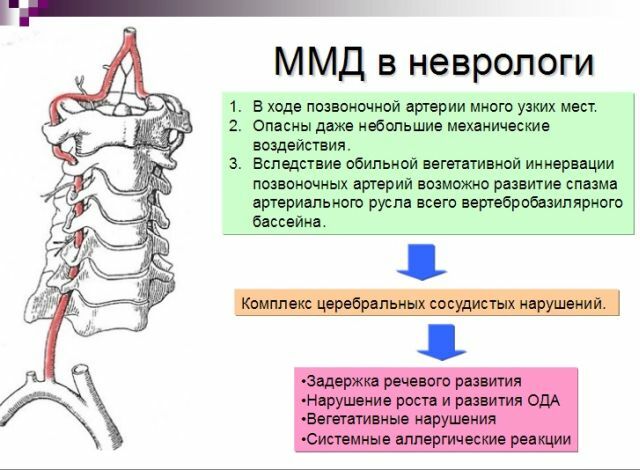
 One of twelve paired cranial nerves is facial. It is mixed, because it consists of motor, sensitive and parasympathetic nerve fibers. The motor part of the nerve begins in the rhomboid fossa of the fourth ventricle of the brain from the processes of nerve cells of the motor nucleus.
One of twelve paired cranial nerves is facial. It is mixed, because it consists of motor, sensitive and parasympathetic nerve fibers. The motor part of the nerve begins in the rhomboid fossa of the fourth ventricle of the brain from the processes of nerve cells of the motor nucleus.
Its composition includes an intermediate nerve. These are two different nerves, but their fibers are intertwined. They simultaneously reach the surface of the brain and move into the channel of the facial nerve. In the place of its bending is the elbow( gustatory) node of the intermediate nerve. Hence, sensitive nerve fibers originate, secretory ones from cells of the upper salivary nucleus in the medulla oblongata.
Peripheral fibers of the intermediate nerve enter the structure of the branches of the facial - the large stony nerve and the drum string. These branches are formed in the facial canal.
Sensitive( taste) fibers in the composition of the rock nerve innervate the mucus of the soft palate, connecting with the winged nodule.
The taste of the drum string innervates 2/3 of the anterior part of the tongue mucosa, reaching the lingual nerve.
The first branch of the nerve departs from the knee joint and, moving along the pterygoid canal, enters the pterygoid ganglion. In its composition innervates mucous membranes of the soft palate and nasal cavity. Next, some of the nerve fibers enter the maxillary nerve and go to the lacrimal gland.
The second branch separates from the facial nerve in the lower part of the canal and the fibers of the intermediate nerve in its composition through the tympanic cavity move to the lingual nerve and unite with it. Part of the fibers further continues to move into the hyoid nerve node, and part - in the submaxillary.
In addition, in the cranium of the facial nerve, the branches separate to the auditory and vagus nerves, to the stremal muscle.
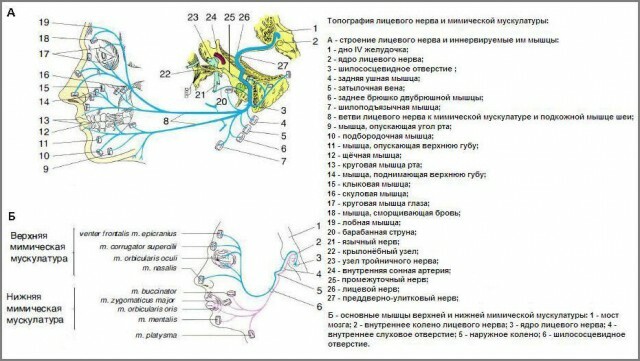
Leaving the canal, the facial and the intermediate nerve are separated. In this case, the motor fibers of the facial, moving through the stylophyllium of the temporal bone, are introduced into the tissues of the parotid gland. Two branches of the facial nerve are formed here:
- upper;
- lower.
Small branches are branches of the second order. Connecting in the gland, they form the parotid plexus. Leaving the gland, go radially to the maxillofacial muscles.
Anatomico-physiological structure of the facial nerve and a variety of functional connections determine a large number of different diseases.
How the facial nerve works, its anatomy and functions:
Contents
- Facial nerve diseases, their features
- What is dangerous for the facial nerve?
- General manifestations and diagnosis
- Neuritis - when the nerve is excessively inflamed
- Colds facial neuritis
- Symptoms and treatment of neuropathy
- Neuralgia - pain permeating
- Paresis
- Jamming of the facial nerve
- Preventive measures
Facial nerve disorders, their features
Facial nerve pathologies can strikeseveral branches at once and involve other nerves in the process.
Major lesions of the facial nerve:
- neuritis or Bell's paralysis( catarrhal facial, inflammation);
- neuralgia;
- pinched nerve;
- Neuropathy;
- paresis.
