Considering the question: "left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart, what is it and how can I treat it?" I want to note immediately that hypertrophy is a manifestation of a disease, not a separate pathology.
Most often this is a symptom of a cardiovascular system, it is detected in all age groups, including young and children, with a mortality rate of up to 4% of all cases. People with hypertrophy of the ventricle have stable hypertension.
Contents of
- 1 What is it?
- 2 Signs and symptoms of left ventricular hypertrophy
- 3 Why is left ventricular hypertrophy dangerous?
- 3.1 Diagnosis
- 4 Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart
What is it?
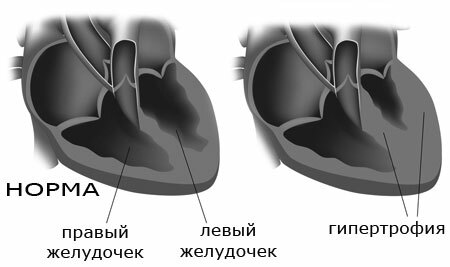
Hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart - this thickening of the wall of this department compared with the norm. The volume of the internal space remains unchanged, and the thickness of the muscle layer increases toward the outside. When hypertrophy is often undergoing changes and the septum between the ventricles.
The wall loses its elasticity, and the thickening is even or present only in some of its areas. Often the myocardium widens unevenly when the heart valves - aortic and mitral valves - are broken.
Thickening can also affect only the upper part of the myocardium( apical hypertrophy), be symmetrical or circular.
The causes of hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart are two groups of factors:
- Physiological, associated with excessive loads in athletes and people whose work is associated with heavy physical labor.
- Pathological, among them congenital disorders( poor outflow of blood from the ventricle, irregular structure of partitions and walls) and acquired( obesity or overweight, inactivity, bad habits, illnesses).
Of diseases of myocardial thickening is most often provoked:
- hypertensive disease, in which the left ventricle contracts with great force to push blood;
- stenosis of the aortic valve prevents normal blood flow, which also serves as a load on the myocardium;
- atherosclerosis of the aorta;
- pulmonary edema;
- heart failure;
- glomerulonephritis;
- myocardial infarction.
An important factor is the influence of heredity - the risk of hypertrophy is increased if this problem is present in the family history of the disease.
Signs and symptoms of left ventricular hypertrophy

When hypertrophy of the left ventricular wall symptoms may not be for a long time, and the person does not feel any pain or discomfort. This is due to the fact that in the first stages the enlarging walls are still quite elastic and are coping well with the task of pumping blood. In this case, the thickening can be detected by chance during the passage of the ECG.However, the symptomatology may appear at the first stages of the development of the problem.
Stenocardia is a characteristic symptom of hypertrophy of the walls of the left ventricle. It arises from the constant contraction of blood vessels that deliver nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle.
Angina is manifested by pain in the chest, heart area and shortness of breath - these are the two most important features of it. The pain usually constricting, can give in the left arm or shoulder, under the collarbone. Attacks of angina pectoris initially last about 5 minutes, and as the walls of the ventricle thickens, their duration increases. Often, they can be provoked by physical activity, overeating.
Dyspnea often accompanies pain and appears due to the fact that the contractile activity of the heart is impaired, which is facilitated by the development of a deficiency of the left atrium. At later stages, it occurs not only under loads, but also at rest.
Other symptoms of hypertrophies are as follows:
- dizziness;
- rapid fatigue, weakness;
- increased pressure;
- poor sleep;
- arrhythmia;
- heart fading;
- headaches;
- syncope.
All these manifestations serve as a good reason to go to a cardiologist and undergo an electrocardiographic examination.
Why is left ventricular hypertrophy dangerous?
Hypertrophy of the walls of the left ventricle is dangerous because it can provoke a heart attack or stroke, and in the worst case - sudden cardiac arrest and death( about 4% of all patients).
The risk group includes people who are overweight, smokers and alcohol abusers.
A great danger is also the situation when an untrained person with a sedentary lifestyle puts himself under intense physical stress.
Diagnosis
In the diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy, the following methods are used:
- ECG;
- Echocardiogram( Doppler and two-dimensional);
- PET( positron emission tomography);
- MRI;
- The degree of hypertrophy is determined by calculating the mass index of the myocardium.
On ECG with left ventricular hypertrophy, the deviation of the electric axis of the heart to the left and the high tooth RV5, V6 are characteristic( see ECG decoding).
Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart
To treat hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart begin with the identification and elimination of its cause. Of the drugs in the case of acquired cardiovascular disease, funds are used to improve the functioning of the myocardium and its nutrition, to restore the correct rhythm.
Among them:
- Calcium channel blockers - Diltiazem, Verapamil( with infarction, angina pectoris, rhythm disturbance), Amlodipine, Nimotop( with hypertension);
- Beta-adrenoblockers - Betaxolol, Sotalol, Bisoprolol, Atenolol and others - reduce the need for myocardium in oxygen, in particular, under stress and physical exertion, relieve pain in angina pectoris;
- Hypotensive drugs - Ramipril, Enalapril.
Admission of beta-blockers is carried out with a gradual increase in dose and strict control of blood pressure and heart rate.
If the drugs do not give a result, then they resort to surgical treatment, it is also shown in congenital heart diseases that led to hypertrophy.
The operation is to give the wall of the ventricle a normal shape and thickness. In the postoperative period, symptomatic therapy is performed.
The success of treating the left ventricular hypertrophy largely depends on the patient's lifestyle. It is important to give up bad habits, do not forget about daily moderate activity( walking, swimming, aerobics).The diet should be rich in vitamins, easily digestible vegetable fats, calcium, magnesium, fiber and contain a minimum of salt, sugars, muffins and fatty foods.
People with hypertrophy of the ventricle should closely monitor their health and undergo a systematic examination with a cardiologist.