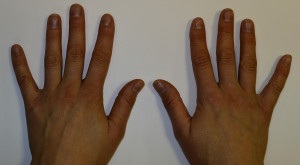
Hands are a part of the body that is always in sight. Any changes and deformations on the hands or on the fingers are very noticeable.
Hands are a part of the body that is always in sight. Any changes and deformations on the hands or on the fingers are very noticeable.
There are many such anomalies. Often they are only a cosmetic defect, but sometimes they can interfere with the full functioning of a person: work, study, communicate.
Among the most common deviations in the development of brushes is clinodactyly.
Determination of anomaly
Cleododactyly is a common congenital anomaly of the development of the bones of the fingers. Data on the prevalence of the disease in various statistical sources vary greatly - from 1 to 19%.
Most often clinodactyly affects little fingers or ring fingers, but there are cases of changes on other fingers.
The disease affects both arms symmetrically. With this pathology, the finger axis shifts sideways at the level of the middle phalanx relative to the limb. Fingers curved medially or laterally, there are abnormalities in intra-articular relationships.
Sometimes in childhood this defect remains unnoticed, as the deformation can be of varying degrees and continues until puberty. Its anomaly reaches its peak at the age of 18-20 years and usually no longer progresses.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by external examination and X-ray examination. It is important to differentiate clinodactyly from a similar disease - camptodactyly, which is caused by tendon-muscle pathology.
Classification and physiology of the process
Usually the disease does not cause pain or discomfort and treat it in the case when the finger is very strongly deflected from the axis and this causes  severe discomfort and difficulties in daily life.
severe discomfort and difficulties in daily life.
There are several types of clinodactyly:
- Type I .The proportions of the finger are normal, the angle of deflection is small( up to 10-15 degrees).
- Type II .The proportions of the finger are changed( shortening), the angle of deflection is insignificant( no more than 10-15 degrees).
- Type III .Strong curvature, inclination angle more than 20 degrees.
Deformation occurs due to changes in the growth zone( epiphysis) of the middle phalanx. Usually the epiphysis is located at the base of the bone and is a flat plate.
In the case of clinodactyly, the growth zone curves around the middle phalanx from the proximal to distal bone of the finger, forming the letter C.
Due to this deformation, the growth of the middle phalanx occurs unevenly and resembles a trapezoid or triangle, because of this, it is also called delta phalanx.
Causes of the development of the pathology of
Clindactyly may occur as an isolated disease, or in combination with other abnormalities. It can develop for three reasons.
As an independent hereditary disease transmitted by an autosomal dominant type. In this case, someone from close relatives must find such anomalies. They can differ in severity( for example, in the mother of the second type, and in the daughter of the third).
As one of the components of more serious diseases of genetic origin. These can be syndromes associated with changing the set of chromosomes( aneuploid syndromes):
- Down syndrome( clinodactyly in 60% of cases);
- Klinefelter's syndrome;
- trisomy in 18 pairs of chromosomes;
- Turner Syndrome.
Syndromes associated with gene mutations:
- Roberts syndrome;

- Russell-Silver Syndrome;
- anemia of Fanconi;
- syndrome Cornelia de Lange;
- Feingold's syndrome;
- or other non-syndromic abnormalities( brachidactyly).
May occur as a sporadic disease. This means that a spontaneous mutation of the gene occurred, which led to a defect. Or clinically, the disease manifested itself for the first time, since it has a recessive type of inheritance.
Clinodactyly can be detected during routine ultrasound screening during pregnancy. If there is such a deviation, the pregnant woman may be referred for consultation to geneticists and, if necessary, the karyotype of the child is used to exclude chromosomal abnormalities.
Operation - the only way out
Clinodactyly is a problem that can only be solved surgically. When the child is small, many parents do not always decide to perform the operation, but this is not right, because it is in childhood that the operation is best tolerated and the result is better.
Eliminate the defect in adolescence and adulthood. Such an anomaly of finger development does not lead to disability and does not interfere with a person.
With the exception of clinodactyly of the third type, when the angle of curvature is very large and leads to a disruption in the function of the organ - the joint is restricted in motion, grasping movements are difficult.
There are several methods for solving this problem:
- Vine-shaped closed osteotomy of abnormal phalanx .The most simple method, but may require correction, and in the future does not retain the length of the finger. Most often they spend children. To fix the phalanges in the correct position, two
 spokes and a plaster bandage are used, which are removed after 4-5 weeks. On the skin there is a small hem.
spokes and a plaster bandage are used, which are removed after 4-5 weeks. On the skin there is a small hem. - Wedge-shaped open osteotomy of the phalanx from its short side and insertion of part of the iliac crest. A complex operation for carrying out in a small child, since it is required to use bone material for transplantation, but the child does not have enough. In addition, the operation is accompanied by a corrective Z-plasty, i.e. Excision of triangular flaps of skin to improve the appearance of the finger. The length of the finger is saved.
- Reversed wedge-shaped osteotomy .The most rational choice of surgical intervention for adults with
 is clinodactyly. Technically difficult operation. The wedge-shaped part of the bone is cut from the wide side of the phalanx and it is inserted from the narrow side. Also accompanied by plastic counter triangular rags. The length is preserved.
is clinodactyly. Technically difficult operation. The wedge-shaped part of the bone is cut from the wide side of the phalanx and it is inserted from the narrow side. Also accompanied by plastic counter triangular rags. The length is preserved. - Resection of the median part of the growth zone in the delta-phalanx and the establishment of a fatty graft in the formed gap. This method allows to normalize the function of the epiphysis. It does not require prolonged immobilization, which is very important for a young child. The technique is used in America for children under 6 years, ideally the age of the child should be up to 3 years.
The results of the operative treatment of the clinodactyly of the little finger can be seen by comparing the photo above with the hands before and after the intervention.
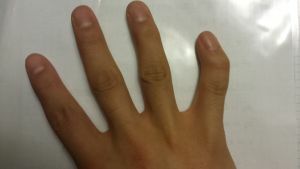 Since this is a genetic disease associated with anomalies of bone structures, it does not undergo conservative therapy.
Since this is a genetic disease associated with anomalies of bone structures, it does not undergo conservative therapy.
The only way out is surgical intervention. However, it is not always necessary, because often the curvature is almost imperceptible and does not prevent a person from living fully. In severe cases, it is necessary to correct the situation promptly.
Specialists are choosing the most appropriate way to solve the problem. After the operation, the result is visible immediately. The curvature is eliminated almost completely. On the skin there may be small scars from the intervention. It is best to deal with this problem in early childhood.