 Neurology is a field of medicine that examines the human nervous system, its structure and functions in the norm and in the development of a neurological disease.
Neurology is a field of medicine that examines the human nervous system, its structure and functions in the norm and in the development of a neurological disease.
Neurology is divided into general and particular. The general unit is based on the study of the functions and structure of the nervous system, as well as diagnostic methods. Private neurology deals with certain diseases of the nervous system.
The central system represents the spinal cord and the brain. Peripheral system includes all kinds of structures that connect the central nervous system and other organs and tissues of the human body.
The nervous system is responsible for the normal functioning of the whole organism and the response to changes from the external and internal environment.
Contents
- How is the conclusion about the diagnosis of
- Who is a neurologist and what does it check
- Neurological examination objectives
- The hammer is the main tool of the neurologist
- The history of
- General examination
- The study of higher brain functions
- Checking the reflexes and evaluation of the
- syndrome Meningeal syndrome -
- assessment Diagnosticmethodologies and research
- Neurological examination of infants
How is the conclusion made about the diagnosis of
Neurologic examination for diarrheaNoz is built on three diagnostic «pillars»:
- medical history;
- analysis of hereditary predisposition and general examination;
- instrumental diagnostic and clinical examination methods.
Inspection from a neurologist and is currently the most important stage in the detection of a particular disease of the nervous system, despite the latest laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis.
When receiving the results of instrumental diagnostics and after the examination, the specialist will be able to prescribe conservative or surgical treatment to his patient.
Who is a neurologist and that he checks
A neurologist is a specialist who examines a neurological patient, assigns instrumental diagnostic methods and recommends methods of treatment for diseases of the nervous system.
The neurologist checks the presence and, if necessary, treats the following diseases of the nervous system:
- osteochondrosis;

- Multiple Sclerosis;
- Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease;
- stroke;
- migraine;
- sleep disturbance;
- hereditary diseases of the nervous system;
- of the nervous system;
- VSD;
- various neuralgia;
- radiculitis;
- neoplasm of the brain;
- dizziness;
- hydrocephalus and others.
Also, a neurologist should be examined if there are such symptoms:
- frequent headaches;
- occurrence of pain in the neck, chest, lower back, upper and lower extremities;
- after head injuries;
- speech becomes vague;
- decreased motor activity.
Objectives of neurologic examination
What the neurologist checks and assesses:
- examination and general assessment of the performance of all organs and systems in the human body;
- examines the skin;
- is determined by the body type;
- in communication specialist draws attention to the shape, symmetry and size of the head;
- is then used to diagnose the neck and check the rigidity of the occipital muscles;
- thoracic examination;
- are palpated in the peritoneal organs;
- is examined by the spine.
Specifically, the neurological examination includes the following parameters:
- assessment of the state of consciousness and the presence of its disorders;
- as a patient can orient in space, self and time;
- assessment of cerebral symptoms;
- examination of the function of cranial nerves;
- study of the motor sphere;
- reflexes are checked.
The nervous system performs many functions in the body and controls the operation of all organs and systems. Therefore, the examination of a neurological patient, depending on the patient's condition and the necessary diagnostic methods, can last from 15 minutes to several hours.
Very important is the qualification of a specialist in the inspection and diagnosis.
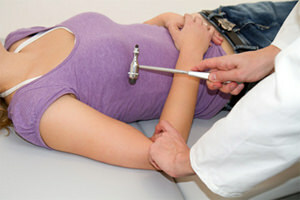
Hammer - the main tool of a neurologist
 A neurological hammer is designed to check the patient's reflexes during a primary examination with a neurologist.
A neurological hammer is designed to check the patient's reflexes during a primary examination with a neurologist.
This is the most important and indispensable tool for neurologists.
It is a source of pride for specialists who work in the field of development and research of the central nervous system, develop methods for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases.
Gathering anamnesis
At the first admission the doctor gets acquainted with the patient, his passport data, the kind of activity and collects an anamnesis. An active position here is assigned to a specialist, not a patient.
Initially, the neurologist listens to the patient's complaints. Each complaint is a symptom of the disease. Anamnesis plays a big role in the diagnosis. It is very important to listen carefully to the patient.
The doctor asks questions about the occurrence of patient complaints:
- when the first symptoms of the disease appeared;
- disease progression;
- duration of pathology;
- rehabilitation period;
- frequency of exacerbations.
When collecting anamnesis, the specialist concentrates on the following symptoms:
- pain;
- is a disorder of consciousness;
- memory corruption;
- presence of depression;
- decreased function of craniocerebral nerves;
- sphincter disorder;
- signs of impaired limb function.
The specialist also finds out all the chronic pathologies in the patient, the presence of hereditary factors, the fact that he previously suffered  infectious diseases. An experienced doctor immediately assesses the gait of the patient, movement, facial expression when examining and collecting an anamnesis. All these indicators play a leading role in the diagnosis.
infectious diseases. An experienced doctor immediately assesses the gait of the patient, movement, facial expression when examining and collecting an anamnesis. All these indicators play a leading role in the diagnosis.
Standard optimal neurological examination:
- examination of the neck and head;
- palpation of the abdominal organs;
- brain function study;
- study for the presence of twilight consciousness.
