 The upper brain neurons responsible for movement are located in the hemispheric cortex, descend and contact in the bulbar with their processes with cells of the spinal cord.
The upper brain neurons responsible for movement are located in the hemispheric cortex, descend and contact in the bulbar with their processes with cells of the spinal cord.
Spinal cord motoneurons are also common in the lumbar, thoracic and cervical divisions( based on the type of muscles where the signals regulating their contractions are directed).The motor neuron spends a nervous impulse from the spinal cord to the cortex of the brain.
Motor neuron disease( MND) is a neurodegenerative pathology with an increasing character, resulting in damage to the motor neurons of the spinal cord and brain. As a result of the gradual dying of nerve fibers, muscle weakness increases with increased symptomatology and lethal outcome.
Because of damage to motor neurons, the functions of the spinal cord and spine disappear, paralysis gradually begins, speech is lost, swallowing is difficult.
The incidence rate is 2-5 people per 100,000 people per year. The disease manifests itself at the age of 50-70 years, sometimes in patients younger than 40 years. On average, patients live 1-4 years after diagnosis.
Contents
- Affected areas
- Pathogenesis and pathomorphology of the disease
- What causes death of motor neurons?
- Basic and rare types of MND
- Symptoms and clinic MND depending on the form
- Differential diagnosis
- Treatment options
- ALS - motor neurons die completely
- Diagnosis and treatment
Affected areas
With gradual development of motor neuron disease, patients experience increased respiratory problems, swallowing, movement and communication with other people. The following difficulties may appear: 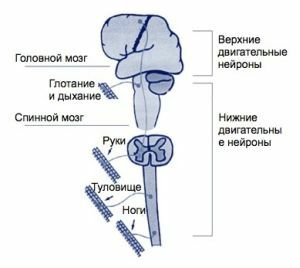
- Brushes, hands .Even with daily tasks( washing dishes, turning the tap, pressing the keys), there will be increasing difficulties with increasing weakness in the palms and hands.
- Feet .Because of the weakening of the legs, the patient will find it increasingly difficult to move around.
- Emotional state of the .Sometimes zones that are responsible for emotional reactions can be affected, which is manifested by involuntary laughter or crying of a physiological nature.
- Shoulder, neck .After a certain time, the patient becomes difficult to breathe because of the weakening muscles of the neck.
- Breathing .Basically, the disease spreads to the respiratory muscles, making breathing difficult.
- Swallowing, speech functions .There may be difficulties with eating, drinking and talking.
In some patients, MND causes memory impairment, reduced concentration, difficulty with word selection, and learning. That is, there is an inconspicuous and hidden change in mental functions.
With MND, the intellect remains intact, patients realize everything that is happening. Many people are not affected by sight, taste, touch and hearing, the functions of the bladder, intestines, genitals( up to the later stages) and heart muscle remain functional.

Pathogenesis and Pathomorphology of the
Disease of motor neuron disease is considered a pathology of a multifactorial type, the development of which comes from the effects of genetic heredity with surrounding factors.
In 10% of cases, the disease is associated with family forms, where 25% - are characterized by the mutation of the SOD-1 gene. Sometimes sporadic types of pathology are associated with changes in other genes( neurofilaments) as a result of violations of functions or structures, in which the motoneurons begin to degenerate. The mechanism is triggered by the action of provocateurs( age, sex, heavy metals, etc.).The relationship between the onset of the disease and infectious agents is unlikely.
Clinically, neurons degenerate upon destruction from 80% of cellular structures, which makes it difficult to timely treat pathology and needs diagnostic studies during the preclinical stage.
Near the frontal lobes, in 3, 5 layers of the central convolutions, motor nuclei 5, 7, 9 and 11 of the nerves of the skull in the brain stem degeneration of neurons and change of corticospinal tract is determined. At different stages of motor neuron change, eosinophilic, basophilic inclusions and Bunin's body are determined.
Axonal spheroids are formed in the proximal axon sections. Based on the data obtained, violations of the movement and degradation of proteins are noted. In the muscular structures, denervation atrophy is determined.
What causes death of motor neurons?
According to experts, the main causes of MND are heredity and environmental factors that increase the risk of pathology.
 Approximately 5-10% of patients with motor neuron disease had a family hereditary form. Basically, MND was diagnosed( 90-95% of cases) with sporadic form, which appears for unknown reasons.
Approximately 5-10% of patients with motor neuron disease had a family hereditary form. Basically, MND was diagnosed( 90-95% of cases) with sporadic form, which appears for unknown reasons.
Epidemiological studies have identified a possible association of shock, mechanical injuries, high sports loads, harmful substances on the development of the disease.
Surveys of mechanisms of damage to intracellular processes are currently under way, due to which motor neurons with surrounding cells die.
