Cholecystitis can be hidden under many masks. And although his main sign is pain in the right hypochondrium, sometimes the disease simulates a heart attack, rheumatic pains, an allergic reaction.
In time to recognize cholecystitis and to appoint its correct treatment is the main goal of doctors. On this depends a successful outcome and the elimination of serious consequences.
Contents
- 1 Cholecystitis, what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of cholecystitis according to forms of the disease
- 3 Treatment of cholecystitis in adults
- 3.1 Exacerbation of cholecystitis - therapeutic tactic
- 4 Diet: features of nutrition in cholecystitis
Cholecystitis, what is it?
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the gallbladder that proceeds acutely or chronically. It is for cholecystitis that bitterness in the mouth, periodically arising pains in the right hypochondrium( the liver itself does not hurt!) And an unpleasant sensation of nausea are characteristic. Most often the disease is already in chronic form diagnosed in women after 40 years. However, cases of acute cholecystitis in children are not uncommon.
Mandatory factors for the occurrence of cholecystitis: violation of bile outflow and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms entering the gallbladder through the ducts and intestines, with blood or lymph from the foci of chronic infection.
Causes of cholecystitis:
- dyskinesia of bile ducts( with congenital abnormal structure of bile ducts, liver infection with Giardia);
- cholelithiasis( stones in the gallbladder can be both a cause and a consequence of cholecystitis);
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract - hepatitis, pancreatitis, pancreatic reflux, enterocolitis, dysbiosis, ascariasis;
- endocrine pathology - diabetes, obesity;
- pregnancy and oral contraceptive use;
- severe poisoning.
The following lifestyle biases and some diseases can be attributed to provoking factors:
- low motor activity;
- irrational food - excessive consumption of fatty and fried, snacks, addiction to fast food;
- pernicious habits - alcohol, smoking;
- increased emotionality, stress;
- foci of infection in the body - pyelonephritis and cystitis, tonsillitis and sinusitis, adnexitis and prostatitis;
- violation of the blood supply of the gallbladder( with atherosclerosis, hypertension);
- taking certain medicines and allergic reactions.
An important role is played by hereditary predisposition. However, the risk of cholecystitis in such cases is minimal if a person leads a correct lifestyle.
Symptoms of cholecystitis according to forms of the disease
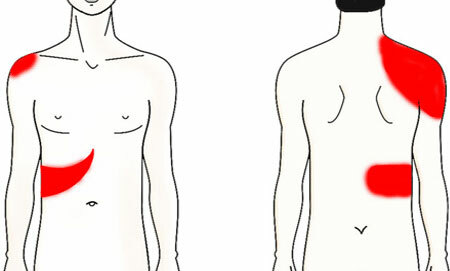
symptoms of pain in cholecystitis, photo
Cholecystitis( ICD K81) can begin acutely after exposure to a provoking factor or slowly( a chronic form) with the gradual development of symptoms. The symptoms of the disease and the tactics of its treatment depend on the form of cholecystitis.
Acute cholecystitis( ICD 81,0)
Acute inflammation can occur in two ways: calculous cholecystitis( with the formation of concrements in the gallbladder) and acalculous( proceeds without stone formation).

bitterness in the mouth - the first sign of cholecystitis
The main symptoms of acute cholecystitis:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium - periodically arising intense character with spasm of w / in ways, blunt constants - with cystic hypotension. Often irradiate in epigastrium, lower back, shoulder blade.collarbone and neck on the right side.
- Dyspeptic phenomena - bitterness in the mouth, belching bitter, nausea and vomiting( yellow / orange vomit - a sign of the presence of bile), bloating.
- General symptoms - weakness, sweating, irritability, insomnia, fever.
Depending on the severity of the inflammatory reaction, cholecystitis is diagnosed:
- is catarrhal - a non-intensive soreness, the temperature is normal or up to 37.5 ° C;
- phlegmonous - severe pain, worse when turning the body or coughing, the temperature reaches 38.0-39.0 ° C, pronounced tachycardia( 110-120 per min) at rest, reflex lag when breathing the right side of the abdominal wall, weak intestinal noises;
- gangrenous is a consequence of the absence of treatment in the phlegmonous stage, the rough course and the severe condition of the patient, this condition threatens the patient's life.