All neuritis is an inflammatory disease. They can develop acute, but often occur with an increase in symptoms. The second  name for neuritis of the facial nerve testifies to the main sign of the disease - paresis or paralysis of facial muscles. Colds of facial neuritis often arise from hypothermia.
name for neuritis of the facial nerve testifies to the main sign of the disease - paresis or paralysis of facial muscles. Colds of facial neuritis often arise from hypothermia.
Neuralgia is characterized by severe paroxysmal pains in the face area. The disease is rapidly progressing.
When the facial nerve is pinched, the pathology develops with different pains and characteristic localization behind the ear from the side of nerve damage.
Neuropathies are characterized by progressive asymmetry of the face, uncontrollable facial expressions.
Paresis is characterized by a decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles. With paralysis, it is generally absent.
What is dangerous for the facial nerve?
The factors of external influence become provocative for the appearance of lesions of the facial nerve. This and stay in a low temperature, and cold wind, and drafts, and running air conditioning.
Pathologies of the facial nerve can be the consequences of surgical interventions in the treatment of purulent inflammation in the ear, salivary glands, in the structures of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. This is facilitated by craniocerebral trauma, inflammation in the middle ear, in the brain and its membranes. Heredity also matters in the diagnosis of neuritis.
Neoplasms in nearby tissues are another cause of nerve damage.
Prolonged stressful conditions, heavy physical exertion, toxic poisoning, reduced immunity are causative factors of nerve diseases.
Some diseases of internal organs and systems are the main cause of facial nerve damage:
- infectious( ARVI, ARI, influenza, herpes and neuroinfections, tuberculosis, syphilis);
- diabetes;
- stroke;
- Multiple Sclerosis.
For the occurrence of inflammation of the facial nerve, any of the factors matters. Neuralgia often appears due to mechanical effects on the nerve at its exit from the canal.
Inflammation of the nerve, its edema or anatomical narrowing of the channel leads to the fact that the nerve is entrapped in it. The main causes of neuropathy of the facial nerve are severe colds and systemic diseases. The appearance of paresis( paralysis) of the nerve is associated with otitis, trauma and jamming.
General manifestations and diagnosis
Symptoms of nerve diseases are demonstrative, therefore they are determined visually. The main symptoms are that the facial nerve is affected by one or another disease:
- dysfunction of the maxillofacial muscles( paresis, paralysis);
- change in the sensitivity of facial muscles and skin in the maxillofacial zone;
- speech and chewing process;
- violation of the secretory function of lacrimal and salivary glands;
- pain along the nerve.
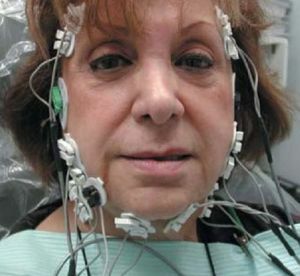 Nerve damage can recur. The most vulnerable part of the nerve is in the facial canal.
Nerve damage can recur. The most vulnerable part of the nerve is in the facial canal.
These pathologies are treated by a neurologist. The diagnosis begins with an examination and collection of an anamnesis of life and illness. Next, check the functions of the nerve and the reflexes that it provides.
To clarify the diagnosis, special testing is carried out - hearing, salivation, teardrop, balance, taste buds. Tests help establish the location and extent of nerve damage.
In addition, a blood test for sugar, biochemistry, a general blood test, testing for syphilis is prescribed.
More modern - electrophysiological testing, which determines the violation of conductivity along the trunk of the facial nerve. These tests are performed using an electroneurograph and an electromyograph. They more accurately confirm paralysis.
Neuritis - when the nerve is excessively inflamed
Neuritis of the facial nerve - one-sided lesion, develops gradually, manifests itself with symptoms:
- weakness in mimic muscles, paresis appears( paralysis);
- change in the sensitivity of the skin and muscles of the affected part of the face;
- involuntary twitching of facial muscles;
- skew of the face, it stretches;
- impairment of motor function of the eye, lacrimation or dryness;
- increased salivation;
- taste disorder;
- pain in the ears, hearing change from deafness to hearing enhancement.
- variable pain in the muscles.

Medication for neuritis of the facial nerve:
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs( Indomethacin, Piroxicam,);
- corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs( Dexamethasone, Methylprednisolone, Prednisolone);
- decongestants( Lasix, Diacarb);
- pain medication( Pentalgin, Ibuprofen);
- antispasmodics( No-sppa, Drotaverin);
- anticholinesterase drugs that restore neuromuscular conduction( Nivalin, Galantamine).
According to indications prescribe drugs that activate metabolic processes in the nervous tissue( Nerrobolil, Dinabolon).
Apply massage, exercise therapy, reflexology, electro pulsed current therapy, ultrasound, ozokerite applications.
If the disease is secondary - treat the underlying disease.
Facial nerve facial massage:
Catarrhal facial neuritis
Begins acutely, develops rapidly, can recur. If the facial nerve is chapped, then such symptoms appear:
- decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles;
- asymmetry of the face, relaxation of facial muscles;
- numbness of facial muscles;
- pain behind the ear;
- distorted perception of loud sounds;
- does not close the eye, water.
