Fetal hypoxia is an acute or chronic lack of oxygen that occurs as a result of impaired functioning of the placenta( child's place).The placenta is the main organ that connects the developing fetus with the mother's body. Blood flows through the blood vessels of the placenta, saturated with oxygen and nutrients. The baby's lungs during the fetal development period are filled with liquid, therefore the fetus can not breathe on its own and receives oxygen necessary for growth and life through the general blood flow.
If there are pathologies in the work or structure of the placenta, the movement of blood through its vessels is disturbed, and oxygen starvation occurs, which in medicine is called "hypoxia".Hypoxia is dangerous due to its consequences, among which there may be diseases of the heart and blood vessels, neurological pathologies, diseases of the hematopoietic system. The most dangerous consequence of acute hypoxia is intrauterine fetal death, therefore it is important to pass the examinations and tests scheduled by a doctor on time to help identify the signs and symptoms of the existing pathology.
Hypoxia of the fetus: consequences for the child
Content of the material
- 1 Why does hypoxia occur?
- 2 Consequences of chronic hypoxia for a child
- 3 What is the danger of acute hypoxia?
- 3.1 Fetal pneumonia
- 3.2 bowel necrosis
- 3.3 pathology of the nervous system
- 3.4 Prematurity
- 3.5 Video - Fetal Hypoxia: Causes and Consequences Consequences
- 4 future
- 5 Prevention
hypoxic hypoxia Why there?
There are a lot of reasons that can cause intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus. They can be divided into two groups:
- irreversible causes related to abnormalities in the work of internal organs, abnormal course of pregnancy and complications arising during gestational period;
- reversible causes( abnormal lifestyle and non-compliance with the recommendations of the doctor leading the pregnancy), which can be eliminated on their own.

1 group of causes of fetal hypoxia
Almost 30% of cases of chronic fetal hypoxia occur as a result of insufficient attention to the regimen, lifestyle and doctor's recommendations. Rare, short walks, unbalanced food, abuse of harmful products, stress - all this can provoke oxygen starvation. Eliminating these factors is simple enough, but the expectant mother should understand that the child's organism continues to form up to 36 weeks of gestation, so failure to comply with the regime at any time may lead to the beginning of irreversible processes.
For example, the fetal cardiovascular system is pawned for a period of 5-6 weeks, and if during this period the woman did not walk, smoked or eat poorly, the congenital heart defects and vascular disease can result.

2 group of causes of fetal hypoxia
2 group of causes of fetal hypoxia

2 group of causes of fetal hypoxia
Among other negative factors that women can control themselves, doctors distinguish:
- use of potent drugs without prescribing a specialist;
- drinking and smoking tobacco;
- non-observance of a mode of work and rest;
- sexual intercourse( in the case when they were banned by a doctor).
Infectious diseases transmitted during pregnancy( especially in the early stages) can also affect the functioning of the vascular system of the placenta and the transport of oxygen to the fetal tissues. Infectious diseases include not only diseases of the respiratory system, diseases of the genitourinary system, but also infectious gastritis, as well as sexual infections.

