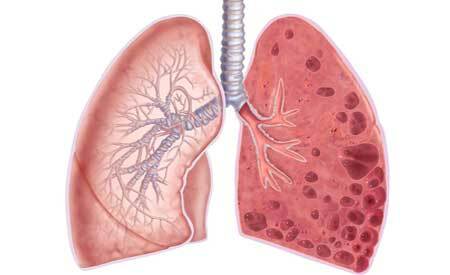
Pneumonia in adults and children( inflammation of the lungs) ranks first among inflammatory diseases of man. It is an infectious pathology.
To the section of pneumonia, a group of bacterial and viral diseases of different symptomatic, but similar in the localization of inflammatory processes developing in the tissue structure of the lungs, is classified. Among similar pathologies, occupies a leading place in the lethality.
Contents
- 1 Forms and features of pneumonia in adults
- 2 Causes and mechanism of onset
- 3 Symptoms of pneumonia in adults
- 4 First signs of pneumonia in adults
- 5 Pneumonia without temperature and symptoms
- 6 Complication of pneumonia in an adult
- 7 Diagnosis examination
- 8 Treatment of pneumonia in adults
- 9 Pneumonia:ICD 10
Forms and features of pneumonia in adults
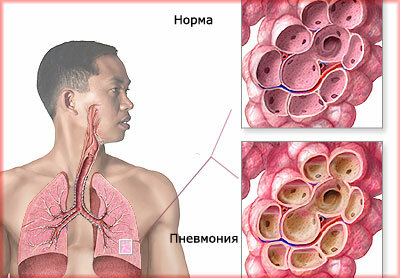
The characteristics of inflammatory reactions in the pulmonary system are due to various forms of their manifestationand severity of clinical signs.
Acute inflammation of is possibly an independent manifestation caused by infection, or due to complications of background pathologies. The inflammatory reaction originates in the bronchial system, spreading gradually into the structure of the lung tissue, affecting the vessels.
The seasonality of morbidity is characteristic - during the progression of cold infections.
The form of chronic pneumonia is due to a progressively developing inflammatory process. The constant, gradual development of inflammatory reactions goes beyond the focal borders of the lesion, spreading to the large tissue area of the bronchi and lung tissue.
The cause of the development of the chronic course of the disease, may serve not completely resolved the foci of inflammation, left after acute inflammatory processes in the organ.
The chronic process in childhood is usually born. This form of the disease is rare.
The form of croupous manifestation of pneumonia in adults is characterized by acute inflammation that affects the lung completely, or a large part of it. Destructive processes in its tissues occur cyclically, in stages expressed:
- Increased blood flow to the capillaries, followed by its deceleration for 12 hours or two days.
- Red hepatization( compaction of the lung parenchyma) caused by coagulation of red blood cells( diapedesis) and filling them with fibrin luminal alveoli, depriving them of airiness. The duration of the process is up to three days.
- Gray hepatization, manifested by granularity and gray-green color of the lung, due to accumulation in the alveoli of exudate, consisting of their epithelium and leukocyte cells. The duration of the process is up to a week.
- The last stage is characterized by resorption of fibrin and leukocytes in the lumens of the alveoli and partial withdrawal of them with sputum during expectoration. With time, airiness returns to the alveoli, but the swelling of the alveolar septa and the density of the lung tissue remain for a long time.
Focal inflammation of the lungs combines several forms of the disease. The connecting link of all forms is localization of inflammation in a separate pulmonary site and not spreading it into other segments of the organ. Sometimes there is a fusion of foci of inflammation( draining pneumonia).
Causes and mechanism of the onset of
The cause of the development of inflammatory reactions in the pulmonary structure most often become the most diverse bacterial and viral pathogens.
- Representatives of bacterial infection - pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci, Richard Preyfer's wand( hemophilia).
- Viruses of the family of paramyxoviruses, picornaviruses, adenoviruses and influenza.
- Vnekksonomicheskie( yeast) fungal parasites, moldy mushrooms aspergeliusy, mushrooms ascomycetes( pneumocysts).
- Chlamydia viruses, mycoplasma and Legionella bacteria, intracellular toxoplasma parasites.
