The disease affects mostly elderly people, but with predisposing factors, the disease "rejuvenates."Arthritis is characterized by a slow course and constant progression.
Contents
- 1 What is arthritis of the knee joint?
- 2 Knee arthritis causes
- 3 Knee arthritis symptoms and symptoms
- 4 Diagnosis
- 5 Knee arthritis treatment methods
- 6 Knee arthritis treatment with folk remedies
- 6.1 Knee arthritis complications
- 6.2 What is arthritis of the knee joint?
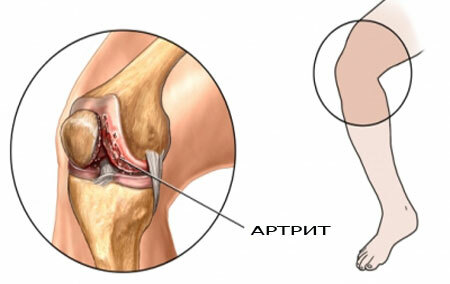
Arthritis of the knee joint is a pathology characterized by damage to the synovial bag, cartilaginous and bony tissues of the knee joint. Each type of disease has a certain pathogenesis and the nature of origin. Regardless of this, it is always accompanied by the main signs( see photo):
- marked pain syndrome;
- limited mobility of the joint;
- is an inflammatory process that occurs in the intraarticular tissues.
Depending on the form, three types of arthritis are distinguished:
- Acute - a single occurrence of the inflammatory process in the tissues of the knee joints is characteristic. Flows with the presence of acute pain.
- Chronic - a long course of the disease with periods of remission and exacerbations. As a result of prolonged inflammation, the inner membrane of the articular cartilage gradually thickens, which leads to complete destruction of the cartilaginous tissue.
- Subacute - an intermediate form of the disease, which has much in common with acute and chronic arthritis. A subacute gonitis is characterized by a prolonged course and gradual destruction of the joint. It is accompanied by a short-term manifestation of symptoms, but is not as pronounced as with acute arthritis.
It's important to know! Many are interested in the difference between arthritis and arthrosis of the knee joint. The first disease in any case is accompanied by the presence of inflammatory foci in the articular cavity of the knee. The second is degenerative, and proceeds in the absence of inflammation.
Depending on the nature of development, arthritis is divided into several types.
1. Gouty
This type of gonarthritis is caused by a violation of metabolic processes in the body. As a result of metabolic disruption, small crystals of salt are formed in the knee joint bag, which have sharp edges.
Crystals systematically injure joint tissues, which leads to the development of inflammatory process and acute pain.
2. Deforming( arthrosis-arthritis)
With arthrosis-arthritis, deformation of cartilage of the knee joint is observed. The process takes place against the background of disturbed blood flow in the bone and joint tissues.
3. Rheumatoid
The disease lasts for years. Often begins asymptomatically, but for a long time is steadily progressing. The etiology of the disease has not been clarified by the doctors so far. In most cases, rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joint leads to disability.
4. Septic
The course of the disease is acute. As a result of penetration into the joint of pathogenic microorganisms, an inflammatory process develops. Symptoms: the knee becomes edematous, there is a sharp pain. There is a noticeable increase in knee joint in size.
5. Juvenile( idiopathic)
In most cases, the development of this type of gonitis is observed in children who have reached the age of 8 years and have a genetic predisposition to the occurrence of joint pathologies.
6. Reactive
Develops after a pathogenic microflora enters the knee joint. Often the source of infection are bacteria that have penetrated into articular tissues from the urinary or digestive system of the body.
7. Post-traumatic
Occurs as a result of a meniscus injury, rupture or sprain.
8. Age
This type of arthritis is caused by the wear and tear of the cartilaginous tissue of the joint, referred to in medicine as hyaline cartilage.
Depending on the nature of the joint lesions, these types of arthritis are distinguished:
- purulent-hemorrhagic or serous-hemorrhagic( presence of exudate and blood in the synovial bag);
- dry( no pathological exudate in the synovial bag);
- serous( there is abundant exudate);
- purulent( in the joint secret there is an admixture of pus).
The causes of knee arthritis
arthritis of the knee, photos of inflammation
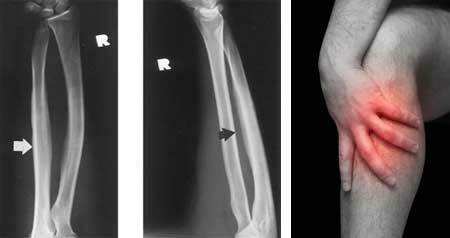
Infectious arthritis occurs due to penetration of the "capsule" of the joint of the following pathogenic organisms: fungi, viruses, bacteria( gram-negative), streptococci, staphylococci and gonococci.
