In the offices of a neurologist, in polyclinics, you can rarely hear about such a diagnosis. It seems that the lot of neurology is osteochondrosis, radicular syndromes or hypertensive encephalopathy.
But there are severe, and sometimes fatal, diseases of the central nervous system - meningitis and encephalitis.
Previously it was believed that the person who suffered the disease either died or was left insane. In fact, this judgment is fundamentally wrong. What is it, meningitis? We will try to understand the main issues of this vast and very interesting topic.
Contents of
- 1 What is meningitis and the causes of
- 2 Types of meningitis and features of
- 3 What is the risk of meningitis?- Consequences of the disease
- 4 First signs of meningitis
- 5 Symptoms of meningitis in adults
- 6 Treatment of meningitis
- 6.1 Forecast
What is meningitis and the causes of
Meningitis is an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system, namely its meninges. Since there is both a hard and soft shell, there may be pachymeningitis and leptomeningitis, respectively. Diseases in severe conditions are among the most painful in all of neurology and, perhaps, in the entire clinic of internal diseases.
The severity of the condition is due to the excellent sensory innervation of the meninges. They are well aware of pain, which is the main sign of any meningitis.
The causes of the disease, of course, are microorganisms and viruses. The most known are the following:
- Meningococcal purulent meningitis caused by diplococci of the genus Neisseria. It is a "classic" with full development of symptoms, the appearance of hemorrhagic rash and all sorts of complications, among which gangrene of extremities is found. Currently, it is rare to occur, mainly in the form of outbreaks in organized institutions, especially children's ones;
- Tick-borne encephalitis virus. A significant number of cases occur in the form of a meningeal form, without affecting the brain substance and focal neurological symptoms;
- Tuberculosis bacillus. Causes severe, sluggish tuberculosis meningitis, which develops in weakened people, long-term tuberculosis. For this, a primary focus of the tuberculosis process in the body is necessary.
In addition to these reasons, inflammation of the meninges can be caused by a conditionally pathogenic flora or even fungi. The lower the immunity of a person, the higher the risk. In patients with HIV infection in the stage of AIDS, the most innocuous bacterium can cause meningitis, and the course of this disease will be severe.
Types of meningitis and features of
As with any inflammation, meningitis can form pus, this inflammation is called purulent. And when autopsies of patients who died of meningitis, the hemispheres of the brain are covered with a "purulent cap".This is most noticeable in the meningococcal process.
Serous meningitis is much easier, in which there is no pronounced protein production in the cerebrospinal fluid, and the cerebrospinal fluid retains its transparency. An example is the meningeal form of tick-borne encephalitis. As a rule, the clinical course of such serous forms is easier than purulent.
But against the background of a serous process, which is unfavorable, a secondary suppuration may develop. This process is called "secondary purulent meningitis."It can appear, for example, as a complication with an open craniocerebral trauma.
In this case, a post-traumatic inflammatory process develops. If the inflammation of the membranes has complicated the course of purulent otitis media, then such a meningitis is called otogenic, etc.
It is possible to classify the disease according to the affected area. Inflammation on the basis of the brain is called basal, with inflammation of the membranes covering the large hemispheres, convective meningitis develops. There is a meningitis affecting the shell of the spinal cord( spinal meningitis).
On the course of the disease can be from a lightning( meningococcal sepsis) to a chronic( tubercular process).
Also, the disease can be classified by sensitivity to antibiotics, by changes in cerebrospinal fluid and many other symptoms.
What is the risk of meningitis?- Consequences of the disease
Of course, purulent process is more dangerous than serous. Therefore, most complications can be analyzed using the example of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis caused by meningococcal infection. The most common conditions are as follows:
- septic shock;
- edema - swelling of the brain with subsequent dislocation of its substance, the development of various variants of ejections, is the most common cause of death in the first day of the disease;
- transition of infection from the shells to the substance of the cerebral cortex, with the attachment of focal symptoms - development of meningoencephalitis;
- a formidable complication is occlusive hydrocephalus. In this case, spikes, which are abundant in the cerebrospinal fluid after the purulent process, are capable of overlapping these paths to a greater or lesser extent. As a result, a rapidly progressive syndrome of intracranial hypertension develops.
Any purulent meningitis, the consequences of which can not be predicted beforehand, must necessarily be treated in the neuroinfections department of the infectious hospital or in the resuscitation department.
The first signs of meningitis

Symptoms of meningitis in adults, during the first hours and days may not be specific enough: when the headache is not yet, the following symptoms may be of concern:
- fever, with chills, to high figures;
- appearance of cutaneous hyperesthesia - the patient is unpleasant touching the skin( senestophobia);
- also causes photophobia and phonophobia - a person wants to retire in a dark quiet room and, if possible, go to bed.
Of course, such signs can be in many diseases, for example, influenza, or even migraine( except fever).But the next day, meningitis develops throughout its characteristic clinical picture.
Symptoms of meningitis in adults
The leading symptom of inflammation of the membranes is the cerebral symptomatology. And the main sign is a diffuse, diffuse, constant headache of high intensity. Many patients noted even the hour of onset of the disease, and not just the day. And this hour was marked by the appearance of such a headache, which was the strongest in life.
In combination with a fever, such pain exhausts a person. It is not stopped by any analgesics, as its mechanism is completely different - the shells become irritated with local inflammation, hyperproduction of cerebrospinal fluid occurs.
