Leukoencephalitis is a form of encephalitis of viral origin. With leukoencephalitis, the white matter of the brain is mainly affected. In addition, there are dystrophic changes in neurons.
Leukoencephalitis is a form of encephalitis of viral origin. With leukoencephalitis, the white matter of the brain is mainly affected. In addition, there are dystrophic changes in neurons.
Presumably the disease has an allergic-viral nature. At the moment, there are considered versions of the possible origin of the disease from viruses: measles, rabies, herpes virus type 3.
There are three main clinical and morphological forms of leukoencephalitis:
- subacute sclerosing Van-Bogart;
- the periaxial Schilder;
- acute hemorrhagic.
In this study, the brain affected by encephalitis gives the following results: there is atrophy of the gyri and widening of the furrows, areas of demyelination are found in all parts of the brain, mainly in white matter, but also in the gray matter of the cortex. There is a moderate expansion of the ventricles.


content
Aggravating factors
It is suggested that the Van-Bogart leucoenzinfalit is caused by the measles virus that was in thelatent state in brain neurons and activated in certain processes.
As a variant of multiple sclerosis, children are treated with periaxial encephalitis. There was a frequent occurrence of acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalitis after vaccination.
The pathogenesis of the disease is unclear, it is believed that the virus is a trigger in the autoimmune process.
Mechanism of development and manifestation of
The process is most often localized in the basal nuclei. As the disease develops, the associative links between the cerebral lobes
Leukoencephalitis virus
are affected, thereby determining the main role of mental disorders in the clinical picture.
The most common disease is found in childhood, but there have been cases of manifestation of the disease in adults. Usually it begins after a previous infection or vaccination in people with congenital immune disorders or neurological abnormalities.
The first characteristic signs are memory impairment, cortical functions, lethargy, dementia. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by the development of schizophrenic syndrome. There are motor disorders, epileptiform seizures.
Leukoencephalitis progresses rapidly, in an average of 1.5-2 years. At the onset of a lethal outcome, breathing disorders, epileptic status are characteristic.
The most common forms are the leucoencephalitis of Schilder and Van Bogart. The syndrome of Van Bogart is accompanied by extrapyramidal symptoms, epileptiform seizures, dementia.
Schilder's disease is characterized by disorders of the motor system, vision or retrobulbar nephritis.
 Symptoms appear suddenly, they are characterized by steady progress. At first, the disease is accompanied by mental disorders. In young children, this manifests itself in the form of irritability, apathy, aggression, lethargy.
Symptoms appear suddenly, they are characterized by steady progress. At first, the disease is accompanied by mental disorders. In young children, this manifests itself in the form of irritability, apathy, aggression, lethargy.
Gradually begin to disappear the logic of thinking, skills of neatness, the vocabulary is reduced. Against this background, neurological symptoms begin to develop for several months.
It may include hallucinations, increased muscle tone, agnosia, apraxia, polymorphic hyperkinesia. After the violations of the motor system are joined: paresis and paralysis, unstable gait, impaired coordination.
A constant symptom is convulsive syndrome, after trophic and vegetative disorders join.
Symptomatic of every form of the disease
In case of Van-Boggart disease, lesions of the spinal cord and brain stem are more frequent than in other forms. This form of leukoencephalitis is characterized by early manifestations of extrapyramidal disorders, pyramidal symptoms are attached at a late stage. With this form of the disease, epileptic seizures are rare.
In Schilder's leukoencephalitis, in contrast to other clinical forms and multiple sclerosis, early dystrophy of axons is observed. With this form pyramidal symptoms prevail, it is accompanied by frequent epileptic seizures.
With acute hemorrhagic encephalitis, the onset was acute, with a lightening increase in symptoms. They are ill at 20-40 years with a duration of up to 2 weeks. It is accompanied by a headache, a violation of consciousness, rigidity of neck muscles, coma.
This form of leukoencephalitis is characterized by seizures and disorders of the motor apparatus, paralysis. In very rare cases, a subacute or chronic form may develop.
Approach to the diagnosis of
At an early stage of development, the disease is easily confused with schizophrenia, hysteria, neurasthenia. Next, a differential diagnosis with 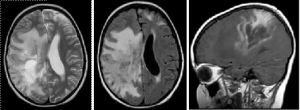 brain tumors takes place.
brain tumors takes place.