There is a certain category among the adult population that constitutes a risk group for the development of the disease. This fact is due to:
- the presence of chronic pulmonary pathologies;
- disorders in the cardiovascular system;
- with chronic immunodeficiencies, provoked by frequent bacterial and viral infections;
- by neuroses and depressions;
- by endocrine pathologies;
- malignant neoplasms;
- as a result of aspiration symptoms, surgical interventions( lung, thorax, peritoneum);
- long stay in one position( lying patients);
- addiction, alcoholism and nicotine addiction;
- age factor( after 60 years).
Inflammatory reactions in the parenchyma of the body can occur, either alone or as a consequence of complications of other diseases. The penetration of infectious agents into the lungs takes place in various ways:
1) Microaspiration of is the main pathway of infection. Even in the healthiest people in the oropharynx there are many microorganisms that do not harm a person. Sometimes they include the causative agents of the disease.
Very many, during sleep, a small dose of the secretion of the oropharynx enters the respiratory tract, carrying an infection with them. If the protective functions of the body are working at the proper level, they easily derive a provocative secret.
Otherwise, the sterility of the lung tissue is disrupted and inflammation develops - pneumonia in adults or children.
2) Upon inhalation of , a high concentration of microorganisms with air. This way of infection is typical for the development of hospital pneumonia, with prolonged stay in the department of the hospital, where patients with pneumonia are treated.
3) Hematogenous by - spread of infection from another focus of infection with blood flow. A common cause of infection among drug users and patients suffering from infectious inflammatory processes in the inner heart( endocarditis).
4) Infection of from a number of lying organs, with purulent-inflammatory processes in the liver or a similar pathology of the pericardium, or as a result of penetrating injury.
As a result of penetration of the pathogen into the pulmonary system, the alveolar membrane is damaged and their functions are disrupted, resulting in insufficient gas exchange between air and blood, disruption of the formation of a surfactant, and a decrease in immune functions.
Simultaneously, in the inflamed zone there is a disturbance of blood circulation and malfunctions in the functions of bronchial tissues, which ensure the secretion and excretion of mucus from the lungs. It is these changes that contribute to the manifestation of various symptoms of pneumonia in an adult.
Symptoms of pneumonia in adults

The manifestation of symptoms of pneumonia in adults depends on a variety of causes - the conditions for the development of the disease, the type of pathogen, the course and prevalence of the inflammatory process. Characterized by typical( pulmonary) and atypical( extrapulmonary symptoms.) Common symptoms are manifested:
- Cough with abundant, wet sputum. In elderly patients, it can be dry.
- Moderate dyspnoea at physical exertion.
- Discomfort and pain in the place of localization of the inflammatory reaction.
- Signs of diaphragmatic irritation, abdominal pain and rapid breathing( if the inflammation process is in the lower part of the lung tissue).
- Strengthening of pain symptoms during coughing, shortness of breath and complete breathing or movement( effect of fluid effusion into the pleural cavity).
- Disturbance of hemodynamic functions;
- Symptoms of cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
Like most infectious pathologies, the disease can be accompanied by an intoxication syndrome, manifested by extrapulmonary symptoms:
- hyperthermia;
- deterioration of the general condition;
- rapid fatigue and weakness;
- headache;
- joint and muscle discomfort.
The first signs of pneumonia in adults
The initial signs of the disease are not easy to recognize. They may not be at all, rarely or mildly expressed. It all depends on the type of pathogen. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to changes occurring in the body.
The first signs can be manifested:
- weakness and fast fatigue;
- with a slight increase in temperature;
- manifestation of dyspnea( lack of air);
- with a prolonged cough( for several days).
Not seen the disease in time, threatens its transition to a severe form with extensive symptoms.
Read more: signs of pneumonia in adults
Pneumonia without temperature and symptoms

Possible manifestation of pneumonia in adults without signs of temperature. Symptoms are manifested by weakness, lethargy, general malaise, frequent headaches, lack of appetite and shortness of breath.
Cough manifests itself in different ways. At the onset of the disease, it can be dry and obtrusive, subsequently with sputum discharge, which is a favorable sign.
Sometimes cough is minor, but painful with signs of increasing shortness of breath. Such signs indicate the accumulation of sputum in the bronchi system and the impossibility of their withdrawal, which threatens the development of obstruction in the airways.
An unfavorable factor is the increase in dyspnea - evidence of stagnation of blood in the lungs or the development of intoxication syndrome. Such a state is dangerous due to the stagnation of fluid leaking from the circulatory system of the organ in its tissue, which provokes swelling of the respiratory organ.