This aggravates the situation: increased pressure of cerebrospinal fluid on inflamed membranes leads to an even greater increase in headache, as well as the emergence of cerebral or central vomiting. This vomiting arises out of any connection with the stomach, food intake, and is in no way connected with the gastrointestinal tract: its cause lies in the irritation of the brain structures by the increased pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
The symptom of this vomiting is complete suddenness. Suddenly, without any previous nausea, the patient tears a "fountain", a powerful jet, where it is necessary.
After a few seconds a person can figure out that next time he needs to remove all the surrounding things away, otherwise they will be spoiled. Vomiting does not bring relief. In addition, with meningitis, there is an extremely painful symptom of concussion of the membranes.
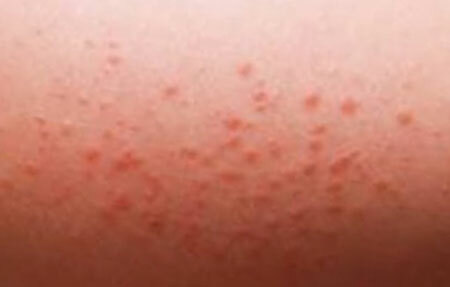
rash with meningitis photo
A weak copy of it is the famous intercostal neuralgia or lumbar lumbago. With each concussion of the nerve root, there is a sharp pain in the lower back, from which the person groans and stops. So, the same pain, only constantly "explodes" in a patient with meningitis in the head. He loses sleep and appetite.
Each lifting of the head, an attempt to change the posture, to rise, sit in bed, brings severe torment. Any deep breath and straining so intensify the headaches, which makes us give up the idea to empty the intestines, and at this stage the infectious intoxication is aggravated by constipation.
In addition, there is soreness in all the tendons of the body, which together with large muscles contract due to painful impulses of the membranes.
Therefore, there is a characteristic posture of a patient with meningitis: it is aimed at "compensating" the pain that arises: the patient lies on his side, the head is unbent( thrown back), and his legs are pulled to the stomach.
A classic symptom of meningitis that distinguishes it from all other conditions is Bechterew's zygomatic symptom: when a neurological hammer is taped on the cheek, a severe headache flare occurs throughout the head, and not at the tapping point. This symptom is a vivid example of the effect of concussion of the inflamed cerebral membrane.
In addition, severe pain causes pressure on the eyeballs. The above symptoms can be accompanied by a painful grimace of the patient, confirming the pain reaction.
Symptoms of meningitis in adults, described by us, characterize both purulent and serous form of the disease. In the event that on the skin of a person appeared foci of rash, which tends to merge - is likely a case of meningococcal meningitis.
Further abandonment of the patient without urgent care of a neurologist and infectious disease causes a progression of symptoms.
The growth of intracranial pressure and infectious - toxic symptoms lead to a gradual loss of consciousness, infectious - toxic shock and development of cerebral edema. There is a slow development of coma and oculomotor disorders( eg, divergent strabismus) against the background of pronounced soporus and oppression of consciousness.
Treatment of meningitis
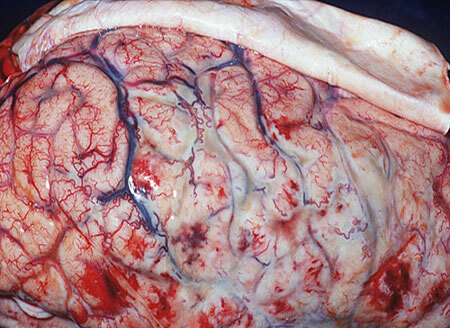
Brain damage in meningitis, photo
Meningitis is an interesting disease: an obligatory and absolutely necessary method of diagnosis is lumbar puncture, almost always, except for the necessary and important information for the doctor( transparency and color of the liquor, flowing with drops or stream) brings the firstand considerable relief: the headache is sharply reduced. Therefore, the treatment of meningitis in adults begins with lumbar puncture.
It is carried out in a hospital, lying down, after a puncture, it is not allowed to get up during the day. Further tactics depend on the composition of the CSF.Thus, the treatment of purulent meningitis begins with the introduction of bacteriostatic antibiotics, and the treatment of tuberculous meningitis - with tuberculostatics and the use of reserve drugs.
Simultaneously, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out: intravenous administration of a solution of dexamethasone or other corticosteroid hormones allows to stop the pain syndrome in serous meningitis, to reduce its intensity in a purulent process.
As a rule, with proper antibacterial and pathogenetic therapy, the intensity of the headache decreases for the first and second days, the temperature normalizes, vomiting stops, and appetite appears.
Forecast
For meningitis, the prognosis is difficult to determine. The later the time has passed since the development of the first symptoms, the easier it is to give some sort of prognosis. And in the first day it is completely unclear. With meningitis, the prognosis depends on:
- Urgency of seeking medical help;
- Levels of fever and signs of intoxication;
- Appearances of hemorrhagic rash;
- Severity of cerebral symptoms( headache, vomiting);
- Appearances of focal symptomatology, signs of oppression of consciousness;
- Results of bacteriological and general investigation of cerebrospinal fluid and patient response to puncture;
- First response to treatment;
- Term for the normalization of temperature and regression of symptoms.
- Presence of concomitant pathology, aggravating factors( age, cardiac, renal and hepatic insufficiency, polyvalent drug allergy).
Long-term results for the quality of life are favorable. Sometimes, subsequent treatment with nootropic drugs, vitamins, resorbants is required. To prevent the growth of intracranial pressure and the treatment of adhesions, it may be necessary to electrophoresed with lidase through the eyeballs, taking diacarb.