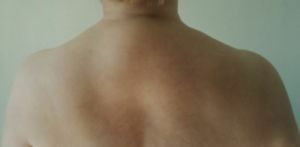
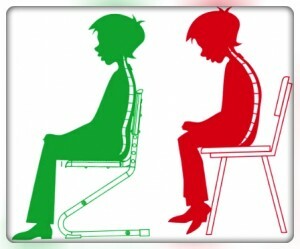
The human spine has physiological curves that ensure its flexibility and mobility under any load. Two bends forward( concavity) are called cervical and lumbar lordosis, two bends back( convexity) - thoracic and sacral kyphosis.
The human spine has physiological curves that ensure its flexibility and mobility under any load. Two bends forward( concavity) are called cervical and lumbar lordosis, two bends back( convexity) - thoracic and sacral kyphosis.
Due to some diseases, injuries or disorders of posture, a pathological kyphosis with an angle of curvature of the spine of more than 30 degrees can form.
Visually it looks like a hump on the back, noticeable when turning into a profile, its localization, shape and severity depend on the features of the pathological process that caused the deformation.
Contents of the article
- The humps are different - fatty and very dangerous
- Forms of kyphosis bending
- Congenital deformation
- Acquired forms of curvature
- The hump "grows" not immediately
- What can I do?
- Conservative treatment
- Surgery as an extreme measure
- Prevention of hump formation and deformation
- Than fraught!?
Humpbacks are different - fatty and very dangerous
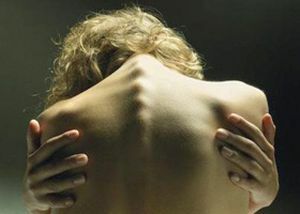
Under the hump can be understood and pathological kyphosis, and fat accumulation in the upper back, more characteristic for women over 45 years old and called the withers or widow's hump.
Withered withers are formed as a result of hormonal changes in the body of a woman during menopause, but may appear at a younger age due to osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, chronic hormonal disorders, and improper metabolism in the body.
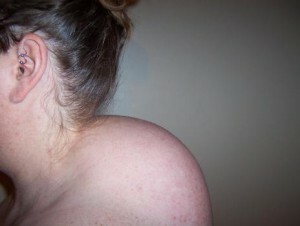
Widow withe
This is not a pathology of the spine, but only a fatty layer, a defect that is more cosmetic. Although such a hump can block blood vessels, disrupting the blood supply to the brain, causing migraines, dizziness, increased pressure, numbness in the hands.
The defect is easily repaired with the help of the correct organization of sleeping and working places, special gymnastics and massage.
Much more serious is the case with the most common cause of the appearance of a hump on the back - kyphosis, whose name is translated from Greek as "humpbacked", "bent".
If in normal it is a physiological bend performing a cushioning function, then in pathology - a severe defect in the shape of the spine, a symptom of many diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Appears arched bulge back or hump on the back, in pronounced form is most often combined with the chest cavity and shortening of the trunk.
Forms of kyphoid bending
Pathological kyphosis can be:
- congenital;
- purchased.
In severity:
- easy( 1st degree) - the angle of curvature of the spine does not exceed 40 degrees;
- moderate( 2nd degree) - angle of curvature of 40-60 degrees;
- heavy( 3rd, 4th degree) - the angle of curvature is more than 60-71 degrees.
According to the degree of deformation resistance:
- fixed, not amenable to correction;
- mobile, corrected in the prone position, corrected by conservative or surgical treatment.
Downstream: 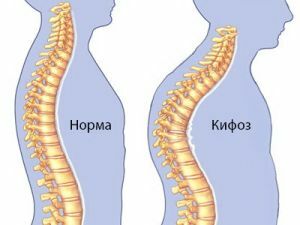
- is progressive, depending on the variation in the angle of curvature in a year, the progression can be slow or rapidly developing;
- is not progressive.
Form:
- angular in the form of a hump with a vertex of 1-2 vertebral vertebrae;
- arc-shaped in the form of an elongated short arc.
Congenital deformity of
Congenital kyphotic deformities are caused by anomalies in the development of the anterior spine - wedge-shaped or half-vertebrae in the thoracic region, by the fusion of vertebral bodies due to intrauterine malformations of the fetus.
Genotypic kyphosis is hereditary, transmitted from generation to generation by a dominant trait.
Acquired forms of curvature
Acquired deformations are caused by impaired posture, injuries, diseases of the musculoskeletal system, bone tissue.
The following varieties of acquired kyphosis are distinguished:
- The postural( sedimentary) or functional , also called the round back, develops in adolescents and people up to 30 years of age, more often girls and women, as a result of constant stoop with muscle weakness supporting the position of the body.