Very often there is a course of pneumonia in adults without symptoms or with a minimal amount of them, which in itself is dangerous. This pathology is called hypostatic, caused by stagnant processes of blood in the lungs( in immobile patients).
Due to the impregnation of blood through the vascular walls, edema of bronchioles and alveoli is formed, their tissue is loosened, which allows easy penetration into the organ by pathogens of the disease.
Symptoms may masquerade as signs of underlying disease, which has caused a prolonged immobility of the patient.
In addition, the manifestation of a cough may be minor, but painful. What should be paid special attention, since with this development of the disease, development of complications in the form of lung abscess or purulent pleurisy is not ruled out.
Complication of pneumonia in an adult
The development of complications of pneumonia in adults can be not only after the disease itself, but also at the time of its acute form. Manifesting both pulmonary and extrapulmonary pathologies:
- Destruction of pulmonary tissues caused by the formation of different sizes of cavities that have the property of being inflated.
- Disorders of bronchial patency caused by edema( obstruction).
- Exudative inflammation of the pleura and serosa surrounding the lung, which can trigger the development of cancer pathology.
- The defeat of all tissues and organs, due to violations of cardiac functions.
- Signs of myocarditis, pericarditis and endocarditis.
- Inflammation of the spinal cord and brain.
- Septic shock - a number of pathological disorders in the respiratory, nervous, cardiac and vascular system.
- Cardiogenic edema and sepsis, the spread of infection by the bloodstream.
If treatment is not timely and adequate, such complications of can lead to the death of .
Diagnostic examination
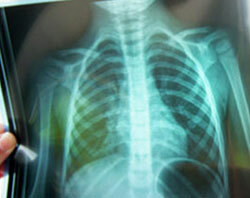 It is impossible to diagnose pneumonia due to symptoms alone, since they are similar to many signs of diseases of the respiratory system. To the diagnosis are connected:
It is impossible to diagnose pneumonia due to symptoms alone, since they are similar to many signs of diseases of the respiratory system. To the diagnosis are connected:
- data of general and biochemical studies of blood and sputum;
- X-ray examination of existing pathological changes in pulmonary tissues and the location of their localization;
- fibrobronchoscopy and CT examination of the thorax;
- revealing the pathogen by the method of blood culture.
In complicated cases, a pulmonologist is involved in the examination.
Treatment of pneumonia in adults
The main principle of therapy is a complex treatment aimed at arresting inflammatory reactions in the lung tissues.
Medical treatment
- The choice of antibiotics for pneumonia in adults is due to the type of bacterial pathogen. The most effective are Levofloxacin, Sumamed, Avelox, Cefix or Amritsiklav. Depending on the course of the disease, it is possible to designate their combinations. In severe cases, combined with the administration of drugs, Tenavik, or Leflocin.
- Expectorants are prescribed for signs of wet cough and a difficult output of viscous sputum.
- The severe course of the process is stopped by detoxification and glucocorticosteroid agents aimed at eliminating toxic shock.
- At a critical temperature, antipyretic drugs are used.
- Severe shortness of breath and a pronounced syndrome of oxygen starvation are stopped by cardiovascular drugs.
- Multivitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
The dosage of medications and the course of treatment is determined by the doctor purely individually. To facilitate breathing, patients are prescribed a series of physiotherapy courses:
- oxygen therapy;
- artificial respiration therapy - IVL;
- various inhalation techniques
Surgery for inflammation of lung tissue is used in complicated processes caused by purulent accumulation in the organ.
The basis for the prevention of pneumonia in adults is the elimination of hypothermia and the systematic hardening of the body. Other factors are also important:
- timely treatment of infectious diseases;
- special breathing exercises;
- vaccination against influenza and streptococcal vaccine( for the elderly-65 years);
- minimizes inhalation of harmful substances and dust.
Self-medication for this disease is not allowed , because it complicates and extends the healing process, can lead to the death of .
Pneumonia: ICD code 10
The international classification of diseases of the 10th revision of pneumonia is:
Class X. Diseases of the respiratory system
J10-J18 - Flu and pneumonia
J18 - Pneumonia without specifying causative agent
- J18.0 - Bronchopneumonia unspecified
- J18.1 - Shared pneumonia, unspecified
- J18.2 - hypostatic pneumonia, unspecified
- J18.8 - Other pneumonia, causative agent not specified
- J18.9 - Pneumonia, unspecified