Parkinson's disease is a brain disease associated with the destruction of some neurons of a black substance( a midbrain patch).Other names of pathology are tremor paralysis, parkinsonism.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
In fact, the latter name is more extensive and includes not only Parkinson's disease, which accounts for about 80% of all cases of Parkinson's syndrome, but also states with similar motor impairments but associated with other degenerative processes in the nervous system.
The incidence of tremor paralysis increases with age. Very rarely pathology occurs in young people, but after 60 years the incidence rate is already 5%.

The development of Parkinson's disease
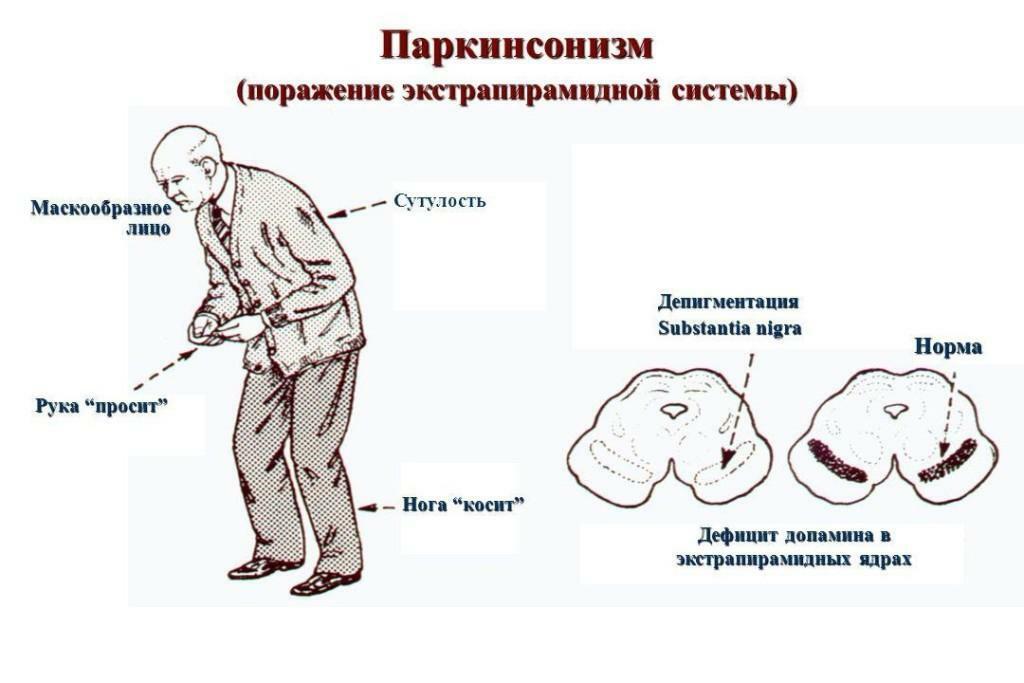
The manifestations of the disease may be different, but all of them are associated with impaired motor activity: rigidity( increased muscle tone), akinesia( limited self-movement, weak mobility), trembling at rest( tremor).

Forms of the disease
Depending on which motor restriction is present, parkinsonism is divided into 3 forms: rigid, akinetic, trembling. Let us dwell on the description of the first type.
Content of material
- 1 How does the rigid form appear?
- 2 The development of the akineto-rigid form
- 3 Causes of the development of Parkinson's disease
- 4 Diagnosis
- 5 How is the trembling paralysis treated?
- 5.1 Video - Parkinson's disease
How does the rigid form appear?
Stiffness means stiffness caused by high muscle tone. Such changes are caused by a simultaneous tension of the muscles-antagonists( extensor and bend).
The rigid form of Parkinson's disease has several properties.
- Tone affects asymmetrically. It develops non-simultaneously throughout the body. Asymmetry is especially characteristic of the onset of the development of pathology.
- The intensity of the increased tone can vary throughout the day. Least stretched muscles after rest. Nervous shocks increase the rigidity of muscles.

Throbbing-rigid form - development and symptoms
- The defeat of articular extensors and flexors occurs more often and leads in the end to the difficulty of gait and other movements, including passive. The wrist often suffers. The main manifestation of this motor impairment is the syndrome of the "cogwheel".This means that the movements are made by jerks, and not smoothly, as is the case with healthy people. This particular feature is revealed by the doctor at the reception.