Complex treatment of the disease is carried out according to the same scheme as treatment of other nerve lesions.
Symptoms and treatment of neuropathy
Neuropathy is a unilateral disease of the facial nerve that provokes the development of paresis or paralysis of muscles. A marked symptom is the asymmetry of the face.
Other manifestations of pathology:
- facial pain;
- loss of management of maxillofacial muscles;
- numbness of the affected part of the face;
- dry or watery eyes;
- change in taste;
- impairment of auditory perception( distortion and amplification of sounds);
- in severe cases - complete immobility of a part of the face.
 For the treatment of the facial nerve neuropathy, anti-edematous, hormonal and non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, the anesthetics are the same as in the treatment of neuritis. Prescribe vasodilators( Nicotinic acid, Copemine, Keonikol, Enduracin).
For the treatment of the facial nerve neuropathy, anti-edematous, hormonal and non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, the anesthetics are the same as in the treatment of neuritis. Prescribe vasodilators( Nicotinic acid, Copemine, Keonikol, Enduracin).
Local treatment - solutions of dimexide and xidifone in the form of applications. If suspected of post-paralytic muscle contracture, anticonvulsant drugs are used( Carbamazepine, Finlepsin).
If necessary, prescribe anticholinesterase drugs and activating metabolic processes, B vitamins.
In case of contracture of facial muscles, corrective operations are performed. Surgically restore the functions of the nerve when it is damaged in the facial canal, "revitalize" the functions of the facial musculature, reinnervate mimic muscles - sew the nerve with healthy motor nerves.
Additional treatment is the same as with neuritis.
Neuralgia - pain permeating through
The main symptom of neuralgia of the facial nerve is pain, the greatest at the exit of the nerve from the skull. It arises suddenly, of different strength and localization.
- Symptoms:
- muscle weakness with development of paresis;
- increased or decreased muscle sensitivity;
- development of face asymmetry;
- profuse salivation and lacrimation;
- a taste disorder before complete absence.
Treatment of neuralgia of the facial nerve is most often medicated, the following drugs are prescribed:
- anticonvulsant( Carbamazepine, Tebantin);
- muscle relaxants to reduce muscle tension( Baclofen, Sirdaloud);
- analgesics, with severe pain - opiates;
- psychotropic drugs for depression( Trazodone, Amitriptyline);
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments, gels, creams( Diclofenac, Diklak-gel);
- preparations containing vitamin B( Neurorubin, Milgama).
Additionally, electrophoresis with lidocaine, acupuncture, UHF, microcurrent treatment is prescribed. Recommend a light massage and special gymnastics.
If this treatment is not effective, resort to operations - decompression and electrostimulation of the motor cortex of the brain.
paresis The main sign of paresis of the facial nerve is facial asymmetry, but there are a number of other important symptoms:
- the motor function of the facial muscles is lost;
- speech and swallowing are broken;
- the eye is open and immobilized, dry or watery;
- abundant salivation;
- distorted perception of sounds;
- change in taste;
- pain in the ear.
 Treatment is complex, the main is medication. Apply antispasmodic, decongestant, anti-inflammatory steroid, vasodilator, sedative and containing B group vitamins, drugs. Recommended drugs that improve metabolic processes in neural tissues. Their list is similar to those prescribed for other pathologies of the nerve.
Treatment is complex, the main is medication. Apply antispasmodic, decongestant, anti-inflammatory steroid, vasodilator, sedative and containing B group vitamins, drugs. Recommended drugs that improve metabolic processes in neural tissues. Their list is similar to those prescribed for other pathologies of the nerve.
For the restoration of motor function of muscles and nerve fibers, additional methods of treatment are used, the same as for neuralgia, but a number of methods are added. This balneotherapy - mineral water treatment, electromassage, laser beam treatment, magnetotherapy, warming procedures.
Surgical intervention is performed with prolonged ineffective treatment.
Pincushion of the facial nerve
Leaks in acute and chronic form. Severe course is manifested by paresis( paralysis), the disease has such symptoms:
- pain behind the ear of various strengths;
- weakening of facial muscles, skewed face;
- numbness of muscles and skin;
- the eye is raised up, tearing;
- saliva from the lowered corner of the mouth;
- increased sensitivity to loud sound.
The absence of treatment for lesions leads to contracture of the facial muscles.
Treatment is carried out according to the standard scheme.
Preventive measures
Prevent facial nerve diseases by adhering to simple rules:
- to exclude hypothermia, stay in a draft;

- monitor the condition of the teeth;
- promptly treat colds, infections, systemic diseases;
- to avoid injuries, nervous overstrain, stressful situations;
- lead a healthy active lifestyle;
- not to allow excess weight;
- to engage in physical culture and sports;
- to abandon bad habits;
- eat properly, take vitamins periodically.
If you suspect a nerve damage, you should immediately contact a specialist.