 Psoriatic arthropathy( arthropathic psoriasis) is a chronic inflammation of the joints that develops against the background of psoriasis.
Psoriatic arthropathy( arthropathic psoriasis) is a chronic inflammation of the joints that develops against the background of psoriasis.
Pathology belongs to the group of seronegative arthritis and is observed in 5-7 percent of patients suffering from squamous lichen.
Contents of the article
- Etiology and pathogenesis of the disorder
- Clinical picture
- Clinical forms of the disease
- Complications and consequences of the disease
- Diagnostic methods
- What can I do. ..
- For the prevention of
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disorder
The causes and mechanism of the development of psoriatic arthropathy are not completely known. It is believed that great importance in the manifestation of pathology is:
- heredity;
- autoimmune reactions;
- infectious diseases of various etiologies;
- constant stress;
- diseases of the digestive and endocrine system;
- individual pharmaceuticals( antimalarials, lithium salts, β-blockers).
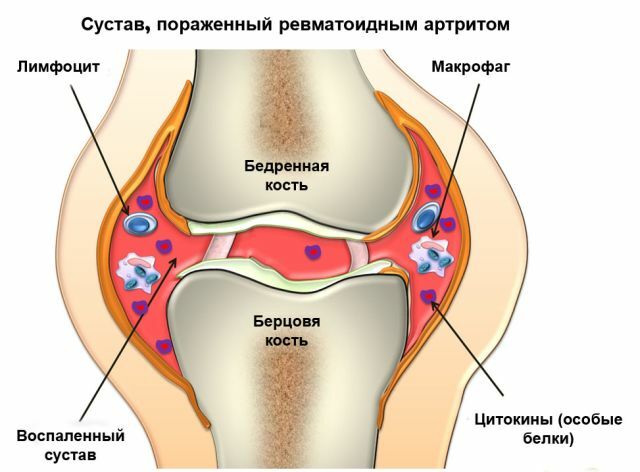
Detection in the skin and in synovial fluid of patients with immunoglobulin joints indicates that immune mechanisms participate in the development of pathology.
It is suggested that the appearance of psoriatic arthropathy is associated with viruses and streptococcal infections, but this is still fully proven.
Clinical picture of
In 70% of patients with psoriasis, changes in the skin are first observed and only then 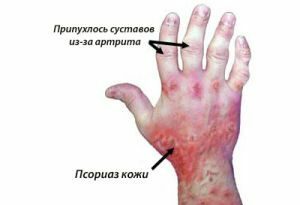 joint damage is associated.
joint damage is associated.
Approximately 15-20% of the diseased in the pathological process are involved in joints and only after a while( sometimes many years) can you see skin manifestations of scaly lichen. In 10% of patients with psoriasis, joint and skin lesions start simultaneously.
Arthropathic psoriasis can begin gradually. In this case, the patient has general weakness, muscle or joint pain.
Others have an acute onset of pathology, similar to gout or septic arthritis, characterized by sharp pain in the joints and their strong pastosity. In 20% of patients, when exactly the disease started it is impossible to determine, and it manifests itself only by arthralgia.
The distal, central interphalangeal joints of the upper extremities, knee and metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal, shoulder joints are the first to enter the pathological process.
Pain syndrome is particularly pronounced at rest, at night, in the morning hours immediately after waking, during the day during the movement the pain subsides a little. In the morning, stiffness is observed in the affected joints.
In most cases, the disease occurs in the form of mono- and oligoarthritis.
One-time all the joints of one finger are involved in the pathological process, except for this, tendovaginitis of the flexors is observed, and the sick finger in form becomes similar to the "sausage".The skin over the abnormal joint acquires a purplish-cyanotic color. Usually this is typical for the toes.
Clinical forms of the disease
Currently, there are 5 clinical forms of psoriatic arthropathy:
- Asymmetric oligoarthritis .The most common lesion of joints with psoriasis. It occurs in 70% of patients.
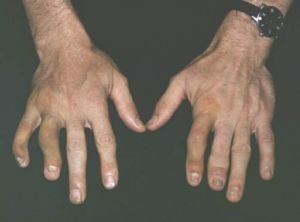 The pathological process affects up to 4 joints on one side of the body or different joints on the left and right side of the body. Suffer large joints: hip, ankle, wrist and knee.
The pathological process affects up to 4 joints on one side of the body or different joints on the left and right side of the body. Suffer large joints: hip, ankle, wrist and knee. - Arthritis of distal interphalangeal joints .One of the characteristic manifestations of arthropathy. As a rule, it occurs in combination with damage to other joints. It is more often diagnosed in men. With this form of the disease, the nail plate usually thickens, its color changes, and dimples appear on it.
- Symmetric rheumatoid-like arthritis .Lesions of the same joints are observed in the left and right parts of the trunk, at the same time 5 or more joints suffer. The metacarpophalangeal and central interphalanal joints of the upper limbs are deformed. This form of pathology is more common in women. Psoriasis, accompanying symmetrical arthritis proceeds particularly hard.
