Catatonia is a whole group of psychopathological syndromes, the key clinical manifestations of which are motor disorders.
Catatonia is a whole group of psychopathological syndromes, the key clinical manifestations of which are motor disorders.
These disorders can manifest themselves in a decrease or increase in psychomotor activity, and are accompanied by symptoms of catatonia: catatonic stupor, catatonic agitation, dizziness or uncontrolled aggression, as well as the so-called "waxy flexibility".
Contents of
- The causes of the disease
- Symptoms of catatonia
- Symptoms of catatonia
- Excitation phase
- Catatonic stupor
- Lucid form of violation
- Oniroid carotonia
- Febrile form of the disease
- Diagnostic criteria
- Medical care
- Symptoms of catatonia
Causes of the development of the disease
Catatonia often develops along with such a mental illness as schizophrenia. However, most often catatonia, also called "tension psychosis," is caused by organic brain damage, such as tumors.
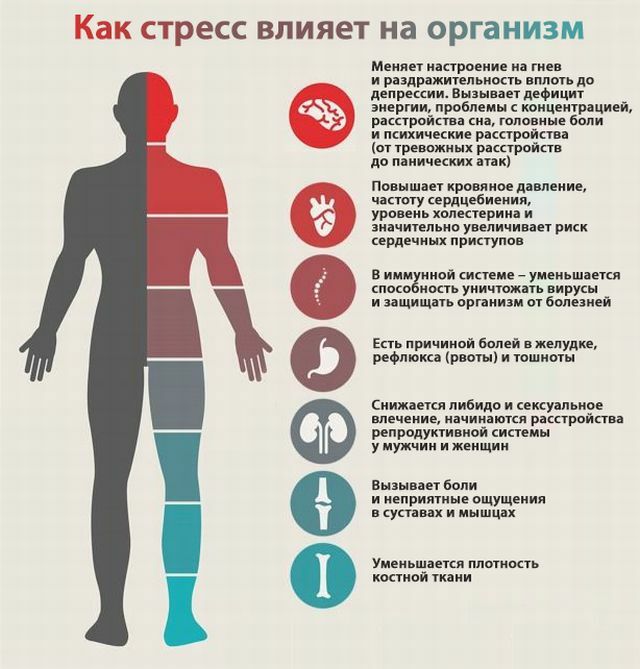
Also, the disease often develops along with organic, intoxication, infectious, somatic, withdrawal symptoms, and other psychoses. The disease is present in a large number of patients with autism, occurs after suffering craniocerebral injuries, with epilepsy, severe infectious diseases, a number of cases of drug addiction, and when taking psychoactive substances.
The motor signs of catatonia, according to experts, are caused by the deficiency of gamma-aminobutyric acid( GABA).Also, many experts believe that the development of symptoms may be associated with blockade of dopamine.
Symptoms of Catatonia
Symptoms of catatonia can be very different. The disease can be manifested by a prolonged or transitory stupor,  arising after impulsive and uncontrolled behavior, silence or negativism.
arising after impulsive and uncontrolled behavior, silence or negativism.
Negativism can be active and passive. With active negativity, the patient does things different from the directions, with the passive one - he ignores the requests, and in the case of the paradoxical - he does the opposite of the request.
The main manifestations of catatonia are catatonic stupor and catatonic arousal.
Excitation phase
Excitation can take various forms:
- Pathetic form .Excitation( verbal or motor) is not expressed clearly. In the patient's conversation pathos is observed, echolalia can be present( the repetition of the phrases heard).The patient's mood is elevated( with signs of exaltation), laughter without reason is observed. As the exacerbation is often observed manifestations of gebefrenia( foolishness, childishness).The patient has no disturbances of consciousness, but impulsive actions are possible.
- The impulsive form of the .This form is characterized by a rather acute development of symptoms, the actions become active, rapid, often destructive and cruel, can be dangerous for others. The patient's speech is constructed from separate words and phrases, echolalia is observed. The patient can try to harm himself. At the peak of excitement, the so-called "dance of St. Witt" - chaotic movements of the choreiform nature can be observed.
- The mute form of the .Excitation of the patient is meaningless and does not have a specific orientation, aggressive behavior is observed, steady resistance. The patient can silently cause damage to himself and others.
Catatonic stupor
There are three types of stupor and all of them are characterized by slowness of movements, lack of speech, increased muscle tone.
The state of stupor can last even a few months, distinguish:
- Cataleptic stupor ( catalepsy, waxy flexibility).The patient freezes for a long time in one pose, even uncomfortable and
 requiring muscle tension, does not respond to sounds, but can react to speech in a whisper. The patient can spontaneously disengage and contact at night. With this form of stupor, delusions, onyroid disorders and hallucinations can occur.
requiring muscle tension, does not respond to sounds, but can react to speech in a whisper. The patient can spontaneously disengage and contact at night. With this form of stupor, delusions, onyroid disorders and hallucinations can occur. - The non-motivating stupor differs not only in motor retardation, but also in the resistance of the patient to attempts to change its position. Negativism is both active and passive.
- Stupor with numbness has the greatest severity. The patient can take and maintain the pose of the embryo for a long time. There can be a phenomenon of yaktation - monotonous swaying of the trunk.
Based on the presence or absence of mental disorders, catatonia is divided into three types: lucid, onyroid, and febrile.
Lucid form of violation
One of the species is lucid catatonia. With this pathology, the patient retains orientation in space and time, awareness of his own "I", as well as preserving memory for events, there is an increased muscle tension.