Possible strike and failure of the work of "editors" in the processing of RNA, changes in chemical communication connections of the spinal cord, disruption of the transport of metabolic products, nutrients, aggregation of protein aggregates in neurons with disruption of normal functions and adhesion, the appearance of free radicals of oxygen,background cells and a lack of nutrients for motoneurons. Also death of motor neurons can occur due to the environment by glial cells, which can be toxic.
Major and rare species of MND
The motor neuron disease has several basic forms:
- ALS( side amyotrophic sclerosis) develops in 80% of people with motor neuron disease, mainly causes weakness, convulsions and muscle wasting, stiffness of the upper and lower extremities;
- PBP( bulbar palsy of progressive type) affects about 10-25% of people, spreads to the neurons of the spinal cord and brain, manifests itself by difficulty in chewing, swallowing, illegibility of speech;
- muscular progressive atrophy ( 8%) is a rare type of MND, extends to motor neurons in the lower limbs, develops weakness, muscle atrophy, fasciculation and weight loss;
- ( lateral primary sclerosis) ( 2%) affects predominantly motor neurons in the upper limbs, developing spasticity of the muscles, unstable walking, and difficulty speaking.
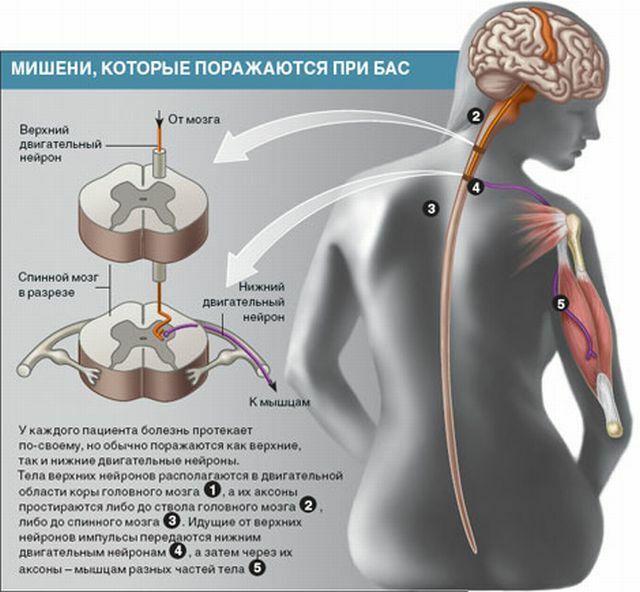
Symptomatology and clinic of MND depending on the form of
The motor neurons are affected by a whole group of diseases. The structure of neurons includes two groups of cells, necessary for arbitrary movements.
The first group includes motor neurons located in the precentral cerebral gyrus, and the second group includes neurons located in the trunk of the spinal cord and brain.
Depending on the location of the deceased motor neuron, the form of the disease and its symptoms will depend.
In spastic paraplegia, the motor neuron of the first group is affected, with spinal muscular atrophy, children's paralysis - the second group, and with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, both groups of neurons.
Forms of MND and their manifestations:
- Spastic paraplegia is determined by increased spastic tone of the legs with gait disturbance. This is caused by the
 genetic mutations.
genetic mutations. - For spinal muscular atrophy is characterized by weakness and diminution of muscles, lack of their activation or innervation by nerve fibers. Depending on the time of appearance of the first symptomatology and the nature of the distribution of muscle weakness, the classification of spinal muscular atrophy is carried out.
- The most common pathology of the musculoskeletal system is the BAS , whose development rate rises with age. As a result, the necrosis of nerve cells progresses, weakness and muscle atrophy increase.
- Children's cerebral palsy , poliomyelitis is a viral disease of the lower neurons.
Differential diagnosis of
 Diagnosis of MND is confirmed by electron neuromyography, which reveals a generalized denervation process. To reveal spontaneity, duration of motor units, fasciculations, fibrillations, a three-level needle EMG is performed.
Diagnosis of MND is confirmed by electron neuromyography, which reveals a generalized denervation process. To reveal spontaneity, duration of motor units, fasciculations, fibrillations, a three-level needle EMG is performed.
Stimulation electroneuromyography can detect slowing of motor fibers, pyramidal deficiency.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals a decrease in excitability in central motoneurons. MRI allows you to exclude other pathologies with a similar clinic( compression of a hernia or tumor).
Treatment options for
Motor neuron disease is incurable, and the goal of therapy is to slow the development of the process, to reduce the severity of symptoms, since there are no methods for complete cure. The effectiveness of Rilutec - presynaptic inhibitor is proved.