- A mutilating or as it is also called destructive or disfiguring arthritis .It occurs quite rarely, it is observed in patients with severe skin manifestations of scaly lichen. Over the years, the disease progresses, as a result of the destruction of small joints of the hands, especially the fingers suffer, they deform and cease to perform their functions. Often the destructive form of pathology is accompanied by lesions of the spinal column.
- Psoriatic spondylitis .It occurs in 40% of patients and is often accompanied by peripheral arthritis. This form of the disease is characterized by back pain, can be accompanied by inflammation of the entire spine, or just the cervical or lumbar region, or the inflammatory process can be observed in the joints connecting the pelvic bone and the spine. With this form of the disease, the stiffness of the spine is possible, although its mobility is not limited to all patients, and someone does not have any signs of spondylitis.

In combination with joint damage, myofascial pain, inflammation of the sternum and acromioclavicular joints, bursitis of the foot and Achilles tendon, damage to the organs of vision( conjunctivitis, anterior uveitis), and sometimes amyloidosis of the kidneys are possible.
In rare cases, the development of a malignant form of psoriatic arthropathy is possible, which is characterized by a number of signs:
- patient exhaustion;
- temperature of hectic type;
- by severe psoriatic lesions of the skin, spine joints;
- generalized polyarthritis with severe pain and formation of cicatricial ankylosis;
- generalized lymphadenopathy;
- lesions of the organs of vision, heart, kidneys, liver, CNS and PNS.
Complications and consequences of the disease
Psoriatic arthropathy can be accompanied by severe pain and affect all new joints even despite treatment. 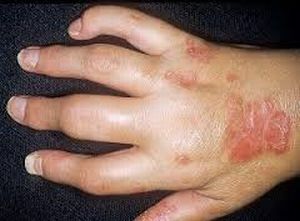
In addition, the disease carries a number of threats and dangers:
- If small finger and toe joints are involved in the process, swells .As a result, it is difficult for a person to perform various manipulations with his hands or because of a tumor it is problematic to pick up shoes.
- enterosopathy is often observed, which is accompanied by pain and inflammation of the tendons. The heel tendon usually suffers. Because of the pain in the foot, the patient is difficult to walk.
- When involved in the pathological process of the joints of the spine , there are painful sensations in the back and neck of the .
Diagnostic methods
The doctor diagnoses on the basis of a clinical picture and laboratory data.
Of the symptoms with psoriatic arthropathy, doctors note:
- Damage to the distal interphalangeal joints of the upper and lower extremities , especially the first toes. The joints are painful, swollen, the skin covers over them are cyanotic or purple-cyanotic.
- Simultaneous defeat of all joints on one finger , as a result of which they become like "sausages".
- Involvement in the pathological process at the onset of big disease.
- Heel neuralgia , which is accompanied by pain.
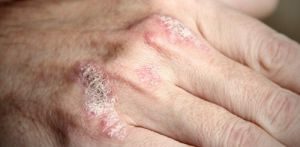
- Skin manifestations of psoriasis , changes in the nail plate( its turbidity, appearance of various lines on it, symptom of a "thimble").
- Scaly lichen in the history of .
A specialist can assign a number of analyzes and studies:
- X-ray .With its help you can see the changes inherent in psoriatic arthropathy.
- Synovial analysis of .Using a needle from the knee joint, take the synovial fluid and examine it for the presence of lactic acid. Exclude gout.
- Increased ESR, hypochromia, leukocytosis .
- Negative rheumatoid factor .
What can I do. ..
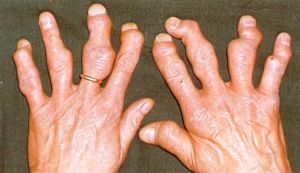 Unfortunately, not much. .. Completely cure the disease is currently not possible.
Unfortunately, not much. .. Completely cure the disease is currently not possible.
Therapy is mainly aimed at arresting the pain syndrome, removing the inflammatory process and preventing the joints from losing their functions.
From medicines prescribe:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs .It is desirable to use selective inhibitors of COX 2, these include preparations based on Meloxicam. They are less likely to exacerbate psoriasis.
- Glucocorticoids , for example, Diprospan.
- Long-acting pharmaceutical preparations or as they are also called basic. This is Methotrexate and Sulfasalazine.
- Immunosuppressive drugs.
For malignant disease, plasmapheresis and UV irradiation of the blood are prescribed.
For the prevention of
 Primary prophylaxis of psoriatic arthropathy does not exist today, since the causes of the disease are not known.
Primary prophylaxis of psoriatic arthropathy does not exist today, since the causes of the disease are not known.
To stop the development of pathology, the patient must maintain normal weight, lead an active lifestyle, avoid stress, viral and bacterial infections, balance eating, take vitamin D.
In addition, there are the following methods of disease prevention:
- Splinting .With the help of tires, the joint can be given the right position, control the inflammatory process, and reduce the erosion of the joints.
- Hydrotherapy .Exercises performed in the water help to strengthen the joints and preserve their function.
- Cold and hot compresses .If they are applied in turn to the affected joints, then they stop the pain and remove swelling.
It is necessary to alternate physical activities and rest, do not overload the joints, if necessary use auxiliary means for movement, for example, walking sticks, carts, they help reduce the load on the joints.
Compliance with all these rules will reduce the risk of disease progression and improve the quality of life.