Feature of movements in parkinsonism
- At the very beginning of the disease a person can not feel stiffness.
- Gradually the symptoms become more pronounced, which leads to the formation of a specific "begging" posture, characterized by a stoop, slightly bent at the elbows of the hand, in the knees and hips - legs. The head is also slightly lowered.
- Constant tension eventually leads to the formation of a pain syndrome that affects the back and joints.
Parkinsonian patient
In its pure form, rigid Parkinson's disease is not common and can exist only at the very beginning of the disease. Often the increased tone is combined with other signs, according to which three types of Parkinson's disease are distinguished.
- A rigid form of shaking occurs in about 20% of cases. In this type of Parkinson's disease, increased muscle tone is supplemented by a general decrease in motor activity.
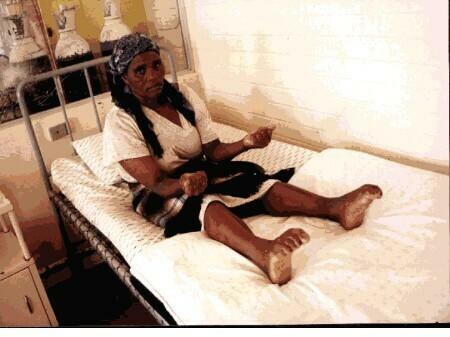
Thoroughly rigid form
- The most common form of asthma. It is detected in almost 40% of patients. The main symptom is trembling, with a predominance of tremors, which is manifested when a person is at rest, and when the motion subsides.
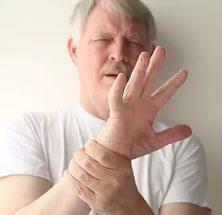
Parkinson's disease( tremor paralysis)
- A third of those suffering from Parkinson's disease do not tremble. This is akinetic-rigid form.

Parkinsonism may not have a tremor
It is the combination of akinetic and rigid symptoms that is more often understood as a rigid form of parkinsonism. A special sign of it is bradykinesia, or slowing down the movements of all muscles, which develops gradually.

Deceleration of movements( bradykinesia)
Development of an AKINETO-rigid form
At the very beginning of the disease, movements are not manifested. Gradually, not only stiffness but also bradykinesia develops:
- is initially affected by facial muscles, which leads to weakening of facial expressions and blinking, and later to a mask-like face;
Parkinson's disease - photo
- simultaneously reduces the size of the swing of hands and feet during walking;
- limbs begin to move more slowly;
- the patient's hand becomes smaller and illegible;
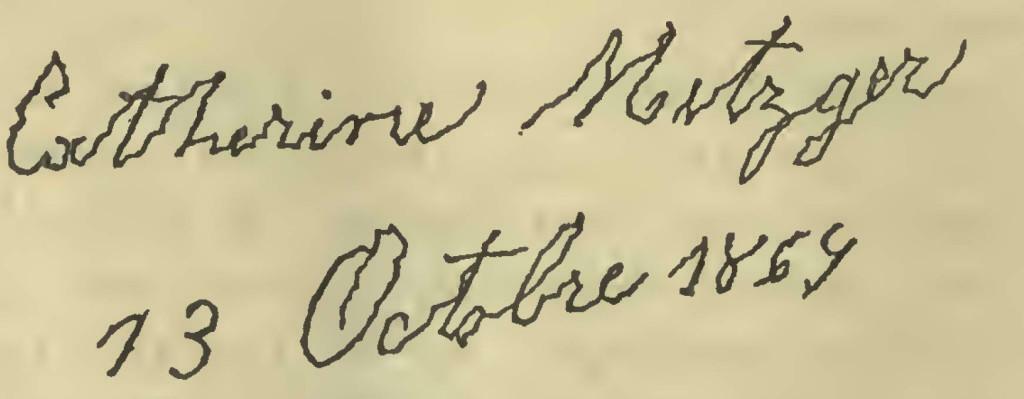
Handwriting for Parkinson's disease
- changes in the gait are manifested in the form of a shortened and uncertain step.
Gradually, it becomes more difficult for a person to service himself: combing, washing, buttoning up clothes.

Care for the patient
For Parkinson's disease in general and for akineto-rigid form in particular, vegetative transformations and changes in the psyche are also characteristic:
- slow movement of food through the digestive tract and constipation;
- weight loss;
- mild perspiration, which is especially dangerous in hot periods due to high risk of overheating;
- increased sebum and related seborrheic dermatitis;
- increased urge to urinate and urinary incontinence;
- violation of sexual functions;
- depression;
- grumbling;
- egocentrism;
- slow switching from thought to thought;
- obtrusiveness;
- irritability.

