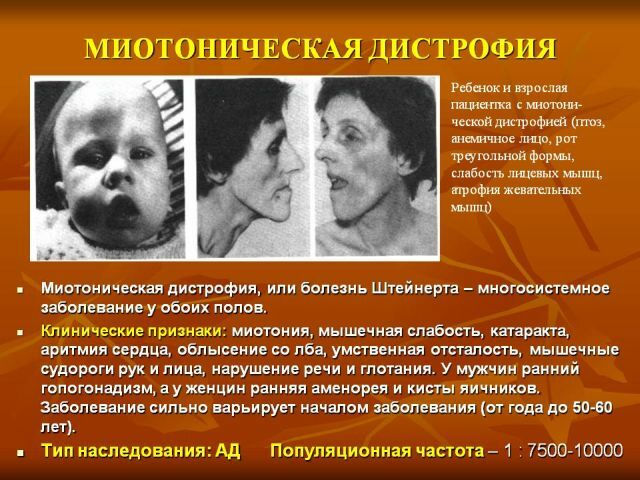
 The pain is different - acute and chronic, strong and not very much. Basically, pain occurs due to specific causes - stroke, swelling, nerve damage.
The pain is different - acute and chronic, strong and not very much. Basically, pain occurs due to specific causes - stroke, swelling, nerve damage.
But sometimes there is pain, but there is no apparent and definable cause. In this case, we are talking about myofascial pain syndrome( myofibrositis, muscle tension pain).
Pain in myofascial syndrome occurs as a result of the action of the trigger - the so-called hyper-irritability point. This point is located in the muscle tissue and in the muscular membrane - the fascia. From her painful impulse spreads throughout the muscle, can move to neighboring ones and grab even a bone.
Aggravating factors
The main cause of the formation of myofascial syndrome is static tension - a prolonged muscle finding in the non-physiological position.
Additional provoking factors are the performance by this muscle of monotonous work, hypothermia, emotional load.
Myofascial syndrome can be a professional disease - for surgeons, oculists, dentists, machine operators, machinists.
Myofibrositis develops and for some diseases: 
- shortening of the foot - constant finding of the spine in a skewed, unphysiological position, leads to the formation of trigger points in the muscles of the back;
- shortening of the shoulders - in this case myofascial syndrome is formed in the cervical region and the shoulder girdle;
- stoop - chronic pain develops in the thoracic spine;
- arthritis, arthrosis, osteoarthrosis - in all these cases the myofascial syndrome develops in the muscles surrounding the affected joint;
- vitamin A deficiency In - pains appear due to impaired nerve conduction.
Clinical picture
The main symptom of myofascial pain syndrome is pain. It is localized in one or more muscles. Appears at rest, with movement, with palpation of muscles. Because of pain, the motor function of the muscle is impaired.
With palpation of the muscle, when the needle stabs, the pain not only increases, but also radiates to other areas. This is called a reflection of pain.
Pain syndrome has a cyclic development:
- first appears the strongest pain , which does not have certain characteristics, it changes its character, disappears and resumes on its own;
- then pain attacks subsiding somewhat and appear only with movements of ;
- the final stage - the pain disappears completely, but the triggers remain in the dormant state, so the attacks can recur.
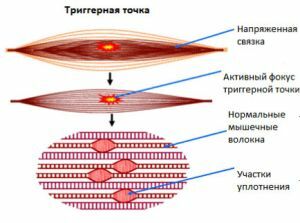 Reflected pain is a characteristic feature of myofascial syndrome. It arises in other muscles and their membranes, where there are not even trigger points.
Reflected pain is a characteristic feature of myofascial syndrome. It arises in other muscles and their membranes, where there are not even trigger points.
The pain differs from the main one - it is of medium intensity, dull or aching, lasts a long time - sometimes it persists even after the cessation of the underlying pain.
Factors have been identified that can enhance or relieve myofascial pain.
Strengthening factors include:
- static muscle tension;
- impact on trigger points;
- passive effect on muscle;
- cold.
To reduce painful sensations are capable of:
- short-term rest and change of position;
- warming of the trigger points area;
- medications.
Chronic course of myofascial syndrome leads to the development of other symptoms - sleep disturbance, changes in the psyche, muscle atrophy due to involuntary shaking.
Palpation for diagnosis
To diagnose myofascial pain, you must first exclude all possible organic causes of pain. After this, special muscle palpation is performed to identify the stressed area and trigger points.
Special palpation techniques:
- muscle gently stretches and probes all of its areas , normally a relaxed muscle of a homogeneous
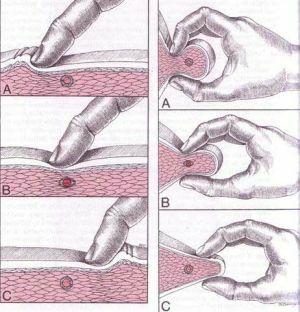 consistency, the existing tight area is felt as a dense tourniquet among the soft tissue;
consistency, the existing tight area is felt as a dense tourniquet among the soft tissue; - sliding palpation is carried out by slow rolling of fingers on a surface of a muscle;
- tick-borne palpation - the muscle is clamped between the thumb and forefinger and rolled between them.
With the help of such techniques it is possible to identify and trigger points. When the maximum painfulness is achieved by palpation on this point, it is necessary to press - if this causes severe pain, and the strained muscle begins to shrink rapidly, this indicates the detection of a trigger point.
This contractile response is a diagnostic sign of the myofascial syndrome and is called a local convulsive response.
Methods of therapy and prevention
Successful treatment of myofascial syndrome is concluded in the correct diagnosis and elucidation of its cause. If the cause is anomalies in the development of the skeleton - surgical treatment is prescribed( if possible), correction with special devices, orthopedic footwear, corsets.
If myofibrositis is of a professional nature, recommendations are given on the correct working regimen: working posture, the length of stay in the same position, the provision of appropriate temperature conditions, the presence of short breaks in work, and gymnastic exercises to relax the muscles.
The specific treatment consists of several techniques:
- Active relaxation of the muscle - the technique is to stretch the muscle maximally, and then, without changing its length, any movement is performed for a few seconds. After this, it is relaxed and returned to a physiological position.
- Stretching of the muscle with simultaneous analgesia with spray or Novocaine solution .
- Intramuscular injection of lidocaine or Novocain into the trigger point area.
 After elimination of painful attacks it is recommended to conduct a course of massage and therapeutic gymnastics in order to inactivate the remaining trigger points.
After elimination of painful attacks it is recommended to conduct a course of massage and therapeutic gymnastics in order to inactivate the remaining trigger points.
Prevention of myofascial pain is the timely detection and elimination of the pathology of posture and abnormalities of the skeleton.
To prevent the development of a professional myofascial syndrome, it is necessary to follow certain rules:
- does not stay all the time in the same position;
- perform a five-minute charge every two hours;
- periodically change the type of activity.