predict how the baby will behave with this syndrome.
While most patients have frequent attacks of epileptic seizures and other various disorders, in some cases, adequate treatment produces fairly good results and a reduction in the number of seizures.
For the first time children's myoclonic epilepsy was isolated as a separate syndrome in the 50's.the last century, and after ten years the neurological community recognized it as an independent nosological form.
This disease varies according to different data from 3% to 10% of all cases of epilepsy in children. The prevalence of pathology is equal to one or two cases per 10 thousand people. It is more common in boys than in girls.

Contents
- Pathogenesis of the disorder
- Seizure characteristics
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Medication therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Feeding characteristics
- Complications and prediction
Pathogenesis of the
disorder Although the first symptoms occur in children aged two to eight years, a separate focus group of patientswhich  disease manifests itself in 4-6 years of age.
disease manifests itself in 4-6 years of age.
In some cases, the disease is transformed from Vest syndrome, the diagnosis of which puts the children to a year. Then the syndrome will develop according to one of the scenarios:
- infantile spasms of the Vest syndrome are replaced by tonic attacks, skipping the latent form and passing into the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome;
- children's spasms Vesta syndrome pass, there is an improvement in psychomotor development.
Complex of provoking factors
To date, specific causes of this type of epilepsy are not known. The risk factors include:
- oxygen starvation of the fetus in the prenatal period ;
- lesions of the child's brain in the prenatal and natal period - premature birth, physiological underdevelopment;
- infectious brain lesions of due to rubella, encephalitis, meningitis;
- cortical dysplasia - a disorder of the structure of the cortex of the brain;
- Tuberous sclerosis - benign tumors in a variety of tissues and organs.
- idiopathic factor - the disease develops for unknown reasons;
- genetic predisposition .
Seizure characteristics of
Children with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome suffer frequent attacks of epileptic seizures in severe form. The clinical picture of the disease is as follows:
- Atonic seizures of .There is a sudden decrease in the tone for a few seconds, there may also be a brief disturbance of consciousness. In the case of a minimal duration of the attack, the symptoms have the form of knee-flexing, head-hanging or even nodding, with a prolonged fit the child can completely lose consciousness and fall. Tonic seizures .The muscle tone rises, they become stiff. Seizure can last from a few seconds to several minutes. Often come at the time of transition from sleep to wakefulness. If the child does not sleep at this moment, it can fall
 due to loss of consciousness.
due to loss of consciousness. - Absence seizures of .Consciousness "turns off" for a few seconds, with the child freezes, the view is focused at one point. There are also twitchings of the eyelids. Falls with such seizures do not occur, the attack goes by suddenly. Very often such seizures remain undetected for several years.
- Myoclonic seizures .They manifest themselves in the form of involuntary jerking of the hands and feet, less often the whole body. The patient can fall or drop objects from the hands.
Many children with Lennox Gasto's disease have mental underdevelopment, and as a result - learning difficulties, as well as cognitive( behavioral) disorders, for example, lack of self-preservation, demonstrativeness, impulsiveness.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the following activities:
- The history of - at what age did the first symptoms appear, how did the birth take place, did the family have epilepsy, and how did the child's mental and physical development proceed.
- Neurological examination of - conversation with the child, use of special tests and scales to identify delays in mental development.
- Electroencephalography is an analysis of electrical activity in the brain. Diffuse slow acute waves are found in patients. The procedure is carried out for a whole day in a state of wakefulness and rest, which allows you to track the frequency of seizures.
- MRI and CT - a layer-by-level examination of the brain structure in order to detect damage to its structures.
Treatment of Lennox-Gastaut disease involves several methods.
Medication Therapy
The goal of therapy is to reduce the frequency of seizures. The drugs are selected individually, taking into account the minimal occurrence of side effects.
The following anticonvulsants are prescribed:
- Clobazam;
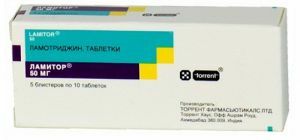
- Rufinamide;
- Sodium divalproate;
- Lamotrigine;
- Topiramate;
- Depakin;
- Carbamazepine;
Often the use of one agent does not give the desired results. Preparations are appointed in a complex, and the reception is strictly controlled by the attending physician.
Surgical treatment of
In the absence of a positive effect after medical therapy, surgical treatment is performed using various methods:
- Implantation of the vagus nerve stimulator .It is performed by sewing in the area of the clavicle a special device with an electrode transmitting electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. This method reduces the amount of
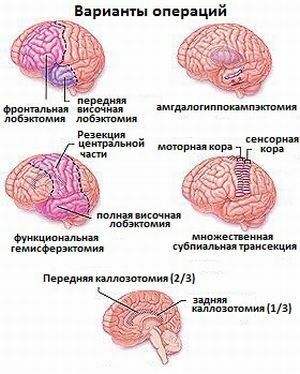 seizures. As practice shows, more than half of patients due to this method, the frequency of attacks is significantly reduced.
seizures. As practice shows, more than half of patients due to this method, the frequency of attacks is significantly reduced. - Implantation of the RNS-stimulator under the scalp, which generates electrodes in the brain area. Electrodes continuously fix the electrical activity of the brain, and at the time of the onset of an attack, the stimulator gives electrical impulses that suppress the epileptic focus.
- Callozotomy is a dissection of the corpus callosum, which is a bundle of nerves that connects the hemispheres of the brain and transmits epileptic impulses from one part of the brain to the other. After the operation, the seizures do not disappear at all, but become less intense, since impulses are not generated from one hemisphere to another. Usually, this treatment is used in cases of uncontrolled epileptic seizures.
Features of nutrition
Very often, along with other therapeutic methods, a ketogenic diet is used. It is a reduction in carbohydrate intake and an increase in fat intake.
In addition, products with a low glycemic index, i.e. those that lower blood sugar levels, are recommended. These include: fruits, vegetables, legumes, wholemeal products, skimmed milk.
During such a diet the doctor should control the possibility of reducing the doses of the drugs taken.
Complications and prognosis
 The disease in most cases has an unfavorable prognosis. About 10% of patients die at the age of ten, this is due to severe injuries during seizures.
The disease in most cases has an unfavorable prognosis. About 10% of patients die at the age of ten, this is due to severe injuries during seizures.
Virtually all sick children experience mental retardation to some extent, half of patients are not capable of self-service.
Also to complications it is possible to carry:
- resistance to seizures due to resistance to treatment;
- the safety of an intellectual defect that does not disappear;
- disorder of social and labor adaptation.
It is not possible to prevent the onset of this disease. The main preventive measures in this case can be considered:
- Maintaining a high quality of life - a healthy lifestyle, a full eight-hour sleep, proper nutrition, avoidance of stress factors.
- Qualified lifelong treatment .In no case can you yourself change the scheme of treatment or interrupt it.