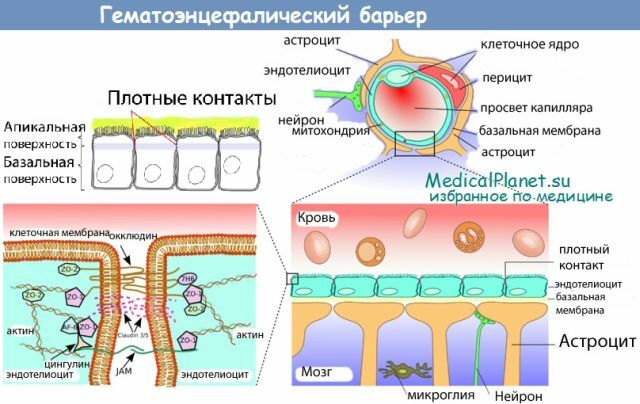
Serous meningitis is a serious infectious disease in which an inflammatory process of the serous nature of the brain envelopes occurs, most often caused by fungi and viruses.
Serous meningitis is a serious infectious disease in which an inflammatory process of the serous nature of the brain envelopes occurs, most often caused by fungi and viruses.
In most cases, the cause of the disease is viral diseases. In the main risk group are children under the age of 6 years, in school children, serous meningitis occurs less frequently, and in adults it is very rare. Therefore, serous meningitis in most cases, is a childhood disease.
When the disease occurs, inflammation of the soft tissues of the brain. The disease can occur in both primary and secondary forms. The primary form of the disease occurs when the virus is attacked, the secondary form is a consequence of some diseases( measles, tuberculosis, etc.).
Contents
- Causes of the disease
- Causes of the disease
- Ways of infection
- Children at risk
- Symptoms of the disease in children and adults
- Diagnosis of
- Therapeutic package of
- Parents and their children
Causes of the disease
The main cause of meningitis is viruses. It can be influenza, herpes, measles, cytomegalovirus, mononucleosis, etc. 
Serious meningitis is affected by 80% of cases, because at this age there are frequent outbreaks of viral diseases, and also because of weak immunity.
Serous meningitis has documented the occurrence of cerebral edema, which leads to increased blood pressure and impairment of cerebral fluid outflow.
Serous meningitis is the least dangerous in comparison with other types of disease, as it does not lead to the death of brain cells. Therefore, with timely treatment does not cause complications and severe consequences.
Ways of infection
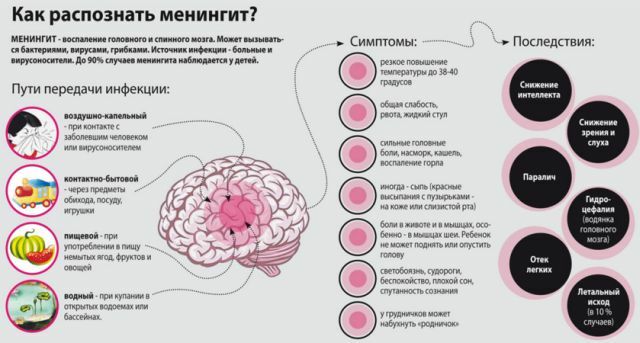
After the onset of the disease, the incubation period lasts from 2 to 4 days. The routes of infection vary depending on the pathogen and may be as follows:
- Contact .The causative agent can be on the mucous membranes of the eyes, in the mouth, in open wounds. From these areas the pathogen can spread to objects. When in contact with a sick person or with contaminated objects, a healthy person can become infected. Therefore it is important to wash your hands before eating and coming from the street, and also to wash the purchased fruits and vegetables.
- Air and mucous membranes .Since the pathogen is located on the mucous membranes, when sneezing and coughing, it can enter the body of a healthy person.
- Water .Increasingly, outbreaks of meningitis infection occur in the summer. It was proved that the virus can penetrate the human body through water contaminated with the virus. After swimming in such water bodies there is a risk of infection.
Children at risk
The peculiarity of serous meningitis in children is that their initial symptoms are often confused with a mild viral illness, but after the day the manifestations of the disease begin to progress, which should disturb the parents and encourage them to call an ambulance.
Each touch to the child causes a cry, also such a reaction may occur when the light or any sound is turned on. Also, serous meningitis in children is accompanied by high fever, resulting in vomiting, sometimes diarrhea.
The child becomes very irritable and moody. In some cases, the disease can not be so clearly manifested, which leads to the establishment of an erroneous diagnosis.
It is very important to determine the type of meningitis, because the treatment depends on this, as well as the severity of the consequences. When confirming serous meningitis, the degree of disease is determined by the amount of protein in the cerebrospinal fluid. With large protein values in the samples, there is a risk of complications in the child, including mental retardation.
With proper treatment, the duration of the disease is 8-12 days.
Symptomatic of the disease in children and adults
After the incubation period has ended, after a couple of days meningeal symptoms may begin to manifest, which may be common, and also differ depending on the occurrence of serous meningitis in a child or adult.
General symptoms:
- feverish condition;
- increase in body temperature to 40 degrees, which decreases after 3-4 days, and then can rise again;
- severe headache;
- weakness;
- nausea, sometimes resulting in vomiting, abdominal pain, lack of appetite;
- visual and auditory sensitivity;
- drowsiness;
- with severe lesions there are paralysis, problems with swallowing.
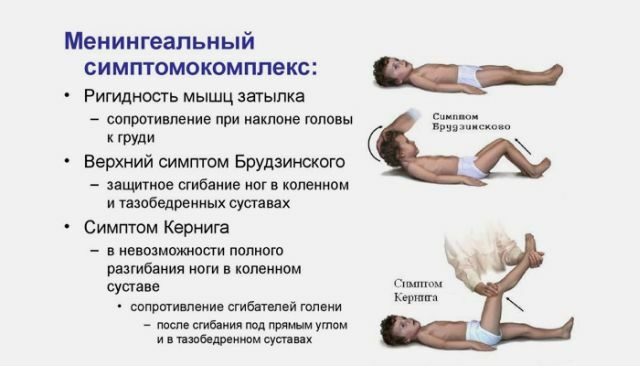
The general symptomatology of serous meningitis can manifest itself in a strong or weak form, depending on the severity and type of pathogen.
In addition to general, children may exhibit specific symptoms that differ from adults in the symptoms of serous meningitis:
- reaction to light and sound;
- cramps of the hands or feet;
- runny nose, sore throat;
- tearfulness;
- cough;
- relief comes in the dark;
- pose of the child in bed: turned to the side, knees bent and pressed to the stomach, hands near the chest, and the head was thrown back;
- diarrhea;
- in the infants swollen fontanel;
- if you take the child's armpits, then he bends his legs in his lap, pressing him to himself;
- neck tension;
- can not straighten the legs at right angles;
- when the head is tilted, legs bend;
- when flexing one leg, the second is unbent reflexively.