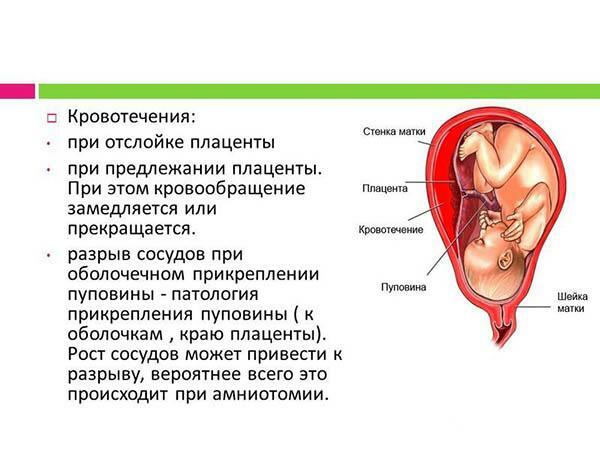
3 group of causes of fetal hypoxia
Other causes of hypoxia development are listed in the table below.(
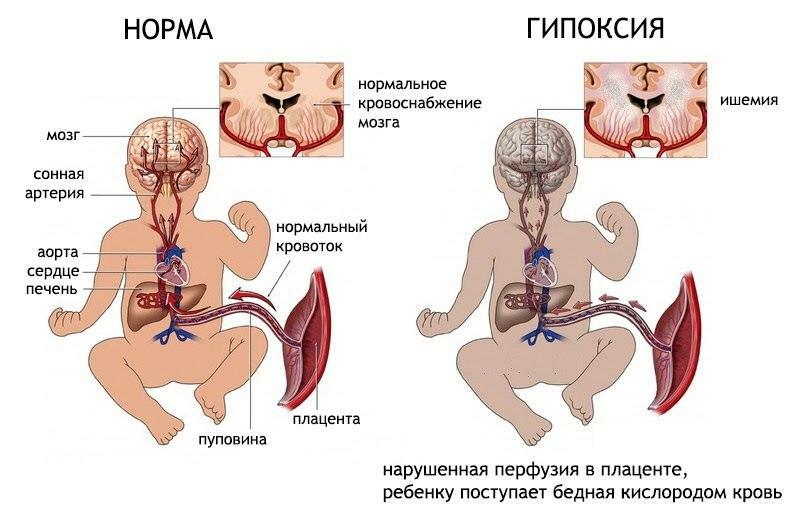
Fetal hypoxia
Consequences of chronic hypoxia for the child
Chronic oxygen starvation is diagnosed less frequently thanacute form, since in most cases, the constant lack of oxygen develops only in the case of an irresponsible attitude of a woman to pregnancy. If a woman walks a lot, eats well, monitors her health and carries out all the recommendations of a specialist, hypoxia usually does not develop. Even if the future mother has health problems, the doctor will prescribe a drug correction that includes drugs to improve blood circulation in the placenta and improve metabolic processes in the fetal tissues.
Consequences of chronic fetal hypoxia are usually detected immediately after birth. A baby can have less weight and height than other children born on this term. The weight deficit can be from 10% to 30%.Children who experience a constant lack of oxygen during fetal growth are poorly adapted to environmental conditions, they have weakly developed vital reflexes( grasping, sucking, etc.).Thermoregulation in these children is often broken, so the baby's limbs can remain cold, even if the socks are worn on the legs, and the baby is wrapped up in a warm blanket.

Causes of hypoxia
Of the diseases most often diagnosed with anemia. At the given pathology the child looks pale, there can be a blueness in a zone nosogubnogo a triangle. Other symptoms of pathology in the infant period include:
- poor appetite;
- capriciousness;
- frequent bouts of crying;
- sleep disturbances.
Poor appetite against a background of low birth weight can lead to a lack of physical and intellectual development, as well as diseases that develop with a shortage of certain nutrients. For example, a deficiency of magnesium can cause irregularities in the work of the heart, the onset of convulsive syndrome and other neurological pathologies. Insufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D increases the risk of rickets, and a lack of ascorbic acid can lead to diseases of the hematopoietic system.

Why hypoxia occurs
Important! Chronic hypoxia of the fetus during pregnancy adversely affects the immune system of the child: it reduces resistance to infectious diseases, and respiratory infections occur in a more severe form than in normal children.
What is the danger of acute hypoxia?
Acute oxygen deficiency occurs most often in the course of labor. The cause may be the imposition of obstetric forceps, a protracted period of attempts, mismatch of the pelvis of the mother and the head of the fetus. If acute hypoxia was diagnosed during pregnancy, the woman immediately hospitalized in the department of pregnancy pathology, as in an outpatient setting it is not possible to carry out constant monitoring of the fetus's condition and heartbeat.
One of the most serious and dangerous consequences of an acute shortage of oxygen is the fading of pregnancy( cessation of growth and development).Pathology can occur at any time, but the most dangerous is the period from 4 to 6 weeks and from 8 to 12. It is not always possible to detect fading immediately - it happens that a woman bore a dead child for several weeks.

