 Meningoencephalitis is an infectious disease that is a complication of meningitis or encephalitis. It is characterized by inflammation in the membranes of the brain and brain substance.
Meningoencephalitis is an infectious disease that is a complication of meningitis or encephalitis. It is characterized by inflammation in the membranes of the brain and brain substance.
There are times when this disease affects the tissues of the spinal cord, which can cause leg paralysis.
According to the frequency of cases of meningitis, it is meningoencephalitis that ranks first and is accompanied by secondary infectious and viral diseases. As a rule, the course of the disease occurs in acute or severe form.
Contents
- Provoking factors
- Variation factors
- Meningoencephalitis in newborns
- Features of the clinical picture
- Diagnosis
- Assisting the patient
- Consequences and prognosis
Provoking factors
The following factors can provoke the development of this disease:
- encephalitis of the primary and secondary group;
- process of destruction of myelin - a white matter of the CNS or peripheral nervous system;
- mumps acute meningoencephalitis;
- inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
Varieties of defeat
Meningoencephalitis has many species that differ in character, provoking inflammation of pathogens:
- amoebae - pathogens live in water or moist soil, this type of disease is diagnosed infrequently, and its practically
 can not be cured;
can not be cured; - brutzelesny - cause bacteria, the disease takes a long time with the appearance of paresis, paralysis, mental disorders;
- vaccine or vaccine is an infectious disease, a complication of which occurs after the initial vaccination. It flows in an acute form, accompanied by convulsions and fainting;
- hemorrhagic - a reactive form of an infectious-allergic disease, provoked by the influenza virus;
- herpetic - pathology is caused by herpes viruses;
- gummy - is caused by the causative agent of syphilis;
- ornithous - develops during ornithosis or as its consequence;
- mumps - the causative agent is the mumps epidemic virus;
- anthrax - occurs against the background of anthrax;
- rheumatic - is provoked by a thrombosis of vessels of a brain;
- typhoid-typhoid - is characterized by a lesion of the gray matter of the brain;
- toxoplasmosis - bacteria affect the embryo in the womb;
- tubercular - occurs as a complication of tuberculosis;
- cytomegal - occurs as a complication of cytomegaly.
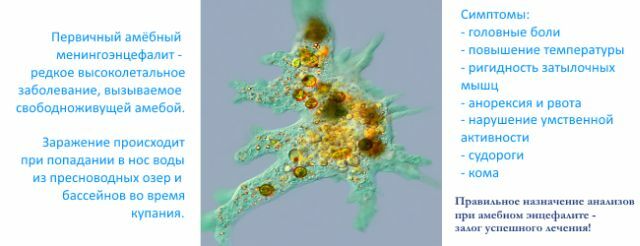
Meningoencephalitis in newborns
 The cause of meningoencephalitis in a newborn child is most often viral. However, there are cases of intrauterine lesion of the embryo.
The cause of meningoencephalitis in a newborn child is most often viral. However, there are cases of intrauterine lesion of the embryo.
This is due to the fact that during the first months of pregnancy the woman was ill with any virus disease, for example, rubella, chicken pox, measles, mumps, glandular fever.
In such cases, as a rule, the child is born dead. If he still survives, later he has symptoms of brain damage. Among them: hydrocephalus;hyperkinesis;focal manifestations.
Meningoencephalitis in infants is accompanied by such common symptoms:
- high fever;
- severe general condition;
- vomiting and diarrhea;
- breast failure;
- prostration of different duration;
- involuntary twitching of the eyes;
- strabismus;
- cyanosis and tachycardia - with damage to the cardiovascular system.
In the diagnosis, rigidity and the Kernig symptom are difficult to determine. In the fluid of the spinal cord, the positive reaction of Pandi is revealed.
Lymphocytic pleocytosis is moderate. Peripheral blood does not show any pathologies. The rate of erythrocyte sedimentation is weak  is accelerated.
is accelerated.
Treatment will consist in the use of such drugs: broad-spectrum antibiotics, gamma globulin, vitamin complexes in large doses. With prolonged vomiting intravenously inject saline and dextrose.
The prognosis for children with meningoencephalitis is very doubtful. One third of children die with this diagnosis. Many surviving children show signs of brain damage.
In the risk zone, children under the age of half a year, after six months, the probability of the disease decreases.
The course of the disease can be different. It can take such forms:
- Lightning fast - manifestations develop very quickly, the condition deteriorates rapidly, which leads to death.
- Acute - symptomatic occurs quickly and contributes to the deterioration of the general condition of the patient.
- Subacute - the disease affects the human body slowly and manifests less pronounced.
- Chronic - the nature of the disease is sluggish, the symptomatology is not expressed, it can become aggravated and stop.
Features of the clinical picture
Symptoms of meningoencephalitis are the consequences of a general inflammatory process. Among them:
- high body temperature( sometimes rises to forty degrees);
- headache;
- nausea with vomiting;
- unclear consciousness;
- stiffness of movements;
- pale skin;
- area of nasolabial folds turns blue;
- shortness of breath;
- increased heart rate;
- arterial pressure increased;
- photophobia;
- convulsions;
- overall hypersensitivity.
