 Degenerative and dystrophic diseases of the nervous system with a predominant lesion of peripheral nerves and muscle fibers occupy a huge share in the structure of human hereditary pathology.
Degenerative and dystrophic diseases of the nervous system with a predominant lesion of peripheral nerves and muscle fibers occupy a huge share in the structure of human hereditary pathology.
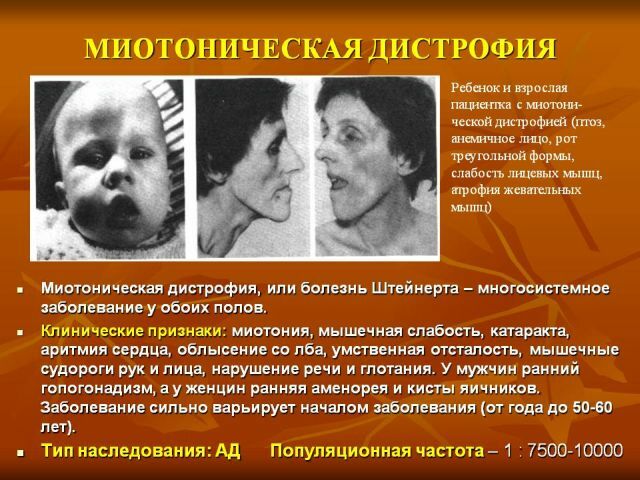
A typical representative is myotonic dystrophy( or dystrophic myotonia), described at the beginning of the last century by several authors and called the disease Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshmana.
This ailment is the most famous disease of the category of myotonia and the most common form of muscular dystrophy in adults. What is this disease and how to fight it?
Discovering and the essence of the
disease Rossolimo, Steinert and Kurshman studied a disease that is a genetic pathology with an autosomal dominant type of inheritance. This means that one parent has a mutant gene, sick children are born with a probability of 50%.The disease has the nature of a family affliction and is transmitted to subsequent generations on a vertical scale.
Sons and daughters in such families are ill with the same frequency, approximately 3 - 5 people per 100 thousand population. The age of onset of the disease, as well as the severity of the symptoms, are markedly variable.
Early neonatal and late forms are described, but most often the disease makes its debut on the second, rarely - on the third decade of life.  It is noted that the transmission of the disease to the child from the mother is more prognostically unfavorable than from the father.
It is noted that the transmission of the disease to the child from the mother is more prognostically unfavorable than from the father.
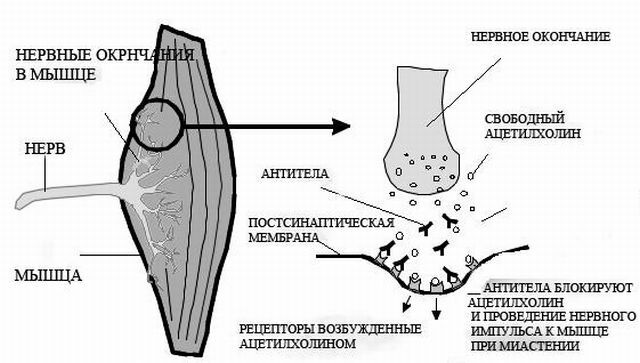
At the heart of the disease is a defect gene from 19 pairs of chromosomes, which is responsible for the synthesis of the enzyme myotonin-protein kinase. This protein is normally present not only in skeletal musculature, but also in the cells of the myocardium and the central nervous system.
That's why for dystrophic myotonia characterized polysystemic manifestations with the defeat of various organs and systems. Incompleteness of myotonin-protein kinase leads to the appearance of muscle spasms together with atrophic changes in the musculature of the head, cervical region, and limbs.
There is a combination of hypertrophy of some muscle fibers with atrophy of others and replacement of them with fatty or connective tissues.
Clinical manifestations of
Due to the variation in the onset of the disease, the following age-related forms are distinguished in the clinic:
- congenital form of - the manifestation of the disease begins immediately after the birth of the child;
- youth version of - debut of myotonia at the age from one year to puberty;
- classical form of - the beginning of clinical manifestations falls on the second and third dozen lives;
- is the minimum version of - the manifestation falls on the late terms - the sixth dozen of life.
Characteristically, the later the disease manifests, the more favorable the course and the better the prognosis. The classical form of Steinert's disease is most common, for which the following clinical symptoms are typical:
- Myotonia - manifested by spasms of the masticatory muscles and flexors of the hands, atrophic changes in different
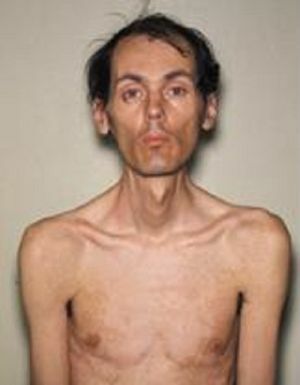 muscle groups are characteristic. Gradually fading of myotonic manifestations and progression of muscular dystrophy occurs, outwardly it is expressed in a sad mask of the face and absence of mimicry. Dangerous is the paresis of the larynx muscles with swallowing disorders, as well as the weakness of the respiratory muscles, as a result of which there are possible bouts of stopping breathing in a dream, the development of pneumonia.