Manifestations of the disease
The combination of delayed motion and increased tone eventually leads to postural instability. This syndrome is associated with the inability to maintain balance and manifests itself in various ways:
- forced periodic transition to a seminal step during walking;
- need to take a few steps in the event of a shock that is out of balance;
- loss of stability when trying to stand or sit down.
Postural instability
Such changes can eventually lead to a fall. Often, patients get fractures.
With the akineto-rigid form, the forecast is often unfavorable. The result of this type of Parkinson's disease is often full immobility, impaired swallowing and breathing problems.
Causes of Parkinson's Disease
Causes of Parkinson's Disease
The etiology of the disease has not yet been fully understood. It is determined that genetic predisposition is characteristic for true parkinsonism. There are suggestions that there are certain external factors that contribute to the realization of heredity.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease are associated with the death of neurons located in the black spot of the midbrain. This eventually leads to a decrease in the production of dopamine( a neurotransmitter involved in pleasure and cognitive process).As a result, the balance of the mediators is disturbed and, accordingly, the correct transmission of nerve impulses.
Changes in the brain
Knowledge of the pathogenesis and the manifestations caused by it allowed in the end not only to conduct the correct diagnosis, but also to prescribe a therapy that slows the development of the disease.
Diagnosis
In the process of diagnosing Parkinson's disease it is important to distinguish it from other pathologies with similar manifestations:
- of vascular parkinsonism associated with strokes and ischemic brain lesions;
- drug parkinsonism, due to the use of certain medications and drugs and is in most cases after withdrawal of drugs;
- multisystem atrophy, which is the degeneration of individual groups of nerve cells and is not characterized by an improvement in the state of taking the main drug for Parkinson's disease - levopods;
- is a progressing supranuclear palsy, for which stiffness is characteristic, as well as a paresis of the gaze not only upward, which happens with trembling paralysis, but also down;
- of Wilson-Konovalov's disease with suspicion of Parkinson's disease in young people.
In rigid paralysis of rigid form, there are several properties that allow it to differentiate from other diseases:
- asymmetry of manifestations in the first stages of the disease;
- positive response to the use of levodopa.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are also commonly used to exclude other pathologies. The most accurate and popular method in recent times is MRI.
Parkinsonism on MRI
Please note! Timely contact with a doctor for Parkinson's disease can slow the development of pathology due to properly selected treatment.
How is paralysis treated?

Parkinson's disease treatment
Parkinson's disease therapy should be comprehensive and aimed at alleviating the condition.
| Type of treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Antiparkinsonian drugs | At the onset of the disease, amantadine is often prescribed, as well as drugs that block the action of acetylcholine, whose concentration is high in parkinsonism against a background of reduced dopamine. It is believed that amantadine, as well as activators of dopamine receptors, selegiline, protect the nerve cells of black substance from death, preventing the development of the disease. But this is not proven. The main drug with severe symptoms of parkinsonism - levodopa. |
| Additional drug treatment | In severe depressive syndrome, antidepressants are prescribed, which can be sedated if the patient has a sleep disorder. To improve the work of the gastrointestinal tract, drugs that stimulate the contractile activity of the intestine are prescribed. |
| Non-drug treatment | Important: gymnastics, physiotherapy, diet to prevent constipation. There is also a surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease, consisting in the destruction of certain areas of the brain, which leads to a decrease in increased muscle tone. These are stereotactic operations. |
Important! Any anti-Parkinsonian remedy in later stages can lead to periodic attacks of psychosis, preceded by nightmarish dreams.
Levopod is the basic medicine for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. This substance is transformed in the remaining cells of the black substance into dopamine, thus replenishing the lack of this neurotransmitter. The downside is the need to increase the dosage. As a result, there comes the syndrome of "end-of-dose exhaustion", when there is an increase in symptoms before taking the next dose of the drug. Gradually, such transitions in the patient's condition become unpredictable and unrelated to taking the medication.
Drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease
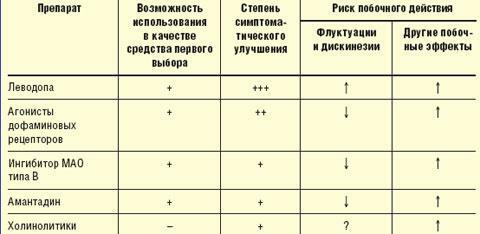
Standards for the treatment of Parkinson's disease
A side effect of levopod is a reduction in pressure and nausea. However, in modern drugs, this property is not very pronounced due to decarboxylase.
Please note! Severe cancellation of drugs or lowering the dose can lead to such dangerous consequences as complete immobilization, violation of swallowing and breathing. This is how the akinetic crisis manifests itself.
In addition to therapy, people with Parkinson's disease need specific treatment. It is important to give them feasible work, not to allow banter in their address, to spare feelings.

Psychological support is very important
There are no measures to prevent the development of trembling paralysis. However, the study found that the use of certain types of flavonoids contained in berries reduces the risk of morbidity.
But completely excluding the possibility of illness is hardly possible, especially if the next of kin has a similar pathology. Therefore at the first suspicions it is necessary to address to the neurologist for statement of the diagnosis and reception of treatment.