What is hypoxia
To suspect fading can be at a gynecologist's appointment, which necessarily hears the heartbeat with the help of a midwife stethoscope. If the contractions of the heart are not tapped, the doctor will send the woman to an ultrasound, which will be able to detect a discrepancy in the size of the fetus during gestation. After this, the woman will be assigned an artificial termination of pregnancy( scraping or artificial delivery - depending on the period of pregnancy).
Intrauterine pneumonia
Pneumonia in the fetus can develop by inhaling meconium - the original feces. If this occurs immediately before childbirth, the chances of rescuing a newborn will be maximized. Immediately after the birth of the baby will be placed in the intensive care unit or intensive care of newborns. In some cases, artificial ventilation may be required using an artificial ventilation device. After relief of the acute process, the child will be transferred to a children's hospital.
What does hypoxia mean?
Important! Newborn pneumonia is an extremely dangerous pathology with a high percentage of deaths, so the expectant mother should take all measures to ensure sufficient oxygen supply and reduce the risk of getting meconium into the fetal lungs.
Intestinal necrosis
Very dangerous pathology requiring urgent surgery. Necrosis of the intestine is the withering away of tissues of a certain part of the colon or small intestine as a result of an insufficient supply of oxygen to the cells of the organ. Even if doctors manage to save the child's life, chances are high that the stool and calipers will have to be installed to divert stool.
Important! Mortality of newborns from this pathology reaches 71%.In most cases, total necrosis begins to develop after a mesenteric infarction - a ligament connecting the posterior wall of the peritoneum with the intestinal tube. If the pathology began to develop until the 28th week of pregnancy, there is practically no chance of saving the baby.

Asphyxia of the newborn
Pathology of the nervous system
The most frequent consequence of acute oxygen starvation that occurs after childbirth is hydrocephalus( cerebral edema).In most cases, the consequences of the disease are cerebral palsy( cerebral palsy) and spastic tetraparesis - the limitation of the mobility of the muscular structures due to constant spasticity.
With a marked defeat of the nervous system, a consequence of hypoxia may be a coma. The prognosis of life in this case is extremely unfavorable, since almost 90% of cases of comatose lesions in infancy result in the death of the child.

Pregnancy management
Premature birth
If a child is diagnosed with acute hypoxia, the doctor may decide that emergency delivery is necessary, despite the length of the pregnancy. If the gestational age of the fetus is more than 30 weeks, the risks are not so serious, but it is impossible to exclude the possibility of dangerous pathologies and severe forms of developmental lag. If an emergency cesarean section is performed for a period of less than 28-30 weeks, the baby will be born with deep prematureness, which is fraught with the following pathologies:
- a violation of intellectual development;
- malformations of the heart muscle;
- neurological diseases( including cerebral palsy);
- blindness and hearing loss.
Important! Only 20% of children born before 28 weeks survive, with most of them having severe congenital diseases that affect the quality of life of the child.
Video - Fetal hypoxia: causes and consequences
Consequences in the future
Specialists believe that if a child survived the first month( the period of newborns) and did not find any consequences of hypoxia, the probability of their development in the future is quite small. However, this does not mean that in the future, pathological symptoms will not manifest. Most often, the consequences relate to behavioral characteristics. Such children are usually hyperactive, irritable, can show unreasonable aggression towards their peers, teachers, educators in kindergarten.
They may have trouble sleeping. Many of these children before adolescence suffer nocturnal enuresis. Treatment of pathology, as a rule, gives minor improvements, but it is possible to achieve full recovery only by 12-15 years, and in some children this disorder in mild form remains for life.
Prevention of hypoxia

Treatment of hypoxia
Consequences of insufficient intake of oxygen during fetal growth and development can be very serious( up to death and disability), so a woman should take a very responsible attitude towards her pregnancy. Long walks in the fresh air are a must at any time. They will help not only to prevent oxygen starvation of the fetus, but also to improve blood circulation, the state of the nervous system of the mother, and to alleviate the manifestations of toxicosis. If the state of health does not allow you to go on a long walk, you can just sit on a bench in some park or on the lake, if conditions permit.
The food should be a sufficient number of vegetables, herbs, berries and seasonal fruits. Meat, fish, nuts, dairy products should form the basis of the diet. From drinks on the table must be present freshly squeezed juices from vegetables and fruits, compotes, fruit drinks, herbal teas, decoctions of wild rose and other berries. Consumption of tea is better cut, and coffee should be discarded altogether.

Prevention of hypoxia
Under strict prohibition are alcoholic beverages and cigarettes. The use of any medicines must be coordinated with the attending physician, since even harmless herbal preparations can withhold influence on the fetus.
Fetal hypoxia is a serious condition that can lead to irreversible effects and the death of the baby. Even if the child does not have any deviations after birth, do not forget that the transferred acute hypoxia increases the risk of sudden infant death( up to 4-6 months), so it is important that the child is constantly under observation, especially during a night's sleep. Very often, such children are diagnosed with a perinatal lesion of the central nervous system, so up to the age of three, the examination of specialized specialists( neurologist) will be prescribed more often than healthy children. If the child is prescribed treatment with drugs of gopatenic acid( Pantogam), you should not refuse: the consequences of refusal of treatment can be more serious than the possible side effects of therapy.