In the modern world, the achievement of advanced age is considered a merit of the development of medical science. Indeed, even some two hundred or three hundred years ago the average life expectancy was limited to thirty to forty years, and the old were a rarity.
The cause was a constant epidemic of infectious diseases. After the appearance of antibiotics, mankind began to live longer, and in our time the main causes of death are cardiovascular diseases.
But the elderly age, apart from atherosclerosis and a high risk of myocardial damage and the likelihood of developing a stroke, results in the appearance of such an unpleasant condition as osteoporosis. Let us examine this problem in more detail.
Contents
- 1 Osteoporosis - what is it?
- 1.1 Osteoporosis Classification - Species and Forms
- 2 Osteoporosis in Women - Features of
- 3 Osteoporosis Symptoms
- 4 Osteoporosis Diagnosis
- 5 What are the tests for osteoporosis?
- 6 Treatment of osteoporosis
- 6.1 Consequences, complications of osteoporosis
- 7 Which doctor should I use for osteoporosis?
- 8 Prevention of disease
Osteoporosis - what is it?
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the density of bone tissue decreases, with the appearance of its fragility and a tendency to pathological fractures. In other words, osteoporosis is an increased "porosity" of the skeleton.
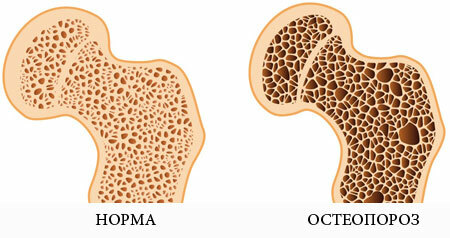
The causes of osteoporosis are very numerous. Briefly, the main reason is the predominance of catabolism( decay processes) in the bone tissue over anabolism( growth and assimilation of nutrients).Most often, the following conditions lead to osteoporosis:
- Climax in women. The lack of estrogen causes osteoporosis, so the risk of bone damage in females is three times higher than in men of the same age;
- Old age. Do not look for any disease, just in the old age there is a decrepit whole body, including bones;
- Prolonged intake of hormonal drugs( glucocorticosteroids).This can be, for example, in the treatment of severe forms of bronchial asthma;
- Alimentary osteoporosis: occurs when there is a lack of calcium and vitamin D in the diet;
- Hereditary factor - the presence of osteoporosis in close relatives and parents;
- Hypodinamy( sedentary lifestyle).With it, blood supply to the deep muscles and bone tissue worsens, and this leads to an inadequate delivery of calcium to the bone;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract( chronic pancreatitis, a syndrome of insufficient absorption in the intestine - malabsorption);
- In women, ovarian disease can lead to osteoporosis, accompanied by a decrease in endocrine function;
In addition to these reasons, there are other conditions that can contribute to an increase in the incidence of the disease in the population. Thus, belonging to a European or Mongoloid race increases the risk of osteoporosis. It is important that African Americans are practically not inclined to this disease.
Classification of Osteoporosis - Species and Forms
First of all, bone damage can be common( common) and local, for example, osteoporosis of the hip joint. Common osteoporosis is also called systemic.
Also, the disease can be primary( if there is no reason) and secondary( for example, with prolonged treatment with hormonal drugs, or with apoplexy of the ovary).
In addition, the structure of bone tissue damage can differ in cortical( superficial bone), trabecular( a violation in the structure of a spongy substance) and mixed.
Osteoporosis in Women - Features of
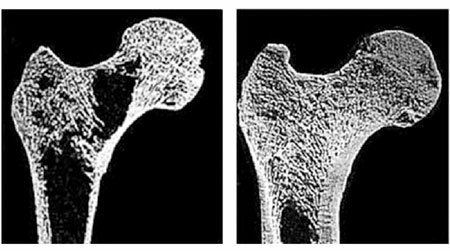
As mentioned above, women are three times more likely to suffer from osteoporosis than men, especially after the termination of menstruation, in postmenopausal age.
This is due to the fact that estrogen, which is produced by the ovaries, prevents the "washing away" of calcium from bone tissue. Looking ahead, we can say that in women, one of the most effective ways to treat this condition is hormone replacement therapy. Symptoms of osteoporosis in women, therefore, are more "numerous" than in men.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
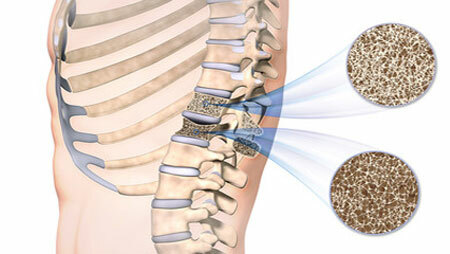
The clinical symptoms of osteoporosis are numerous, but not all are local, that is, they are directly related to the skeleton. So, there are common manifestations of rarefied bone tissue, for example, such as:
- Pathological fatigue associated with systemic calcium deficiency;
- Appearance of increased convulsive readiness, especially in calf muscles;
- Osteoporosis of the spine - its symptoms often include low back pain, both during motion and at rest;
- Nail plates become brittle and often slough;
- Diffuse myalgias, or muscle pains;
- Frequent attacks of tachycardia, or palpitations;
- The emergence of protrusions and hernias in various parts of the spine, most often they occur in the lumbar region, where there is an increased load;
- Appearance of scoliotic deformity of the spinal column, decreased growth.