As for non-infectious arthritis, their development is caused by a number of factors:
- by degenerative transformations of cartilaginous tissue( most often there are age-related changes);
- injuries of varying severity;
- inflammatory processes occurring in tissues that are located in the immediate vicinity of the joint bag and caused by immunological disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- by the formation of crystallized salts that are in synovial secretion. This phenomenon is evidence of a violation of calcium metabolism in the body.
It's important to know! Predisposing factors for the development of inflammation in the joints are permanent emotional overloads, stresses, endocrine diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms and Symptoms of Arthritis of the Knee Joint
Doctors have identified common symptoms of arthritis, which are accompanied by the course of all types of the disease.
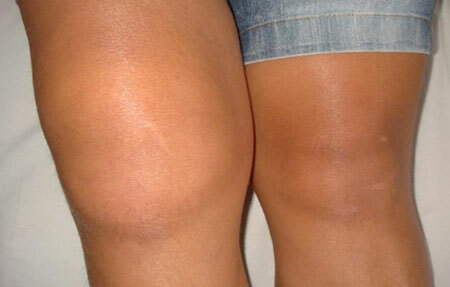
- Inflamed and swollen tissue in the knee area.
- Hyperemia of the skin in the joint zone.
- Deviation of bone tissue.
- Limited mobility of the joint( from minor to significant).
- Periodically occurring acute pain syndrome.
- Deformation of the joint.
- Regular or periodic burning and / or aching pain in the knee.
- Feeling of stiffness in the knee area in the morning.
In addition to these symptoms, for almost all of the types of knee arthritis, there are certain characteristics. For example, with a gouty type of gonitis, the condition worsens after taking alcohol-containing products.
Symptoms of arthritis of the knee joint, if the disease has an infectious etiology, are as follows:
- the strongest joint swelling that spreads over the entire shin;
- elevated body temperature( about 40 ° C);
- is a pain syndrome that can migrate to any organs;
- dermatitis.
Rheumatoid varieties of gonitis are characterized by mild inflammation in both knee joints, as well as in other joint groups( ulnar, humerus, hip).Disease, as a rule, is accompanied by an increased degree of fatigue, subfibril temperature. If the pathology proceeds for a long time, there may be:
- atrophic changes in muscle tissues;
- disorders of the motor function of the tendons;
- formation of Baker cysts.
For arthritis, systemic symptoms can also occur:
- respiratory system diseases;
- disease organs of vision;
- atherosclerosis;
- pathology of blood vessels and cardiac muscle( myocardium).
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of arthritis of the knee joint is quite a challenge. Sometimes, in order to collect a complete clinical picture, consultation and examination of doctors of narrow specializations is required: rheumatologist, physiotherapist, traumatologist, surgeon and arthrologist.
For diagnostics of gonitis, determining the stage of development and the causes of the onset, a number of analyzes are performed.
- Radiography. It allows to reveal the degree of destruction of periarticular cracks, which became the cause of the inflammatory process.
- MRI and CT.It shows the presence of ruptures of ligaments and menisci, cracks and fractures of bone tissues, foci of accumulation of pathological exudates, thickening of tendons.
- Biochemical blood test. Detects inflammation in the tissues of the joint. It is through this analysis that rheumatoid gonitis is diagnosed.
- Clinical examination of blood. He speaks about the main important indicators of blood - the number of platelets, leukocytes, ESR, etc.
- Radioisotope examination of bone tissue of the joint.
- Urinalysis.
- Study for the presence of antibodies to viruses.
- Skin scrapings. Conducted to determine the presence of fungal pathogens of infection.
- Study of exudate, the fence of which is produced from the knee joint. Helps detect leukocytosis, the presence of salt and determine the etiology of the causative agent of infection.
- Mantoux test( if a suspected tuberculous form of arthritis is suspected).
Methods for treating knee arthritis
Traditional medicamentous
Therapy must include the use of the following drugs:
- Immunosuppressive agents. Their use is advisable if there are autoimmune disorders that have caused the development of arthritis( Leflunomide, Ciclosporin);
- Antifungal. Applied if the etiology of gonitis is mycotic( Myconorm, Wilprafen);
- Balsams, gels used externally( Menovasin, Elacourt).Also, an effective Virapine ointment is used;
- Hormonal medications and calcium preparations( in the presence of salt crystals in joint exudate and for the purpose of correction of metabolism);
- Vitamin complexes, including vitamin D( Complivit, Centrum, Vitrum, Nycomed, Calcium D3);
- Glucocorticosteroids. For relief of severe pain syndrome( Flosteron, Diprospan, Prednisolone);
- Antidotal drugs, such as Colchecin tablets( with gouty gout);
- NSAIDs. These drugs relieve pain and inflammation;
- Antibiotics. Assign if there is an infection in the joints( Ofloxacin, Macropen).