- Juvenile kyphosis in Sheyerman-Mau disease develops during the period of active growth of the child, most often in adolescence
 in boys. It is characterized by progressive kyphotic deformation of the thoracic spine with compaction of the affected vertebrae. In Calve's disease, the height of one or more vertebrae is much less than the others, which leads to a wedge-shaped deformation of the spinal column. Most often this disease is diagnosed in boys 7-15 years.
in boys. It is characterized by progressive kyphotic deformation of the thoracic spine with compaction of the affected vertebrae. In Calve's disease, the height of one or more vertebrae is much less than the others, which leads to a wedge-shaped deformation of the spinal column. Most often this disease is diagnosed in boys 7-15 years. - The paralytic hump of develops against the background of diseases that cause muscle paralysis - infantile cerebral palsy, polio, muscular dystrophy.
- Ricky appears in infancy or in older children who have had rickets at an early age. Due to the softness of the bone and the weakness of the muscles, the vertebrae change shape and are shifted.
- Postdraumatic deformity of occurs after spinal injuries - compression and comminuted fractures, dislocations, unsuccessful stabilization of the vertebrae after operations.
- Degenerative kyphosis develops as a result of diseases leading to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the anatomical structures of the spine - osteochondrosis, spondylarthrosis, spondylosis.
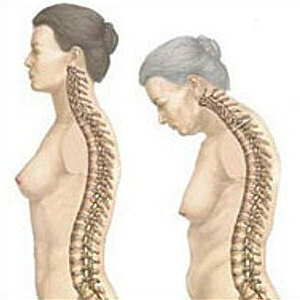
- The old hump develops and progresses after 60-70 years, mainly in women due to pathological dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs of osteoporotic vertebrae, which change the position, degenerating and sprouting connective tissue.
- The tuberculous spondylitis of causes the development of kyphosis with deformation in the form of a pronounced pointed hump.
- In the later stages of the , the spine from the beginning of the neck to the sacrum forms a continuous arc.
The hump grows not immediately
The hump on the back appears gradually and it manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Light degree - moderate violation of posture, stoop with a slight angle of inclination, quick fatigue of the back muscles, minor back pain, increasing with physical exertion.
- The average degree of is pronounced flexion, a humpback of the back, a hollow chest, a protruding abdomen, retracted shoulders, dilated scapula. After a long sitting, the back assumes a C-shaped shape, remains convex in the supine position. Chin due to the displacement of the position of the neck protrudes strongly forward.
- Heavy grade - the back takes an S-shape, as compensating lumbar lordosis intensifies, growth is reduced due to deformation of the trunk, muscle tone in hands and feet decreases, intolerance of prolonged physical activity appears. There are not only external changes, but also pronounced violations of the internal organs due to the reduction in the volume of the chest and the descent of the diaphragm. Children with severe pathological kyphosis lag behind their peers in physical development.
The form and severity of the disorder is confirmed by radiography, MRI, computed tomography.
What can I do?
Physicians from the following specialties will help to get rid of the hump: orthopedists, vertebrologists, manual therapists, neuropathologists, traumatologists, rheumatologists. The choice of methods of treatment depends on the cause, form and severity of pathology.
In kyphoses associated with degenerative changes or systemic diseases, therapy should be directed to the treatment of underlying pathology.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment methods are effective in mobile kyphosis, and should be used in a complex:
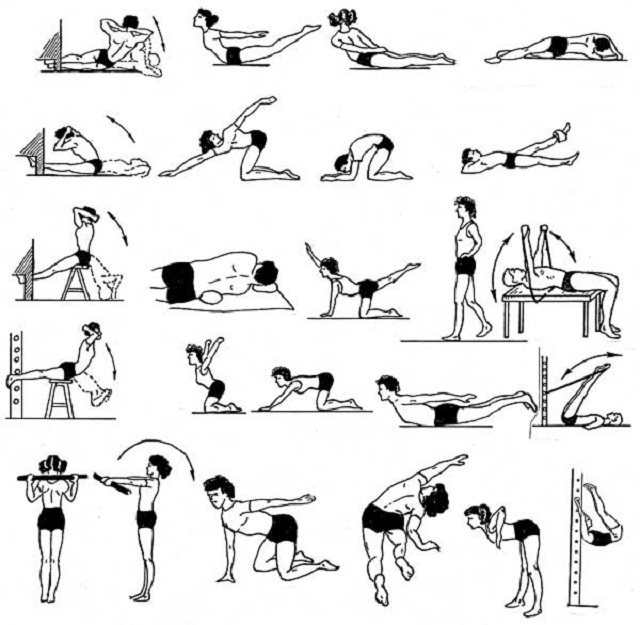
- Therapeutic physical training is an obligatory technique that allows to correct the deformation, increase the mobility of the
 spine, correctly arrange all its parts. All gymnastic exercises should be prescribed strictly individually depending on the form of pathology, with an emphasis on the development of strength and static endurance to strengthen the skills of correct posture.
