Any disease in the adult human body is shown abnormalities of blood parameters. Therefore, this analysis is the key and the first in the diagnosis of diseases.
The content of the article:
-
1 Types of blood tests
- 1.1 General blood analysis
- 1.2 Blood chemistry
-
2 Decoding performance analysis of blood
- 2.1 Hemoglobin (HGB)
- 2.2 Erythrocytes (RBC)
- 2.3 Gemotokrit (HCT, Ht)
- 2.4 Average volume of red blood cell (MCV)
- 2.5 hemoglobin in an erythrocyte (MCH)
- 2.6 The average concentration of hemoglobin in the red cell mass (MCHC)
- 2.7 Erythrocyte distribution width (RDW)
- 2.8 erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- 2.9 White blood cells (WBC)
- 2.10 Neutrophils (NEUT)
- 2.11 lymphocytes
- 2.12 eosinophils
- 2.13 monocytes
- 2.14 basophils
- 2.15 Platelets (PLT)
- 2.16 Total protein
- 2.17 Glucose
- 2.18 Uric acid
- 2.19 Urea
- 2.20 creatinine
- 2.21 ALT aminotransferase (ALT) and AST (ACAT)
- 2.22 Cholesterol
- 2.23 Bilirubin
- 2.24 Amylase
- 2.25 Minerals: potassium and sodium in the blood
- 3 Videos about normal blood parameters
Types of blood tests
Blood performs many vital functions in the body: transports vitamins and nutrients, provides the cells with oxygen, cleanse the internal organs from toxins. It is very important to maintain all the indicators are normal.
There are 2 main types of blood tests:
- common;
- biochemical.
General blood analysis
His blood counts are normal in adults varies within a certain range. The scatter determined by the individual characteristics of each organism.
Complete blood analysis involves a detailed analysis of the qualitative and quantitative components (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, neutrophils), each of which is responsible for a particular function. The deviations from the norm of any index is judged on the state of the body. To this end, at the laboratory taking capillary (fingerstick) or venous (veins of the hands) sample.

Before any of this analysis, do the following:
- Do not eat for 8-10 hours before blood sampling.
- Do not drink alcohol 1-2 days.
- No smoking 2-3 hours.
- Do not overwork physically and emotionally.
- Drinking water is allowed in small amounts.
Clinical analysis of blood - the most common laboratory tests. He performed in the morning, and the results are ready in about 7-8 hours. There are rapid tests that show the required values in 5-10 minutes.
A more detailed picture is determined by adding the leukocyte formula, which may be included in the overall analysis of the patient. Such an analysis will cost more.
Blood chemistry
Biochemical blood test is conducted to determine disorders of any internal organ: liver, kidney, pancreas and other.
Biochemical diagnostic method requires preparation:
- fasting 8-12 hours;
- quitting smoking 2-4 hours;
- exception of physical and emotional overwork;
- sparing restricted diet acute and fatty foods;
- receiving a rejection of any drugs 7-10 days prior to analysis.
Biochemical changes in the body easily cause food or stress. Therefore, preparation for analysis requires special attention.
The analysis is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach. Venous blood is required -5 ml. Fence made from an arm vein, which is applied above the elbow harness. The puncture site with an antiseptic wipe. Pick up a sample is dispensed into several tubes for detailed studies. Results are prepared in an average of 2-3 days.

Biochemical analysis is assigned to 2 times a year to monitor the status of the internal organs. Complaints or infectious disease are ground to pass active diagnostic method.
Decoding performance analysis of blood
His blood counts are normal adults should conform to certain values. Decipher the analysis correctly can only physician. Evaluation of deviations is based on the clinical picture and patient complaints.
Hemoglobin (HGB)
One of the main components of the blood is hemoglobin. This protein, which includes iron. He is responsible for the oxygenation of body cells. The value of this parameter nonconstant depends on the power, environmental conditions, age and other factors.
Men often measure hemoglobin has a higher value than that of women. Newborn babies may also have elevated hemoglobin.
Standards for human hemoglobin described in the table below:
| Category of people (age / condition) | Normal hemoglobin, g / l |
| Men from 18 to 60 years | 131-162 |
| Men older than 60 years | 121-141 |
| Women from 18 to 60 years | 120-150 |
| Women older than 60 years | 110-145 |
| Pregnant women | 105-120 |
The causes of low hemoglobin may be:
- stress and an unstable mental state;
- restrictive diets;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- bleeding;
- autoimmune disease.
Upon detection of reduction of this parameter is necessary:
- introduce a diet rich in red meat, pomegranate, beans, rose hips, spinach;
- take iron supplements (Sorbifer, durules, totem).