In lucid catatonia, patients do not show signs of delusional and obsessive ideas, hallucinations, seizures, obscuration of consciousness. Characteristic symptoms are involuntary excitation, negativistic stupor, stupor with numbness.
Oniroid catatonia
This form of catatonia is referred to as periodic schizophrenia. According to doctors, onyroid catatonia marks the "apogee" of a schizoaffective attack. However, sometimes this pathology is described to the context of intoxications and organic brain lesions.
Oniroid catatonia has a sudden beginning. Can reach its highest level within a few hours. The disease begins to manifest with an active increase in psychomotor agitation, the appearance of confusion. Quickly change the behavioral reactions of the patient, as well as his motor skills and facial expressions.
 At excitation the maniacal features that accompany plasticity, fun, naturalness of motor dysfunctions appear most, schizophasia appears( speech disruption.) The discrepancy between the behavior and experiences of the patient is characteristic. The patient, living in his own rich and vivid experiences, is in detachment from the world around him.
At excitation the maniacal features that accompany plasticity, fun, naturalness of motor dysfunctions appear most, schizophasia appears( speech disruption.) The discrepancy between the behavior and experiences of the patient is characteristic. The patient, living in his own rich and vivid experiences, is in detachment from the world around him.
In the perception of a patient, reality can be replaced by fictitious circumstances. In this case, the scenes and events occurring in the mind of the patient have a plot and a completed character. The patient perceives himself as the main hero of events occurring in his mind.
One-aireoid catatonia is a dream-like obscuration of consciousness( a waking dream), which is accompanied by fantastic experiences, confusion, rapid change of negative emotional experiences, rapid transition from random excitation to a state of catatonic stupor. The facial expression of the patient expresses all pathological sensations experienced by him, can be expressive and expressive.
After leaving the oniroid, the patient retains fantastic experiences, however, real events amnesize. The duration of this catatonic syndrome can range from several days to several weeks.
Febrile form of the disease
The febrile form of catatonia is characterized by different types of consciousness disorder, and is an acute psychotic disorder.
It is considered a symptom of schizophrenia, because it represents a whole group of diseases, different in nature, and which manifest themselves in acute disorders of the psyche.
It also occurs with affective disorders. The disease is extremely acute, it combines psychopathological and somatic disorders, which affect one another, and all in the aggregate can lead to a fatal outcome. Externally, catatonia febrile seizures are similar to attacks of onyroid, and are expressed in arousal or stupor. It is advisable to start therapy within the first hours after the onset of the disease.
Febrile catatonia appears on the background of a schizophrenic attack and is rapidly developing. A characteristic feature is hyperthermia. In some cases, hyperpyretic fever occurs, in other cases the temperature varies unevenly.
Together with a fever, there is a tachycardia, there may also be external changes: a skin of gray-earthy color, pointed features, sunken eyes, sweat on the forehead, a wandering look, white or brown plaque on the tongue, dry lips.
The patient's condition rapidly deteriorates, blood pressure becomes lower, the pulse increases, and breathing becomes more frequent. Lethal outcome is likely due to vascular insufficiency, which occurs against the background of cerebral edema.
This form of catatonia appears because of hereditary factors, due to the presence of certain genes. Provoke the development of pathology can abuse cannabis smoking, low social and economic standard of living, mental and social stress.
This catatonic syndrome requires hospitalization in a psychiatric hospital and electroconvulsive therapy.
Diagnostic criteria
Diagnosis is made by psychiatrists, based on anamnesis and objective examination.
The examination is performed when there is evidence of catatonia within two weeks. These signs are: stupor, excitement, fading in different poses, negativism, rigidity, automatic subordination, wax flexibility.
The main studies are:
- general( expanded) blood test;
- study of the functional activity of the kidneys;
- thyroid studies;
- urine analysis for the presence of narcotic substances;
- study of the level of creatine phosphokinase;
- blood test for glucose.
According to the results that were obtained during examination, it is possible to pass electrocardiography( ECG), computed tomography( CT), electroencephalography( EEG), magnetic resonance imaging( MRI), urine and blood samplings, blood analysis for autoantibody content. Sometimes a spinal puncture can be necessary.
During the diagnosis, attention is drawn to the presence of schizophrenia, depression, drug use( by prescription or independently), epilepsy, mania, other organic disorders.
Medical care
Therapy is performed in a psychiatric hospital. Patients often pose a threat to themselves and the people around them. In such circumstances, fix the patient and inject sedatives. Patients need quality care, supervision and verification of vital functions.
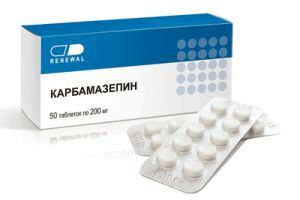 The main strategy for the treatment of catatonic syndromes is the administration of benzodiazepine series( lorazepam, diazepam), as well as electroconvulsive therapy.
The main strategy for the treatment of catatonic syndromes is the administration of benzodiazepine series( lorazepam, diazepam), as well as electroconvulsive therapy.
Normotimics( lithium, carbamazepine, valproic acid), NMDA receptor antagonists( Amantadine, Memantine) are also considered effective drugs. It is also recommended to prescribe dopamine agonists( bromocriptine) and muscle relaxants( dantrolene sodium).
In this disease the patient can not drink and eat for a long time, which causes exhaustion and dehydration. Due to a long stay in motion, thrombosis of the deep veins and pulmonary artery can develop. Also, the development of pulmonary embolism is possible.