 The human body constantly produces spinal fluid( cerebrospinal fluid), which continuously circulates between the cerebral ventricles( here it is produced) and the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord( where it is absorbed into the venous blood).
The human body constantly produces spinal fluid( cerebrospinal fluid), which continuously circulates between the cerebral ventricles( here it is produced) and the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord( where it is absorbed into the venous blood).
Liquor performs different functions - protection against damage, participation in maintaining constant pressure inside the skull, in exchange and trophic processes. In the case of accumulation in the brain of an excessive amount of fluid, they speak of edema or hydrocephalus.
This condition may occur due to increased secretion and impaired absorption of the cerebrospinal fluid( areorbital form) or because of an obstruction to its normal outflow( occlusal hydrocephalus).The latter form is the most complex, quickly leading to serious consequences for human health and life.
About the causes and forms of occlusion
Occlusive hydrocephalus is a serious disease associated with a violation of the physiological circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. This pathology is called a closed or non-communicable form of hydrocephalus, which develops as a result of compression or blockage of a separate area of the liquor system.
 As a result, liquid accumulates either inside the ventricles( internal hydrocephalus) or in the space under the medullary membranes( external hydrocephalus).
As a result, liquid accumulates either inside the ventricles( internal hydrocephalus) or in the space under the medullary membranes( external hydrocephalus).
The causes of occlusal edema of the brain can still affect the fetus in the womb, which leads to a congenital disease, can affect the brain after birth and cause acquired hydrocephalus.
Congenital causes include:
- developmental abnormalities( atresia, stenosis in the CSF);
- embryonic tumors;
- birth injuries;
- infection( such as cytomegalovirus, rubella, or others).
Acquired causes:
- trauma and mechanical damage to the head;
- severe parasitic diseases( echinococcosis, cysticercosis, toxoplasmosis);
- malignant neoplasms of the brain;
- aneurysms of cerebral vessels;
- intracerebral hemorrhages and hematomas;
- acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- infectious diseases( meningitis, meningoencephalitis, arachnoiditis);
- adhesions and scars;
- chronic brain hypoxia.
Predisposing factors include advanced age, neurosurgical interventions, chronic alcoholism.
Clinical picture
A particularly severe clinical picture is observed in the acute form of occlusive hydrocephalus, when there is a sharp increase in intracranial pressure. The severity and nature of the symptomatology depends on the level of occlusion.
The main symptoms in adults:
- headache( often in the morning after waking up), is not stopped by usual analgesics;
- vomiting( can be with or without nausea), brings little relief to the patient;
- weakness and drowsiness during the day;
- dislocation( displacement) of individual brain structures relative to others;
- vision impairment;
- vestibular disorders;
- cerebellar ataxia - with obstruction in the area of this structure of the brain;
- mental disorders.
In children, the signs of hydrocephalus manifest after birth:
- head size increase in comparison with the age norm;
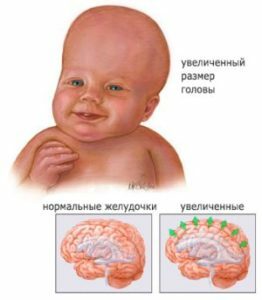
- overhanging the frontal part of the skull;
- swelling of veins on the head;
- voltage and absence of pulsation of the large fontanel;
- frequent regurgitation and vomiting;
- paresis and paralysis of the lower limbs;
- visual and hearing impairment;
- convulsive syndrome;
- delay of neuropsychic development of varying degrees.
With the rapid progression of the disease, children rarely survive to school age. Lethal outcome can come from dystrophy and damage to internal organs.
In adult patients, constant compression of the brain structures and impaired blood circulation contribute to the appearance of severe neurologic symptoms. Decompensated dropsy can lead to disability due to loss of mental or motor abilities.
Irreversible processes are associated with atrophy and necrosis of individual areas of the medulla. One of the most serious complications is the dislocation and compression of the medulla oblongata, leading to respiratory depression and cardiac activity.
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is made by a specialist in neurology based on a characteristic clinical picture and instrumental examination data. With the inherent nature of the disease, it is important to monitor the child in dynamics.
 The level of occlusion is determined reliably by methods such as computer( CT) or magnetic resonance imaging( MRI).
The level of occlusion is determined reliably by methods such as computer( CT) or magnetic resonance imaging( MRI).
Neurosonography( ultrasound scanning of the brain), which can determine even fetal hydrocephalus, is very informative. This safe study is often used for diagnosis in young children, when the seams on the skull and the fontanel zone have not yet overgrown.
Conservative therapy is sometimes possible in children with slow progression of the disease. The main tasks:
- decrease in intracranial pressure - diuretics such as Diacarb or Lasix are used for many months;
- decrease in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid - appointed Mannitol, Glycerin;
- recovery of electrolyte balance ;
- removal of excess fluid through the fontanelle by puncture ;
- general restorative therapy - vitamins.
Acquired hydrocephalus in adults and older children is necessarily treated with the disease, which is the cause of the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
In the absence of the effect of drug treatment or with the rapid progression of the disease, surgical operations are used.
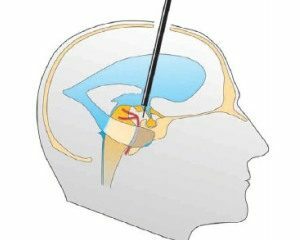
Removal of excess CSF via fontanelles
In the occlusal form of the disease, it is necessary to remove the obstruction to the circulation of the fluid( removal of tumors, cysts, hematomas or aneurysms).For this purpose, shunting is performed.
Along with the elimination of the cause of plugging of the liquor ducts, it is often necessary to create new ways for fluid outflow.
Endoscopic methods of installing shunts and ventricular plasty are considered promising. In some cases, palliative operations are performed to alleviate the patient's condition if full surgical intervention is impossible( for example, spinal and ventricular punctures).
Contraindications for surgery are all acute inflammatory processes, mental states, epilepsy with frequent seizures, irreversible organic changes.
In the postoperative period, patients need treatment and protection regimen and medical support therapy. The amount and duration of treatment depends on the diagnosis, the causes of hydrocephalus, the complexity of the operation, the patient's age, concomitant diseases and other factors.
How to Prevent
Disease Congenital hydrocephalus can be controlled by adhering to a pregnant woman's recommendations of a doctor( avoiding  the possibility of infection, uncontrolled use of drugs, alcohol and nicotine).
the possibility of infection, uncontrolled use of drugs, alcohol and nicotine).
Before planning a conception, it is recommended to pre-vaccinate a future mother against certain infections, for example, from rubella. Adults should be examined at the appearance of the first symptoms and treat diseases of the nervous system, internal organs, spine, lead a healthy lifestyle, strengthen the body's immune defenses, monitor weight.
The prognosis for the occlusal form of the disease depends on its cause, the rate of increase in symptoms and the time of the onset of adequate therapy.
Children receiving treatment have a chance for a long life, but sometimes there is a disruption of the function of speech and intelligence. Adult patients with timely diagnosis and adequate therapy have a fairly high chances of recovery.