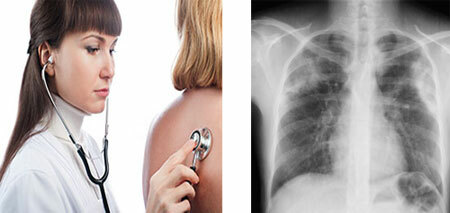
Tuberculosis is the infectious process, the beginning of which is provoked by various types of mycobacteria. If the disease is detected in the initial stage of development, the chances for successful treatment are much higher than in the diagnosis of advanced pathology. The most commonly affected lung tissue, but the disease is susceptible to other organs.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is extremely resistant to various environmental factors and can be in soil or water for a long time, which explains the wide spread of the disease between people.
Contents
- 1 Ways of contracting tuberculosis
- 2 First signs and symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis, photos
- 2.1 Symptoms of other forms of tuberculosis
- 3 How to recognize tuberculosis?
Ways of contracting tuberculosis
In most cases, tuberculosis infection is provoked by Koch's wand. There are several ways of transmitting the disease:
- Through the air - when talking to a sick person or carrier, while communicating and inhaling microparticles of saliva secreted by coughing or sneezing;
- Through the digestive tract - when a person consumes food infected with mycobacteria. This type of transmission of tuberculosis is extremely rare;
- Placental way - from a sick mother to a fetus or during a child's passage through the birth canal.
When mycobacteria of tuberculosis are infected by airborne droplets, the pulmonary form of tuberculosis develops, but if Koch's rod was transmitted to a person in some other way, tuberculosis of other organs most likely develops, in particular:
- Skin;
- Organs view;
- Musculoskeletal System;
- of the CNS or meninges;
- Organs of digestion;
- Organs of the urinary system.
First signs and symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis, photo

photo 1
Symptoms of tuberculosis in adults differ slightly from the clinic of the disease in pediatric practice. At an early stage, there are no clinical signs of the disease for a long time, so it is important for the patient to pay attention to his health and seek medical help at the slightest symptoms of a malaise.
Cautioning and becoming a reason for going to the clinic should have the following symptoms:
- Weakness and lethargy;
- Rapid fatigue;
- Constant causeless dizziness;
- Increased sweating, especially during night sleep;
- Pale skin of the face against the background of pronounced cheeks blush;
- Impairment of appetite, rapid weight loss;
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile markers( no higher than 37.5) in the absence of other signs of viral infection.
Often listed signs are early symptoms of tuberculosis, so the patient should consult a therapist for an examination and a comprehensive diagnosis( see photo).

Photo of symptoms of tuberculosis
As the disease spreads and more lung damage, other symptoms of tuberculosis are added:
- Appearance of chronic cough, dry or with productive sputum;
- Shortness of breath, which first appears during physical exertion, and as the pathology progresses - at rest;
- Various wheezing in the lungs, which are detected by the doctor during auscultation of the patient;
- Subfebrile condition( increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees against the background of relative health);
- Rapid weight loss and lack of appetite, while diseases of the digestive tract are not detected;
- Discomfort and pain in the chest during a deep breath - this symptom of tuberculosis is present if the pathological process involves pleura.
Special attention, when suspected of tuberculosis, refers to the nature of cough and the presence of various impurities( pus, blood) in the sputum. One of the symptoms of tuberculosis at an early stage is the appearance of a cough.
With the development of the inflammatory process in the pulmonary tissue, the respiratory organs can not function fully, as a result of which the patient feels a lump in the chest and constantly tries to squeeze it.
With frequent coughing there is a tension of the diaphragm and pleural sheets, which provokes the appearance of new coughing attacks and involvement of these organs in the pathological process.

Pay attention to discharge with cough
With pulmonary tuberculosis, the patient gets sputum, often with an admixture of blood and pus. In this biological material there is a huge amount of mycobacterium tuberculosis, so to confirm the correct diagnosis, patients are assigned bacteriological analysis of sputum.
There are several stages of the pulmonary form of tuberculosis:
The stage of primary infection of - the pathological process develops in the place directly infected by the infectious agent. Most often in this stage, tuberculosis of lymph nodes develops, the first signs and symptoms appear as the disease progresses and the infection spreads to nearby organs.
Stage of latent infection - with weakened immunity of the patient, mycobacteria from the primary focus of infection with blood or lymph flow spread to other organs and tissues, forming new foci of the disease.
The stage of relapse of the adult type - the formed tuberculosis foci affect the internal organs, in particular the lung tissue. If the cavity of the formed infiltrate breaks into the respiratory tract, then the patient becomes contagious to others and then talk about the open form of tuberculosis.
Symptoms of other forms of tuberculosis
Depending on the site of the localization of the pathological process, the symptoms of other forms of tuberculosis are:
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fever, spastic pains in the abdomen and blood stench in feces - when foci of infection are formed in the organs of the digestive canal;
- Headaches, dizziness, vomiting of the central genesis( irritation of the vomiting center in the brain), rigidity of the muscles, as a result of which normal human body movements are disrupted - in the localization of foci of tuberculosis in the central nervous system;
- Pain in the joints, back, stiffness in motion - bone tuberculosis;
- Cystitis, pain when urinating, res - tuberculosis of urinary organs;
- The formation of seals on the skin surface, which subsequently breaks out and pus is released from them - skin tuberculosis.
These clinical symptoms can be signs of other serious diseases, which can only be diagnosed in a clinic.
How to recognize tuberculosis?
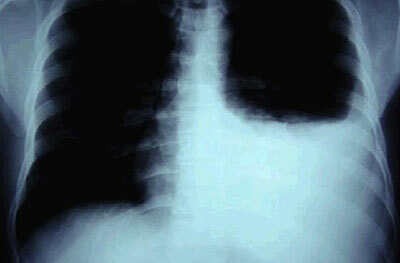
Diagnosis of tuberculosis, photo of a photo of a lung patient
All people are shown for diagnostic purposes once a year to undergo a diagnostic examination - fluorography. FG is an x-ray of the chest, on which blackouts are clearly visible if the patient suffers from a pulmonary form of tuberculosis.
For children, the Mantoux diagnostic test is performed annually, the indices of which allow one to judge the presence of immunity to tuberculosis. The child intradermally injected with 0.1 ml of tuberculin - an incomplete antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis. On day 3 after the test, the diameter of the papule is evaluated.
Normally, the diameter of the papule should not exceed 5 mm, if it is larger or does not appear after the sample, the patient should be shown to the doctor and additional diagnostic methods should be performed.
Bacterial sputum culture allows detecting the presence of mycobacteria or atypical cells in secretions, this study is prescribed for patients with suspected tuberculosis.
To diagnose non-pulmonary forms of tuberculosis it is possible by means of additional methods of research - MRI, CT.