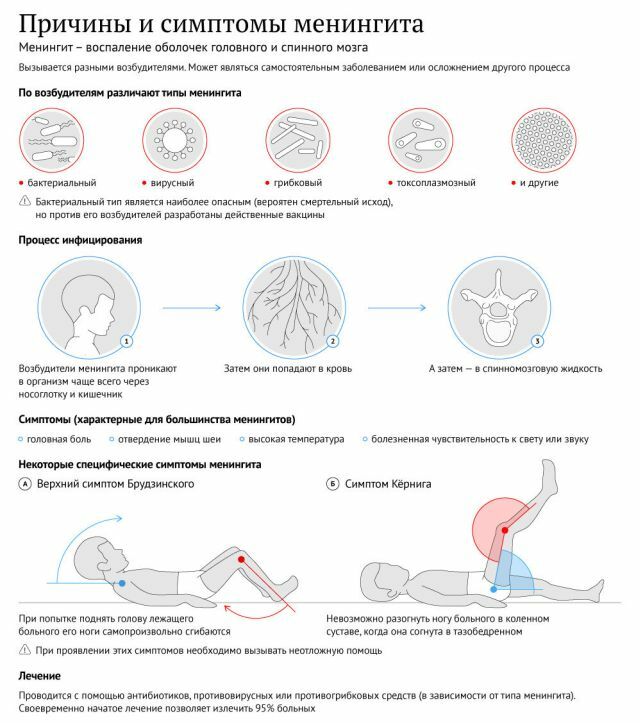
Meningeal symptoms are supplemented with manifestations of brain damage, among which:
- coordination disorder;
- asymmetry of tendon reflexes;
- speech disorders;
- mental disorders.
Diagnosis of
The first and most basic method of diagnosing this disease is the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in the laboratory. It is carried out with the help of a puncture.
If a person is sick, the analysis will show that the cerebrospinal fluid is characterized by a muddy consistency. This is due to the cellular impurity. Also in it will be found an increased level of protein, lowering of glucose concentration and increased blood pressure.
Along with this, the following methods are used:
- polymerase chain reaction - to detect bacterial antigens;
- blood test and smears from the oral and nasal cavities - to clarify the diagnosis;
- chest X-ray;
- CT and MRI - to exclude a purulent process in the brain.
Assisting the patient
 Treatment of meningoencephalitis is carried out in the infectious ward of the hospital. The purpose of therapy is to eliminate the causes of illness, symptoms and prevent the development of complications. If all measures are carried out on time, it will promote a faster recovery and a positive outcome of the disease.
Treatment of meningoencephalitis is carried out in the infectious ward of the hospital. The purpose of therapy is to eliminate the causes of illness, symptoms and prevent the development of complications. If all measures are carried out on time, it will promote a faster recovery and a positive outcome of the disease.
After carrying out diagnostic methods and determining the cause of the disease, the patient is sent to the infectious disease department where he is provided with the necessary conditions for rapid and complete therapy.
During treatment, preparations of various groups are used. Among them:
- antioxidants;
- neuroprotection;
- means for improving blood microcirculation;
- multivitamins of groups B and C;
- sedatives;
- anticonvulsants;
- anticholinesterase drugs;
- for the prevention of herpetic complications is prescribed Acyclovir;
- diuretics - to relieve cerebral edema.
At the end of the treatment, physiotherapy and reflexotherapy procedures are used to prevent complications.
Also, a special balanced diet will be prescribed by the doctor, which includes all the necessary micronutrients.
People who have suffered this serious illness are registered in the dispensary and regularly visit a neurologist. After treatment of viral meningoencephalitis, a person must necessarily undergo a sanatorium-and-spa treatment. Such therapy helps to strengthen the body's immune system. The rehabilitation period lasts a very long time.
Meningoencephalitis affects both adults and children, and very often it is very difficult to determine it by first signs. In case of occurrence of the basic displays of illness it is necessary to address to the doctor as soon as possible.
Consequences and prognosis
Meningoencephalitis is a very dangerous disease in which a high mortality rate is observed. A huge role in this case is played by timely and adequate treatment. Severe consequences are as follows:
- In the case of a viral form of the disease, if the patient's immunity is weakened or the diagnosis and therapy were carried out too late,
 causes paresis, paralysis, epileptic seizures of .
causes paresis, paralysis, epileptic seizures of . - Another very dangerous consequence is the formation of postnecrotic cysts .They provoke in children a delay in mental development and hydrocephalus.
- If a child falls ill at an early age, very often has an impact on the development of mental abilities and the state of mind .
Very serious consequences of this disease will be in newborns with a predisposition to the formation of generalized forms of meningoencephalitis. We can say that the further picture of the patient's life will depend on the degree of CNS damage.
Prevention of this disease consists, first of all, in carrying out procedures for vaccination against hemophilic rods, meningococci and pneumococci. Vaccination is carried out in early childhood.
To prevent disease in close relatives who have directly contacted the patient, chemoprophylaxis with antibacterial drugs is prescribed.