As with ALS, antioxidant agents can be used. Also, specialists prescribe creatine, carnitine, vitamins. Another drug is Riluzole, but the drug is not officially available to patients in the Russian Federation. Like Rilutec, the drug reduces the amount of glutamate released during the transmission of nerve impulses. 
To polyatherapy includes the removal of pain from muscle spasms, which is prescribed Carbamazepine at a dose of about 100-200 mg several times a day. With increased muscle tone, it is necessary to take muscle relaxants( Sirdalud, Baclofen).
Respiratory support is the main factor affecting the quality of life and prognosis. With the progression of the pathology, weakening and atrophy of the muscles of the diaphragm and other muscle groups is observed, non-invasive ventilation of the lungs is required.
This normalizes sleep, reduces fatigue and dyspnea. The device with a special mask is used.
If swallowing is impaired, feeding is performed by a nasogastric tube, installation of gastrostomy. A special diet is prescribed, replenishing the lack of calories.
With MND it is difficult to talk about prognosis. In rare cases, people live for decades. A person can die in a few months. But on average, life expectancy is 2-5 years from the onset of disease detection. There are no specific preventive measures.
BAS - motor neurons die completely
During UAS, the uniform symptoms of central and peripheral paralysis are combined, the predominance of certain symptoms over others( segmental-nuclear or pyramidal variants).At late stages of the disease, the parameters of peripheral paralysis predominate.
During ALS, damage to motoneurons in the anterior horns of the spinal cord begins. With the progression of pathology bulbar disorders are manifested mainly in men.
The thoracic, cervical, diffuse and lumbar debut stands out. The classic option is cervical, the first symptom of which is characterized by weakness and atrophy of the hand, broken by small movements, the presence of fascicular twitches of the affected muscles.
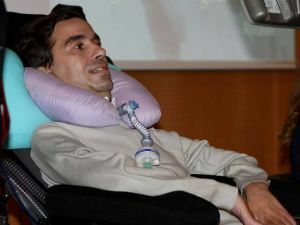
Stephen Hawking - the most famous patient with ALS
In the future, there is weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the shoulder girdle, it is difficult for patients to dress, raise their hands above the horizontal plane. First, one side of the body is affected, then the symptoms appear on the other hand with the development of the upper mixed paraparesis.
The weakness and stiffness of the lower extremities develops, it is difficult for patients to walk long distances, to move along the stairs.
Extensor muscles with manifestation of mixed lower paraparesis are damaged. At later stages pseudobulbar and bulbar syndromes appear, the appearance of dysphagia.
The first symptom of a thoracic debut is fasciculation, muscle atrophy in the abdomen, back and weakness. Patients become difficult to stand and bend over. In the following stages, a mixed one-sided hemiparesis appears with involvement of the musculature of the opposite part of the body. At the initial stage, abdominal reflexes fall out. As a result of respiratory disorders, a fatal outcome occurs.
Diffuse debut is manifested by signs of peripheral motor neuron disorders with pronounced fatigue, respiratory disorders. The weight of the body decreases until the appearance of dysphagia, as a result of respiratory failure, death occurs.
Usually the defeat of masticatory and facial muscles comes later, it is difficult for the patient to stick out his tongue, pull his lips into the tube, inflate his cheeks.
The complications of ALS include paralysis, paresis of the neck muscles and extremities, impaired swallowing, respiratory failure, limb contractures, aspiration pneumonia, urosepsis, depression, painful muscle spasms, cachexia. With the progression of motor disorders, the patient dies.
Diagnosis and treatment of
Diagnosis of ALS is based on a detailed analysis of the clinic. Electroneuromyography( EMG examination) is performed to confirm motor neuron disorders.
There is no effective treatment of pathology. You can delay the lethal outcome for several months by taking Riluzole at a dosage of 50 mg 2 times a day. The basis of therapy is therapeutic gymnastics, physical activity, diet, etc.
Painful muscle spasms are eliminated by Diphenine, Quinine sulfate, Tegretol, Finlepsin, vitamin E400 mg, Isoptin or  with magnesium preparations. When salivation is prescribed Atropine, Buskopn, with spasticity - Sirdalud, Baclosan, Memantine, etc.
with magnesium preparations. When salivation is prescribed Atropine, Buskopn, with spasticity - Sirdalud, Baclosan, Memantine, etc.
Pain symptoms are eliminated by analgesics. Temporary improvement may be from anticholinesterase agents. Also, specialists prescribe antidepressants( Amitriptyline, Sertalin).
The patient should maintain physical activity, with the progression of pathology using special devices. Dysphagia may require feeding through a probe or gastrostomy. Recently, studies of the treatment of pathology by stem cells have been conducted.
ALS is considered a fatal pathology, the average life expectancy at which is 3-5 years. Only about 10% of patients live for 10 years. Negative prognostic indicators include bulbar disorders, elderly age.