muscle groups are characteristic. Gradually fading of myotonic manifestations and progression of muscular dystrophy occurs, outwardly it is expressed in a sad mask of the face and absence of mimicry. Dangerous is the paresis of the larynx muscles with swallowing disorders, as well as the weakness of the respiratory muscles, as a result of which there are possible bouts of stopping breathing in a dream, the development of pneumonia. - Cardiovascular disorders - heart rhythm disturbances, hypertrophic changes of the left ventricle, detected on the ECG, congestive heart failure.
- Endocrine disorders ( mainly affected by sexual function) - reducing the size of the genital organs, reducing sexual desire, in women - menstrual disorders, obesity.
- General changes in the dystrophic nature of - dryness and pigmentation of the skin, partial or complete loss of hair and teeth, early cataract.
- Disorders from the CNS - fatigue, sleep disorders, apathy, loss of intelligence.
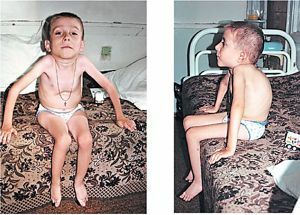
Separately it is worth noting the characteristic clinical manifestations of the congenital form of dystrophic myopathy:
- decrease in active fetal movements in the womb, detected during ultrasound;
- during the newborn period - lethargy, widespread hypotension, especially in the chewing, facial muscles of the eyeballs;
- preservation and even increase of tendon reflexes;
- feeding problems, respiratory distress as a respiratory distress syndrome;
- delay of physical and neuropsychic development, signs of oligophrenia;
- rapid disease progression, high risk of sudden death.
Diagnostic criteria for
Suspicion of Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman disease may occur in the doctor if the patient has a combination of myotonic and dystrophic changes in muscles against the background of loss of intelligence and the presence of cardiovascular and endocrine pathology.
Polysystemic almost always indicates the genetic nature of the disease. Such patients are subject to DNA analysis and genealogical analysis to confirm the autosomal dominant pathology inheritance. As informative methods of research, electrocardiography, electroneuromyography, hormone tests are used.
Due to the multifaceted nature of clinical manifestations, specialists from different branches of medicine - genetics, cardiology, endocrinology, gynecology, andrology, neurology - are usually involved in the diagnosis process.
Differential diagnosis is made between dystrophic myotonia and other types of similar diseases. Unlike the rest, muscular atrophy is characteristic of Rossolimo's disease. Often, to confirm the diagnosis, you have to resort to a biopsy to determine the level of muscle protein, which is increased in tissues in this pathology.
Antenatal diagnosis is also performed using the method of amniotic fluid research.
Medical care
Genetic disease can not be completely cured, therefore, the goal of treatment for Rossolimo-Steinert-Kurshman disease is symptom relief, general improvement and social adaptation of patients.
Principles of treatment are as follows:
- diet low in potassium salts ( apples, asparagus, cabbage, cucumbers, grapes, greens, corn, berries, radish, tangerines,
 grapefruit, onions, carrots, aubergines, peas);
grapefruit, onions, carrots, aubergines, peas); - suppression of supercooling to avoid spasms;
- use of quinine preparations to stabilize cell membranes, such as Diphenin, Novokainamide, Diacarb - to relieve muscle spasms and reduce stiffness, seizures, reduce intracranial pressure;
- use of anabolic steroids ( Metanandrostenolone, Retabolil, Nerabol), B vitamins, ATP to stimulate muscle mass;
- LFK, massage, electromyostimulation, orthopedic adaptations .
The listed measures give a good positive effect both in classical and congenital form of the disease. Completely rid the patient of dystrophic myotonia, they can not, but to prolong his life and improve its quality are able.
The prognosis is worse in the congenital form - the lethality is high, children may not live up to 3 years. The juvenile version of myotonia proceeds enough 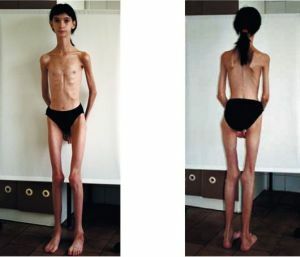 is difficult and can lead already in young years to disability and early disability.
is difficult and can lead already in young years to disability and early disability.
In the case of the classical form, the disease can take a long time in the course of timely treatment and correction measures. The most favorable prognosis in late-onset forms of the disease.
Preventive measures are reduced to the fact that a woman from a family with a dysfunctional anamnesis at the planning stage of pregnancy should undergo an examination for the presence of abnormal genes responsible for the development of muscular dystrophy. It is also advisable to do this if the pathology of the father's relatives is present.
The opportunities for the birth of children should be decided individually in each case by geneticists after the consultation.