It's important to understand! It is not necessary to independently treat arthritis of the knee joint. The medicines listed above should only be prescribed by a qualified specialist, taking into account the individual dosage and the regimen. Do not self-medicate, relying only on symptoms and signs.
Traditional non-drug
- Cryotherapy( improves metabolism in tissues, eliminates pain).
- Massage, therapeutic exercises, hydrotherapy, cardiostimulation of muscle tissues( improve blood flow, prevent atrophy).
- Infrared irradiation, ultrasound, laser therapy( eliminate the inflammatory process).
- Plasmapheresis( prescribed if there is arthritis of an infectious or rheumatoid type).
Surgical
- Aspiration, installation of drainage( with purulent persecution).
- Necrectomy. It is indicated in case there are extensive necrotic patches of articular tissues.
- Synovectomy. It presupposes removal of the synovial sac and is prescribed if conservative methods of treatment have not been successful.
- Endoprosthetics of the joint.(If the patient is diagnosed with a deforming drive).
- Arthroscopy( removal of large salt crystals).
Treatment of knee arthritis with folk remedies
To remove the pain syndrome, stop inflammation and improve blood flow in the tissues of arthritis of the knee, you can use folk remedies - very much helped by herbal baths. They should be prepared at the rate of 300 g of grass per bath.
A herbal mixture( or one kind of plant) is poured into 4 liters of water and boiled for 10-15 minutes, after which it is infused for about half an hour and poured into a bath filled with water.
Pay attention to the water temperature in the tub, one must not exceed 36-37 ° C.Also, make sure that the water does not cover the heart area.
For the preparation of baths, you can use the following herbs individually or in combination with each other: pine needles, chamomile, sage, sporegrass, ledum, sweet clover, juniper, St. John's wort and birch buds.
Compress
In the form of compresses you can use ordinary mustard plasters, flax seeds, radish and horseradish. In the tissue flap, wrap one of the selected means, which is preheated. Fold the fabric several times and attach to the knee for an hour. Top with polyethylene and a warm scarf.
Razmka
To prepare the flour, mix the olive oil and sunflower oil in equal parts, for example 100 ml each. To the oil mixture, add 200 ml of kerosene( purified).Stir thoroughly. After that, add 10 pods of hot pepper.
Place the mass in a glass container, insist for a week in a dark cool place and periodically shake. Rub the joint daily before bedtime for 15 days. The rest of the time, make sure that your knees are warm.
Application
To make the application, add a white( you can use black, yellow or green) clay( 80 g) a couple of drops of lime juice( permissible to replace lemon) and 20 ml of boiled water. You will get a lot of thick consistency. From it, blend a cake 3 cm thick.
Lay the clay cake on a napkin or cloth and attach to the diseased knee. From above the joint can be bandaged and wrapped with a woolen cloth. Hold for half an hour.
"Folk Ointment" for the treatment of arthritis
For the preparation of the ointment, you will need grass sweet clover( 20 g) and Vaseline( 35 g), which can be replaced with the same amount of butter.
Pour the herb with 300 ml of water and boil until the water is halved. Then strain the broth and add oil or petroleum jelly into it. To treat arthritis of the knee, rub the ointment into the joint three times a day.
Complications of knee arthritis
- Osteoarthritis, including the presence of contracture.
- Vessel dysfunction.
- Severe muscular weakness, up to muscle atrophy.
- Functional heart rate abnormalities.
- Respiratory system disorders.
- Visual impairment.
- Kidney pathology.
- Diseases of the digestive tract.
Prophylaxis
- Regular independent massage of the lower legs and thighs.
- Timely normalization of the functions of any systems and bodies.
- Prevention of the transition of infectious diseases to the chronic stage of development.
- Try to avoid work associated with excessive physical exertion, for example, lifting weights.
- Regular sports( except for high loads on your knees).
- Keep your posture.
- Timely treatment of pathology of the feet and spine.
- Curative gymnastics classes.
- The correct diet.
If you feel the slightest discomfort in the knee area, immediately consult a therapist who will make an anamnesis and send you to a specialist doctor for advice.
Arthritis of the knee joint, the symptoms and treatment of which largely depend on its etiology, requires comprehensive diagnosis and treatment. Remember that promptly conducted examination and appointment of competent therapy is the key to achieving the most positive result!