spine, correctly arrange all its parts. All gymnastic exercises should be prescribed strictly individually depending on the form of pathology, with an emphasis on the development of strength and static endurance to strengthen the skills of correct posture. - Physiotherapy strengthens the muscular corset, eliminates muscle dystrophy and pain syndrome, removes blocks of vertebral segments. Methods: magnetotherapy, heat therapy, electrostimulation of back and abdominal muscles, electrophoresis, ozocerite applications, paraffin treatment, hydrotherapy, mud therapy, ultrasound.
- Manual therapy allows you to change the condition of the vertebrae, vertebral discs and surrounding tissues by manipulating the hands of the doctor on the problematic part of the spine with a strictly dosed load. The procedure is held every 3 days.
- Spine massage has a toning effect on the muscles, strengthening their
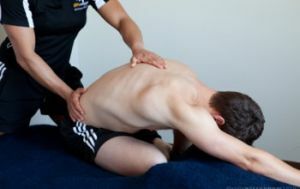 activity and improving trophic tissue, improves blood flow and restores nutritional functions. Pauses the destruction of bones and intervertebral discs, strengthens the back muscles, prevents the progression of the disease.
activity and improving trophic tissue, improves blood flow and restores nutritional functions. Pauses the destruction of bones and intervertebral discs, strengthens the back muscles, prevents the progression of the disease. - Orthosis - wearing individually selected orthopedic recliners, corsets.
- Medical swimming should be conducted only under the supervision of the instructor, it helps to correct deformation, strengthen the muscles of the back, improve the function of breathing. The training program is created individually in accordance with the specific pathology.
How to remove the withers on the back for a few minutes a day:
Surgery as an extreme measure
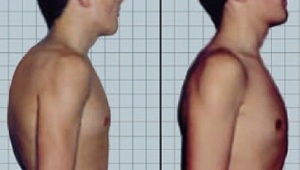
On the hump of the hump before and after the surgical treatment of
If conservative treatment with pronounced kyphosis with a violation of the functions of internal organs and compression of the roots does not yield a result, it may be requiredoperative intervention.
Operations allow you to correct the angle of the bend of the spine, stop the progression of deformation, remove the hump, eliminate the compression of nerve trunks and protect them from damage in the future.
The spine is fixed by structures of inert metals. After the operation, the bed rest is shown, followed by the wearing of the corset.
Prevention of hump formation and deformation
To prevent the development of abnormal kyphosis and hump formation in adults and children, the following recommendations should be observed:
- observe correct posture, posture in training sessions;
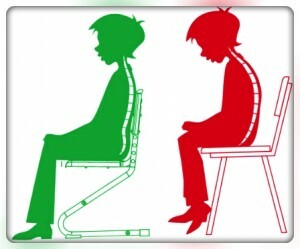
- does not slouch when sitting and walking;
- more to move, more often to be in the open air;
- spend less time at the computer and in front of the TV;
- make sure that the height of the chair and the table for training corresponds to the height of the person, the workplace was well lit;
- sleep on hard mattresses and low pillows;
- perform physical exercises that strengthen the muscular back skeleton;
- to engage in physical culture and sports, regularly visit the pool, do exercises in the morning;
- in time to treat spine diseases;
- at the first signs of stoop to consult a doctor;
- to eat fully, balanced and correctly.
What is fraught!?
In severe progressive forms of kyphosis with the formation of a hump, multiple complications occur:
- compression of roots, which develops by narrowing the spinal canal, leads to paresis and paralysis of the lower extremities , impairment of the functions of the pelvic organs;
- occurs rapid aging of the spine , which causes severe back pain, interfering with normal movement;
- intervertebral disks are affected, develops osteochondrosis ;
- excessive mechanical loads in the dystrophy of the discs lead to the formation of disc hernias , inflammation of the roots of the spinal nerves;
- displacement of the center of gravity creates an excessive load on the feet, resulting in flatfoot , in turn flat feet leads to an increased load on the knee and hip joints of the legs with subsequent arthrosis changes in them;
- hinders the mobility of the chest during breathing, which leads to the formation of chronic respiratory failure, hypoxia, cardiac disorders ;
- changes in the position of the heart and blood vessels causes circulatory disorders , omission of the diaphragm increases intra-abdominal pressure, which creates the prerequisites for the development of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.