The diffuse nature of the lesion, presence or absence of increased intracranial pressure, signs of displacement of the median brain structures on the EEG are taken into account. To confirm the diagnosis, CT and immunological studies are performed.
Laboratory studies have moderate pinocytosis in the cerebrospinal fluid, increasing levels of gamma globulin and protein. Changes in the Lange reaction are observed. The EEG records the complexes of Rademekker. The most informative are CT and MRI.
The initial stages of acute sclerosing encephalitis are similar to schizophrenia. At this time, it is difficult to isolate it, but there are a number of symptoms that still make it possible to exclude schizophrenia: memory loss, speech disorders, rapid exhaustion in intellectual activity.
At laboratory data the raised maintenance of fiber and gamma-globulin is observed.
For the therapy of
 Corticosteroid medications are used. Prednisolone 1-1.5 mg / kg body weight, for 2-3 weeks gradually lowering the dose. If therapy gives a positive result, I continue it in maintenance doses. Increase in episodes of exacerbation of the disease.
Corticosteroid medications are used. Prednisolone 1-1.5 mg / kg body weight, for 2-3 weeks gradually lowering the dose. If therapy gives a positive result, I continue it in maintenance doses. Increase in episodes of exacerbation of the disease.
In parallel, antibiotics are prescribed: Penicillin, Erythromycin, Tetracycline.
Increase the intake of potassium salts, while decreasing the amount of sodium salts. If necessary, prescribe vitamins, as well as psychotropic drugs.
Prognosis and mortality
The disease progresses steadily, always leading to death. The duration of the disease is from 0.5 to 3 years.
In some cases, it is possible longer, while the disease proceeds chronically, remissions are observed periodically. During the remission, the symptoms of the disease may be completely absent.
The real clinical case
Patient Vadik, 10 years old he entered the hospital with complaints about poor schooling and poor progress. Heredity: phobia in the mother, father is healthy. 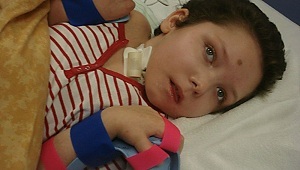
Father's sister committed suicide. In the family of the father there is a mentally retarded relative. Born from the third pregnancy, the first two ended with labor before the term, the children did not survive.
The third pregnancy was fainting, born during. The patient developed without deviations, visited the kindergarten, often sick. In 10 years I began to suffer from bedwetting. Shortly thereafter, unfounded fears arose, progress deteriorated. He began to lag behind in development, grimacing, became very inconsiderate.
Survey results: the skin is dry, reddish, the turgor is lowered, it feeds satisfactorily. There is an enhanced pigmentation on the trunk. Periodically diarrhea, cholesterol 303 mg%, protein in liquor 0.67.A positive result of Nonne-Apelt's reaction.
Mental state of the child: normally supports the conversation, a rich set of words, after a while starts to wave his arms, twirl his hair, especially to bend his finger. Quickly gets tired, does not focus, there are headaches.
Conclusion of the endocrinologist: There are no signs of dysfunction of the adrenal cortex.
The conclusion of a neurosurgeon: bilateral Kerning syndrome, the limitation of the gaze upward, a tumor in the frontal lobe is possible.
 Results of pneumoencephalography: the arrangement of the ventricles is symmetrical, the absence of a tumor in the cerebral hemispheres. Internal hydrocephalus with changes in the meninges.
Results of pneumoencephalography: the arrangement of the ventricles is symmetrical, the absence of a tumor in the cerebral hemispheres. Internal hydrocephalus with changes in the meninges.
Treatment with Penicillin and Biyohinol. After this, the boy was discharged with a diagnosis: an unclear process in the frontal lobes.
After a couple of months I re-entered the treatment.
On admission: disorder of eye convergence, flattening of left nasolabial fold. Decreased reflexes of the cremaster and abdominal. The presence of protein in the liquor 1.32.
At inspection: sharp infringements of mentality, fast intellectual fatigue. With disabilities, but retained the skills of reading and writing. There is a security on the date with the parents. The diagnosis is leukoencephalitis.
In the future, the disease progresses from the onset of the disease until the appearance of epileptic seizures after 24 months. After the hospitalization a year later, he stopped getting up. Last months completely helpless, plaintively wept. He died in the fall of heart activity.