Finally, the most frequent symptom of osteoporosis is also its complication - it is a pathological fracture.
In this disease, a fracture can occur under the influence of a very weak load, for example, if you try to lift a pot of water, a fracture of the radial bone in the area of the wrist occurs. To avoid this, it is necessary to diagnose osteoporosis long before he "does ill".
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Some people think that the radiography of bones can give an affirmative answer for any degree of osteoporosis. In fact, this is not the case: on the X-ray, only a "neglected" process is seen, in which the loss of bone tissue exceeds 25-30%.
One of the best ways to diagnose a disease is densitometry. It is absolutely painless and safe way of direct measurement of bone tissue density, as well as the mutual correlation of mineral and organic component in bones.
But, despite the conduct of densitometry, in the diagnosis of osteoporosis, some laboratory tests are required.
What tests are taken for osteoporosis?
Research methods reflecting the balance states in the body of phosphorus and calcium are of great importance, since these two elements are found in bone tissue in certain relationships:
- The amount of calcium in the blood plasma;
- Concentration of inorganic phosphorus also in blood plasma;
- The level of parathyroid hormone - it is produced by small parathyroid glands and is responsible for regulating the level of calcium and its utilization from the blood. This substance is one of the most important in the regulation of calcium;
- Osteocalcin protein. It is examined with the observed changes in the level of calcium in the blood. This substance rises in the blood with osteoporosis, but also with certain endocrine diseases;
- The level of vitamin D in the blood plasma;
- Study of the concentration of the hormone calcitonin;
- In extreme and unclear cases, a biopsy is possible, most often the bone of the iliac crest is taken in an insignificant amount.
Osteoporosis treatment
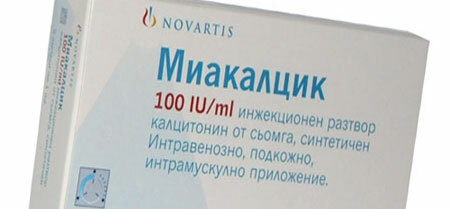
Osteoporosis preparations, photo
Modern treatment of osteoporosis is a complex exercise and is inseparable from proper nutrition, vitamin D supplementation, preparations containing phosphorus-calcium supplements. The most known are the following treatments:
- Use of bisphosphonates, for example alindronate. This drug prevents the destruction of bone tissue and almost twice reduces the risk of pathological fractures;
- Application of Miacalcic, which is a natural analogue of calcitonin, improving the phosphorus-calcium metabolism;
- An effective treatment for osteoporosis in women has hormone replacement therapy, which is performed after the onset of menopause. Estrogen therapy should be performed only after careful examination by a gynecologist, mammologist and taking into account the severity of side effects, the most frequent of which is venous thrombosis.
In addition to the above methods of treatment, patients with osteoporosis are shown a special non-loading exercise therapy, as well as a mild massage.
Consequences, complications of osteoporosis
The most famous and at the same time severe consequence of osteoporosis are fractures. You can even put the sign of equality between these concepts: osteoporosis = fracture. And one of the most dangerous is a fracture of the neck of the hip.
The fact is that immobility and bed rest with this type of fracture can cause hypostatic pneumonia, intestinal paresis, and pressure sores, and as a result, an elderly person can die from the development of infection and auto-toxication in a very short time after fracture.
Therefore, with the slightest suspicion of osteoporosis, the appearance of pain or other symptoms, it is better to conduct a densitometry.
Which doctor should I use for osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease that lies at the junction of many medical disciplines. The search for its causes often begins in the office of a gynecologist, endocrinologist or therapist.
Sometimes, when the manifestation of the disease manifests itself at the same pathological fracture, it can be a traumatologist - an orthopedist.
Prevention of the disease
Prevention of osteoporosis is the quintessence of what can simply be called "a healthy lifestyle. Of course, preventing the rarefaction of bone tissue is much easier than treating its neglected forms, or dealing with multiple fractures.
The most important areas of prevention is a diet with the use of products containing calcium and vitamin D, exposure to the sun, physical activity.
It is important to know that not all physical exercises are equally useful: there must be pressure on the bone, so this kind of load, like swimming, will not be enough.
But riding a bicycle, doing aerobics and dancing - all these are excellent means for preventing such an unpleasant disease as osteoporosis.