Atypical variants of the course of cholecystitis( ICD 81.8-81.9):
- cardiac - pain in the heart, arrhythmia;
- rheumatic - joint and heart pain, characteristic for rheumatism changes on the ECG;
- gastrointestinal - predominance of symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract( broken stool, flatulence, nausea, vomiting);
- thyrotoxic - high irritability, low-grade fever, intermittent rapid heartbeat;
- neurogenic - migraine-like headaches, insomnia, depression, increased sensitivity and irritability;
- allergic - recurrent urticaria, attacks of suffocation, eosinophilia in the blood.
Chronic cholecystitis( ICD 81.1)
Symptoms of cholecystitis in adults often develop gradually due to a prolonged disruption of diet or with the formation of gallstones. Exacerbations of chronic cholecystitis proceed according to the type of acute inflammation.
However, even during the period of remission( temporary improvement), the patient often has subfebrile condition, weak jaundice of the skin and sclera, skin itching( as a result of the entry of bile pigments into the blood).
Treatment of cholecystitis in adults

The diagnosis of cholecystitis is based on the patient's characteristic complaints and the results of diagnostic tests( ultrasound, blood tests - general and biochemistry, contrast X-ray, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, computed tomography, bile planting).
Medication-based treatment of cholecystitis in adults includes:
- To eliminate spasm - No-sppa, Papaverin, Platyphylline, Analgin, Baralgin;
- With detected hypotension of the gallbladder - cholagogue( Allochol, Holenzym);
- With severe inflammation, broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- With cholestasis and the beginning of stone formation - Ursodeoxycholic acid, admission 1-3 months;
- To normalize the synthesis of bile - hepatoprotectors( Hofitol, Gepabene, Karsil);
- With expressed autonomic dystonia - soothing( Motherwort, Valerian).
Additional activities:
- phytotherapy - teas with immortelle, St. John's wort, corn stigmas, mint;
- procedure for blind sounding( tjubazh) - is performed 1 time in 7 days, only in the absence of adhesions and pronounced narrowing of the bile ducts;
- physiotherapy - electrophoresis, diathermy, mud therapy, inductothermy;
- cholecystectomy - surgical treatment is indicated only with complicated calculous cholecystitis( large stones), gangrenous form with peritonitis threat.
Exacerbation of cholecystitis - medical tactic
Often, chronic cholecystitis exacerbation in the form of biliary colic. Acute pain in this case is accompanied by increased jaundice, a drop in pressure, indomitable vomiting, discoloration of feces and darkening of urine.
Platifillin is used for quick relief of the pain syndrome, and spasmolytic drugs are used intravenously.
If biliary colic is caused by blockage of the bile ducts with large stones( more than 2 cm) and is not stopped in the shortest possible time by medicines, the risk of peritonitis is significantly increased.
In such cases, an emergency laparoscopic( through minisections) or an open( wide dissection of the abdominal wall in the right upper quadrant) is performed.
Diet: features of nutrition in cholecystitis
Dietary nutrition is an integral part of the successful treatment of cholecystitis. The diet for cholecystitis is observed for a long time in order to avoid relapse of the disease and prevention of stone formation.
Prohibited products:
- fatty meat and fish, fat, by-products( liver, kidneys);
- fried food, egg yolk;
- beans( peas, beans);
- baking, cakes;
- marinades and homemade pickles, sauces( ketchup, mayonnaise);
- fruit with a sour taste;
- garlic, sorrel, radish, onion, spinach;
- fungi;
- spices, vinegar, mustard, horseradish;
- alcohol;
- lemonades, coffee, chocolate, cocoa, ice cream;
- sugar( restrict use to avoid changes in the composition of bile).
Authorized products of for cholecystitis:
- lean meat, fish and sausages;
- low-fat dairy products( low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream, cheese, yogurt);
- grain bread, an unhealthy cookie;
- unrefined oils( olive);
- some sweets - jam, natural marmalade, marshmallow, honey( has a pronounced choleretic effect);
- non-acidic fruit;
- Hercules, buckwheat, pasta;
- jelly, compotes, sweet juices, loose tea, coffee with milk;
- turmeric as a condiment to dishes.
In chronic non-calculous cholecystitis, dietary nutrition can help prevent the development of acute colic attacks and severe complications. Even after cholecystectomy, the patient must follow a diet to maintain normal digestion.