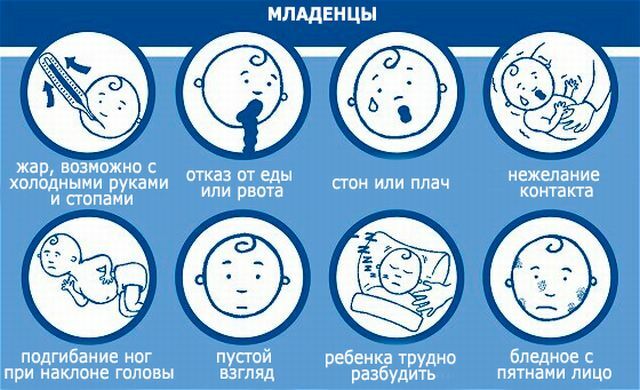
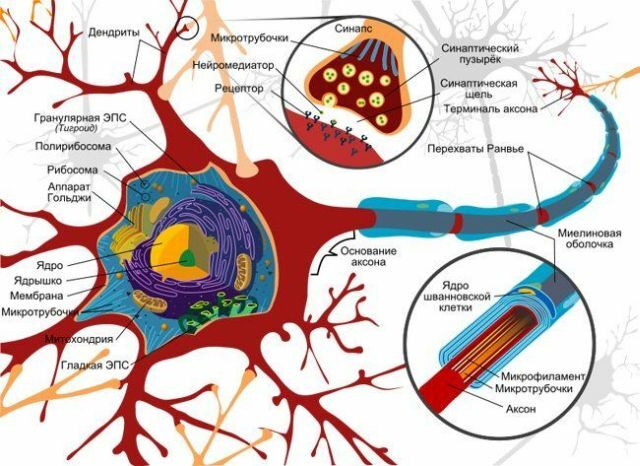
 Polyradiculoneuritis - is an acutely developing disease of the peripheral nervous system , characterized by the destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers and manifested as muscular weakness, numbness of limbs and flaccid paralysis( result of lesion of spinal roots, spinal and cranial nerve trunks).
Polyradiculoneuritis - is an acutely developing disease of the peripheral nervous system , characterized by the destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers and manifested as muscular weakness, numbness of limbs and flaccid paralysis( result of lesion of spinal roots, spinal and cranial nerve trunks).
Guillain-Barre syndrome is a separate form of polyradiculoneuritis, characteristic of which is areflexia( absence of reflexes), caused by damage to a large number of nerves due to an autoimmune attack.
Immunity in this regard their own tissues as foreign and develop antibodies against them. Thus, the envelope of its own nerve cells is destroyed.
Causes and risk factors
The cause of the disease lies in the autoimmune reaction: the immune system begins to attack the myelin sheath of its own nerve cells.
In most patients, the symptoms of Guillain-Barre syndrome begin to appear several days or weeks after surgery, infection or vaccination.
The destruction of the nerve membranes leads to disruption of the nerve impulses. What is the cause of this autoimmune reaction is not fully understood.
The development of the reaction is believed to be facilitated by the following factors:
- Campylobacteriosis ( acute infectious intestinal disease).Infection causes diarrhea in children and adults. A few weeks may be the development of the syndrome.
- Herpes infections : cytomegalovirus, affecting all cells of the body( when observed under a microscope, the affected cells are enlarged and look like an owl's eye).
- Epstein-Barr virus , which causes inflammation of the tonsils and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Hereditary factor .If the pathology is found in the genus, the patient automatically falls into the risk group( minor head injuries or infectious diseases can trigger the development of the disease).
Other causes include:
- allergic reactions;
- vaccination against diphtheria or poliomyelitis;
- transfer of complex operations or chemotherapy.
Clinical picture
The disease manifests itself in the form of symmetrical muscle weakness( flaccid paresis), which first affects the proximal parts of the muscles of the lower limbs.
Within a few hours or days of paresis, muscle weakness spreads to the hands. The condition is often accompanied by numbness of the fingers of the feet and brushes.
Weakness can occur first in the hands or in both hands and feet at once. In the cerebrospinal fluid, the protein content increases( from the second week of the disease).
In severe form, paralyzes of respiratory and cranial muscles occur, mostly mimic and bulbar muscles. There are pains in the back and shoulder girdle.
Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus are prone to decubitus formation.
The disease is often accompanied by pronounced vegetative disorders:
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- orthostatic collapse;
- sinus tachycardia;
- cardiac rhythm disturbance;
- urinary retention.
The symptomatology stabilizes after reaching the peak( the rise phase lasts from two to four weeks), after which the recovery begins( lasting from several weeks to two years).
Death can occur as a result of respiratory failure caused by paralysis of the respiratory center, pneumonia, thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries, sepsis, cardiac arrest.
Modern intensive care methods have reduced the death rate to 5%.