Symptoms may manifest themselves as a whole, or not at all.
Adults may manifest themselves as general symptoms of serous meningitis, which can be detected only during the examination, and expressed. Distinctive symptomatology in adults is:
- headache strengthens with movements of eyeballs;
- appearance of pain in the joints and muscles;

- abdominal pain;
- impaired consciousness;
- paresis and strabismus;
- herpes sores on the lips or nose;
- worry;
- general malaise and lethargy;
- insomnia.
Symptoms of the disease in adults can also manifest themselves as a whole, or not at all. In any case, if any of the symptoms occur, you need to urgently consult a doctor for a diagnosis to make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of
Diagnosis of meningitis in adults occurs in a combination of symptoms, as well as the parameters of cerebrospinal fluid, with the existing inflammation of the brain in the fluid will be increased protein, as well as altered other parameters of cerebrospinal fluid.
Puncture of the spinal cord fluid is performed with a clear suspicion of the disease, because the procedure is not safe.
The doctor also prescribes an MRI scan of the brain to track the progression of the disease. The main diagnostic index of the development of the disease in children is the swelling of the temples.
A set of therapeutic measures
When confirming the diagnosis of a patient, regardless of whether he is an adult or a child, they are placed in a hospital. What treatment will be prescribed and its duration directly depends on the course of the disease.
For mild disease, children are prescribed vitamin therapy: ascorbic acid, vitamins B6 and B2.Enter intravenously for detoxification of albumin and blood plasma.
A drug complex that is prescribed for the treatment of serous meningitis in pediatric patients:
- if a disease of a viral etiology, prescribe drugs for antiviral therapy( Interferon);
- for the disease caused by the herpes virus or Epstein-Barr is prescribed Acyclovir;
- for infants, as well as for children with reduced immunity for therapy, is prescribed Immunoglobulin intravenously;

- is prescribed funds to reduce spasms( No-shpa, Drotaverin);
- for the lowering of high temperature is prescribed Ibuprofen or Paracetamol;
- Domosedan and Seduxen are prescribed with cramps;
- therapy with vitamins of groups B and C;
- recommended nootropic drugs( Glycine, Pyrocetam).
Lumbar punctures are also performed to reduce pressure.
Treatment of the disease in adults is practically the same as for children. The basis for the treatment of serous meningitis are antiviral drugs, as well as aids to relieve the condition:
- for diuretics, diuretics are prescribed( Furosemide, Lasix, Azzazolamide);
- antiviral drugs( Acyclovir, Interferon);
- anti-inflammatory drugs( Prednisolone);
- intravenously injected saline solutions to reduce the toxic effect of the disease( saline is prescribed with Prednisolone, as well as ascorbic acid);
- when a risk of heart failure is assigned to colloids( Albumins, Hemodesis);
- recommended antispasmodics( Drotaverine);
- succinic acid, Inosine, Riboflavin - for the nervous system.
Bed rest is required for 10-14 days, muffled light.
With proper treatment both in children and in adults there are rarely complications.
With proper treatment and timely access to the doctor for serious complications of the disease should not be. But often in the background of serous meningitis, there may be such consequences:
- speech impairment;
- paralysis;
- occurrence of hallucinations;
- coma;
- lethal outcome.
With adequate and correct treatment, the disease recedes within 10-12 days, but a part of the symptoms: weakness, fatigue and headache may appear even for a month.
Parents, as well as their children
Despite the fact that with timely treatment of serous meningitis does not have dangerous consequences, yet the disease is very serious.
Therefore, it is necessary to take timely preventive measures, both to prevent the disease at all, and to exclude its recurrence. Basic preventive measures:
- wash hands after street;
- wash vegetables and fruits;
- do not snack on the street;
- to increase immunity;
- when swimming in open reservoirs, ensure that water does not enter the body through the nose or mouth.

In addition to everything else for prevention it is important to do sports and eat right.