General examination of
During the collection of anamnesis, there is a need for additional methods of examination of the remaining systems of the patient's body. Everything depends on the presence of chronic processes and the individual characteristics of the organism. But there is a mandatory minimum of a neurological examination of the patient.
Objective diagnosis begins with examination and evaluation of the following systems:
- cardiovascular;
- respiratory;
- digestive;
- endocrine;
- musculoskeletal;
- urinary.
Study of higher brain functions
When collecting an anamnesis, a doctor can quickly determine the patient's mood, his attention, his manner of answers to questions posed, and the nature of his clothes. When the patient listens attentively to the neurologist, specifically responds to questions, understands their meaning, then this behavior of the patient is assessed as normal, and further testing does not make sense.
If the patient does not behave appropriately, his thoughts get confused, aggression manifests, then an in-depth study of cognitive functions should be made. The task of the specialist is to conduct a diffodiagnosis between impaired brain functions and mental disorders.
In addition, the patient is assigned a study:
- cranial nerves;
- arbitrary movements;
- coordination of movements;
- sensitivity;
- pathology of movements;
- of the autonomic nervous system.
Carrying out of laboratory methods of research the field of anamnesis and general examination of the patient is used. If necessary, the patient is lumbar puncture. It is prescribed for the following purposes:
- measurement of liquor pressure and for obtaining a sample of cerebrospinal fluid for a number of studies;
- as a therapeutic manipulation for the administration of a number of drugs directly into the spinal cord;
- introduction of air during the passage of myelography.
Reflex check and assessment of
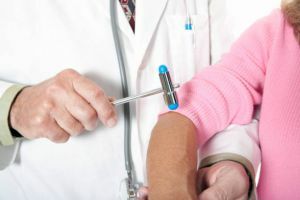 syndromes The most common reflexes include checking the tendon reflex of the patella. The doctor with the help of a hammer strikes the tendon just below the knee cap. With normal reaction, the leg is straightened.
syndromes The most common reflexes include checking the tendon reflex of the patella. The doctor with the help of a hammer strikes the tendon just below the knee cap. With normal reaction, the leg is straightened.
The reflex on the muscle of the biceps in the elbow joint region is checked in a similar way. As a result, the hand twitches and resembles bending. You can check and the presence of reflexes yourself. But such a diagnosis is difficult, a person can not carefully bend over, bend over. Check of reflexes passes without pain and for a short period of time.
Meningeal Syndrome -
Evaluation Meningeal syndromes begin to appear with inflammation of the meninges( meningitis), with hemorrhage of the blood in the subarachnoid region, and increased intracranial pressure. Meningeal syndromes include stiff neck muscles, Kernig syndrome. The examination is carried out on the back.
In a clinical examination of the patient, the neurologist checks the following symptoms:
- cutaneous;
- tendon;
- is vegetative;
- periosteal;
- reflexes with mucous membrane.
Symptoms characteristic of meningeal syndrome:
- the patient can not bend and unbend the neck muscles;
- is observed Kernig's symptom, the patient can not straighten the leg, which is bent at right angles;The
- patient can not tolerate bright light and loud voices;
- is manifested by the symptom of Brudzinsky;
- the patient constantly wants to cry;
- movement coordination disorder and the onset of temporary paralysis.

On the arm the doctor checks the reflex of the biceps and triceps muscles, as well as the carporadial reflex.
The following reflexes are evaluated:
- Double-headed muscle reflex .Above the elbow, the doctor strikes the tendon with the help of a hammer. The patient's arm should be bent at the elbow joint.
- Reflex of the triceps muscle .A neurologist strikes the tendon a couple of centimeters higher from the elbow joint. The forearm of the patient should be freely lowered by 90 degrees or the doctor himself supports the patient by the elbow. Carpodial reflex .A neurologist strikes with a mallet on the subulate bone of the radius. The patient should bend the arm at the elbow at 100 degrees. The radial bone is on weight and is held by the doctor. Also, such a reflex can be checked in a supine position.
- Test of the Achilles reflex .The doctor with a neurological malleus strikes the Achilles tendon, which is located on the gastrocnemius muscle. Thus the patient can lay down and bend a leg alternately at a right angle or become on a chair knees that feet drooped.
Diagnostic techniques and research
Neurological examination of the patient also includes instrumental methods of examination and additional tests:
- dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- echoencephalography;
- conducting survey radiography;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance radiography;
- clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- if necessary taking a cerebrospinal fluid;
- ophthalmic examination;
- examination by an ENT doctor.
Neurological examination of infants
An important role in the diagnosis of a newborn is played by anamnesis during pregnancy. Next, all functions and reflexes are checked, according to the plan:
- examination of cranial nerves;
- motion;
- testing of reflex spheres;
- sensitivity test;
- meningeal symptoms.
On how the child neurologist examines and what he checks, you can find out from the video clips:
Upon examination, the child should not cry, the room temperature should not be more than 25 degrees, the newborn should be fed.
The examination is carried out lying on the back. The neurologist conducts an examination, beginning with the head and ending with the lower limbs. If necessary, the doctor appoints an additional examination.
Modern research methods and qualified neuropathologists will help during the diagnosis and undergo treatment, in order to avoid serious complications and the transition of the disease into a chronic form.



