Type 1 diabetes in children is caused by impaired pancreatic function. In this case, insulin is not produced in the right amount. This chronic disease is different in that it develops very quickly. Therefore it is important to know its first manifestations, in order to apply to the medical institution in time for help. After confirming the diagnosis, all children suffering from this disease are given a disability. Therefore, the first thing to do is adjust to long-term treatment. The second point, which is very important, is that it is necessary to give the child the opportunity to develop normally, without focusing his attention on disability.

The main symptoms of
Diabetes of the first type in children has obvious symptoms, which it is very difficult to not notice to attentive parents. Deterioration of the state of the baby during the development of the disease occurs very quickly. First of all, the constant feeling of thirst in a child should be alerted. The desire to drink develops because of the reaction of the body, associated with the need to dilute the glucose circulating in the blood.
Other symptoms that occur during the development of type 1 diabetes in children:
- Frequent urination;
- Sharp causeless weight loss;
- Constant fatigue;
- Appearance of a constant feeling of hunger;
- Visual impairment;
- Fungal infection.
And the listed symptoms do not always manifest all at once. It is necessary to pay attention to one clearly expressed sign, so it can be a testament to the development of pathology.
Causes of the disease
A characteristic feature of this disease, which leads to disability, is a decrease in the production of insulin by the pancreas. In this regard, this type of diabetes is called insulin-dependent. This means that for the treatment and stabilization of the child's condition, insulin therapy is always required.
To date, the causes of type 1 diabetes have not been fully established by scientists. It is confirmed only that the disease always develops against the backdrop of a malfunction in the immune system. Specialists identified several major etiological factors that contribute to the development of the disease, this is:
- Hereditary factor. According to statistics, in children with relatives suffering from diabetes, the disease occurs 3-4 times more often.
- Genetic predisposition. This means that the child's set of genes predisposes to the development of the disease under the influence of certain external conditions.
- Viral infection, which can cause a malfunction in the immune system. In addition, it has now been proven that some viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, measles, coxsacks, parotitis and Epstein-Barra, can contribute to the emergence of insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Power. It is believed that a child who was on artificial feeding, is more susceptible to diabetes.
- Psychoemotional stresses associated with unhappy relationships in the family.
A child can become ill with diabetes and get disability at any age. Today, physicians distinguish two main risk groups:
- Age 3-5 years. During this period, children begin to visit children's institutions, and the risk of contracting a dangerous viral infection increases at times.
- Age of 13-16 years. During this period, sexual maturation occurs, and, consequently, the load on the body increases.
Diagnosis of
After the first symptoms that may indicate the development of diabetes are seen, you need to urgently go to a medical facility. Diagnosis is carried out in two stages. Initially, the fact of the development of the disease is confirmed, and then its type is established.
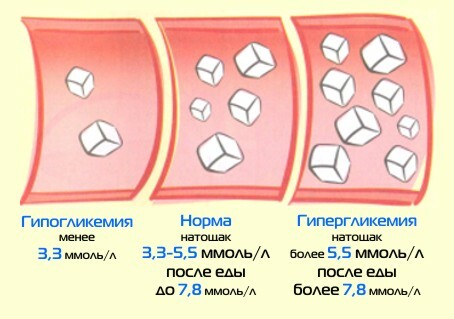
A mandatory test is an analysis that allows you to determine the level of glucose in the blood. Normal values are in the range of 3.3 to 5.5 mmol / l. If this value is exceeded, a test for glucose tolerance is performed. At first, the blood is taken on an empty stomach, after which the child needs to drink an aqueous solution containing 75 grams of glucose( the dose is reduced to half the age of 12 years) and after a couple of hours to donate blood again.
If the indicators are in the range of 7.5-10.9 mmol / l, this indicates a violation of glucose tolerance, that is, there is a need to register the child for continuous monitoring. The index above 11 mmol / l unambiguously confirms the presence of diabetes mellitus. In this case, in the morning portion of urine, glucose and ketone bodies will also be detected. In the next step, a blood test for the presence of specific antibodies is performed to determine the type of diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of
The basis of treatment of type 1 diabetes in children is the use of methods that allow normalizing blood glucose levels and stabilizing the child's condition for a long period. Diabetes type 1 in a child refers to chronic diseases, which can not be cured forever.
A favorable prognosis is guaranteed only with a competent treatment approach, compliance with diet and timely intake of medications. This means that, despite the fact that it is impossible to cure diabetes, children who fell ill at an early age can live as much as ordinary healthy people.

At the initial stage of the disease to get a positive prognosis it is important to choose the right diet. In this case, an individual approach is always practiced. But at the same time, the amount of foods containing sugar is always significantly reduced in the diet, while proteins and fats must be consumed by the sick child in the normal volume.
Insulin therapy for children with type 1 diabetes is selected on an individual basis. In this case, only short-acting insulin is used in childhood. Additionally, if necessary, angioprotectors, vitamins, cholagogue preparations and liver protectors are prescribed.
It is very important also in summer and winter to choose the right physical load for the child. This need is due to the fact that loaded muscles have the ability to independently absorb excess insulin in the blood. In addition, it is necessary to minimize stresses, as it is proved that with psychoemotional overloads, the level of glucose in the blood rises.
Parents should always monitor the course of the disease and correctly assess the condition of the child. To do this, several times a day to conduct blood glucose measurements with a glucometer. Older children need to be taught how to do it themselves.
Complications of
Acute complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus are life-threatening and should be reacted immediately. These include hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis.
Hypoglycemia is characterized by a sharp decrease in the amount of glucose in the blood. This condition is characterized by the following:
- Severe perspiration;
- by the trembling of the limbs;
- Sharp feeling of hunger;
- With a heart palpitations.
Unless urgent measures are taken to increase blood sugar levels, the child may develop a hypoglycemic coma, which is accompanied by convulsive syndrome and loss of consciousness.
Ketoacidosis is characterized by uncontrolled changes in blood glucose levels. The main manifestations of this complication are irritability, loss of appetite and insomnia. With the development of ketoacidosis coma, there are pains in the abdomen and a pronounced odor of acetone from the oral cavity.
Chronic complications develop due to the effect of the underlying disease on internal organs. On the background of diabetes mellitus, heart, kidney and liver pathologies can develop, which will require additional treatment.
Disability for children diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is based on medical certificates regardless of the degree of complication. In 2017, benefits are provided for children with diabetes, providing for the free purchase of medicines and the calculation of pensions. In addition, such children are given free passes to health-improving institutions for the purpose of prevention. For young children a voucher is also paid for the accompanying person.
In addition to this benefits are the parents of sick children. For them, a reduced working day is established, and additional weekends and holidays are provided. This allows, despite the unpredictability of a serious illness, to increase the likelihood of a positive prognosis and improve the quality of life of small patients.