The main symptoms of Guillain Barr polyradiculoneuritis:
- is a muscle weakness that develops first in the limbs and later damages the respiratory musculature;
- inability to breathe independently( develops in a third of patients);
- disturbance of swallowing, the patient is choked by liquid and solid food;
- painful sensations in the back, pelvis, arms and legs, the character of the pains is pulling, prolonged, the pains are hard to treat;
- numbness of the limbs, a feeling of tingling in the hands and feet;
- cardiac rhythm disturbance, blood pressure jumps;
- temporary incontinence( up to three days);
- split in the eyes, strabismus;
- is a shaky walk, poor coordination of movements.
 Inability to perform a series of consecutive movements - adioadichokinesis. What is the essence of the disorder you can find in our article.
Inability to perform a series of consecutive movements - adioadichokinesis. What is the essence of the disorder you can find in our article. Causalgia is a symptom characterized by the appearance of burning pain at the site of peripheral nerve damage. The methods of therapy that modern medicine offers can be studied in the material.
Diagnostic methods
Complex of diagnostic measures includes:
- Analysis of patient complaints and medical history of .The doctor asks how long the muscle weakness, breathing disorder, numbness of the limbs, and gait disturbance began to appear. Find out what preceded the listed symptoms( diarrhea, catarrhal disease, vaccination several weeks before the signs of violation).
- Neurological examination of . The doctor assesses the strength of the muscles of the extremities, examines the reflexes(
 is characterized by areflexia), assesses the sensitivity( determines areas with a feeling of numbness and tingling), assesses the function of the pelvic organs( urination disorder is noted), assesses the functioning of the cerebellumstanding with arms outstretched and closed eyes), studies the movement of the eyes( in case of violation, the total absence of motor activity of the eyes is possible).In addition, vegetative tests are carried out( to determine the degree of nerve damage), the heart reaction to abrupt upstanding and physical exertion is evaluated, and the swallowing function is evaluated.
is characterized by areflexia), assesses the sensitivity( determines areas with a feeling of numbness and tingling), assesses the function of the pelvic organs( urination disorder is noted), assesses the functioning of the cerebellumstanding with arms outstretched and closed eyes), studies the movement of the eyes( in case of violation, the total absence of motor activity of the eyes is possible).In addition, vegetative tests are carried out( to determine the degree of nerve damage), the heart reaction to abrupt upstanding and physical exertion is evaluated, and the swallowing function is evaluated. - The blood test involves the detection of antibodies to myelin and the detection of signs of inflammation( erythrocyte sedimentation rate, white blood cell count).
- Lumbar puncture .Puncture is done by a special needle. Through the skin of the back, a puncture of the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord is carried out at the level of the waist. It takes 1-2 ml of cerebrospinal fluid, which provides nutrition and metabolism in the brain and spinal cord. The number of blood cells, protein and the presence of antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid are counted.
- Electroneuromyography makes it possible to assess the excitability of muscles and the conduction of a nerve impulse along the nerves. With the disease, the conduction of the pulse slows down, signs of damage to the myelin or the processes of nerve cells are found. With damage to the processes, recovery is much more difficult.
- Consultation of the immunologist .
Methods and objectives of treatment
Guillain-Barre syndrome is a serious disorder requiring immediate hospitalization. The need for emergency measures is caused by the rapid deterioration of the patient's condition.
Setting a correct diagnosis is extremely important, as sooner treatment starts, the more chances for a positive result.
The patient is carefully monitored: if necessary, an artificial respiration device is connected.
 Nurses carry out measures to prevent bedsores and injuries: use soft mattresses, turn the patient around every two hours. Physiotherapy is prescribed to prevent muscle atrophy.
Nurses carry out measures to prevent bedsores and injuries: use soft mattresses, turn the patient around every two hours. Physiotherapy is prescribed to prevent muscle atrophy.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is plasmapheresis( removal of toxic substances from the blood) or the introduction of immunoglobulin.
Rehabilitation
The disease affects not only the neurons, but also the periosteal muscles, so many patients have to re-learn to walk, hold objects, etc.
To restore the work, the following measures are taken:
- therapeutic massage, grinding;
- physiotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- relaxing bath, contrast shower;
- radon baths;
- applications with beeswax;
- exercise therapy.
During the recovery period, you need to follow a healthy diet and take vitamin complexes. The organism needs large doses of vitamin B, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
Patients who have suffered a similar disease remain on the account of a neurologist. Periodic preventive examination is carried out in order to identify the prerequisites for relapse.
Complications and prognosis
Possible fatal outcome due to cardiac arrest or respiratory failure.
70% of patients are fully restored, 15% have residual residual paralysis. In 5% the disease arises repeatedly, and chronic relapsing polyneuropathy is formed.
In 30% of patients( more often in children) there is residual weakness during the next three years.
If treatment measures are taken on time, the patient's condition may improve within a few weeks. Otherwise, the process of recovery will take many months.
In time, the therapy started can restore a person to a full-fledged existence, namely, the ability to self-service and the ability to lead an active lifestyle.