The reasons for increasing the level of hemoglobin may be:
- diabetes;
- dehydration;
- burns;
- ileus.
The situation can be corrected with diet restriction products containing iron. Also, the therapist may prescribe blood thinners.
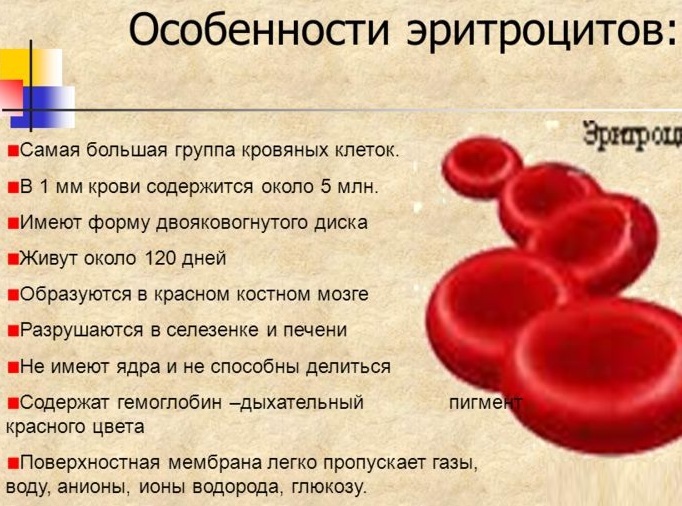
Erythrocytes (RBC)
Red blood cells - red blood cells it. They contain hemoglobin. Function - providing cells with oxygen. The rate for men is 4,3-5,8 million / ml. For women - 3.8-5.2 million / ml. For pregnant women the value is slight decrease physiological norm.
Increase of red blood cells occurs when:
- intoxication (vomiting, diarrhea, increased body temperature);
- lack of vitamins;
- physical exercise;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- disorders of the respiratory system.
The reasons for lowering can be:
- oncological diseases;
- immune disorders.
Red blood cells and hemoglobin are inextricably linked and are responsible for the same function.
Gemotokrit (HCT, Ht)
The hematocrit is associated with the above mentioned parameters and indicate the amount (share) that is occupied by red cells. In the event of normal hemoglobin values, or the number of red blood cells, likely the hematocrit will also be either upgraded or downgraded.
The rate for males - 0,4-0,48. For women - 0,36-0,46.
Reasons for decrease:
- pregnancy due to the increased blood volume woman;
- anemia;

- hyperhydration.
Reasons for the increase:
- renal dysfunction;
- cancer;
- dehydration.
Average volume of red blood cell (MCV)
The indicator is calculated as follows: the sum of all red blood cell volume in the withdrawn portions are divided by their number. Evaluation of the values necessary for the diagnosis of disorders associated with a fall in hemoglobin. The norm is: 80-100 fl. Of sex, she does not. With age, the lower boundary of the rising.
Reasons for the decline of this indicator are:
- anemia;
- failure in the production of hemoglobin.
The indicator increased in:
- thyroid dysfunction;
- leukocytosis;
- vitamin B12 deficiency.
hemoglobin in an erythrocyte (MCH)
The indicator defines the average number of the hemoglobin contained in red blood cell 1, in absolute terms. To calculate the amount of hemoglobin is multiplied by 100 and divided by the amount of hematocrit.
The rate for males: 27-34 m, and for women - 27-32 m.
The reason for the decline is hypochromic anemia. And the reason overstatement - hyperchromic anemia.
The average concentration of hemoglobin in the red cell mass (MCHC)
It shows the average value of hemoglobin per unit volume of packed red blood cells. To determine hemoglobin divided by the hematocrit. The rate for men is equal to 324-366 g / l for women - 321-356 g / l.
Value increases with:
- hyperchromic anemia;
- deviations of water-salt balance.

Decreases when:
- hypochromic anemia;
- gene mutation.
Most often caused by low values are not diseases, but wrongly calculated indices of hemoglobin and hematocrit.
Erythrocyte distribution width (RDW)
Figure responsible for the homogeneity of the red blood cells in the total mass. If there is blood, and large and small red blood cells, the width will be more important. The norm for adults, regardless of gender is 11,6-14,4%. The parameter value increases with anemia. If the analysis shows a numeric value below normal, you should retake the analysis, because it is extremely rare.
However, there is still may, at:
- cancers;
- hemolysis.
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
His blood counts are normal in adults may differ from the reference (normal) values for pregnant women. ESR parameter - a vivid example. This value indicating the relative distribution of the fractions of plasma proteins. Due to the difference in densities of red blood cells with varying speeds settle to the bottom of the tube.
The rate may be influenced by many factors, so this study is not specific. However, at elevated results is a good reason for further examination. The rate for men is 2-10 mm / h for women -8-25 mm / h. Pregnant women can reach the value of 40-50 mm / h. This physiological norm.
Elevated ESR says the following violations:
- failure of the hematopoietic system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart attacks, strokes);
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases;
- neoplasms;
- overweight, obesity;

- diabetes;
- digestive system diseases;
- inflammation of viral or bacterial nature.
The jump in the value of ESR is not talking only about the presence of any disease.
When changing your lifestyle, diet or fasting figure may also grow. Allergy sufferers will almost always have an abnormal value of this parameter. It is important to know that there is a category of people who ESR does not respond to the above annoyances.
For them, the timely diagnosis and detection of diseases is becoming a problem. Therefore, 1 time in 6 months, a full examination of the body.
ESR decreases with:
- Failure of water-salt balance;
- muscle atrophy;
- liver diseases;
- reception of hormonal preparations;
- smoking.
It is important to understand that a laboratory method for determining the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is mechanical in nature and is completely determined by the competence and care laboratory technician. In case of deviations from the reference values it is recommended to repeat the analysis in another lab.
White blood cells (WBC)
Leukocytes - white blood cells. Their main purpose - protection. This is one of the most important indicators that are measured in a clinical blood test.
White blood cells are divided into:
- eosinophils;
- basophils;
- neutrophils;
- monocytes;
- lymphocytes.

The challenge of all types - to meet foreign cells and destroy it. The norm for men and women is 4,1-9,1 • 109 /л. Pregnant women may be the rate of up to 15 • 109 /л.
Elevated values can occur when:
- emotional and physical stress;
- bacterial infections;
- periods of exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- allergies;
- open wounds;
- Blood loss.
The reasons for the low content of leukocytes can be:
- viruses;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- unbalanced or unhealthy eating habits.
Neutrophils (NEUT)
The largest group of white blood cells. Divided into stab neutrophiles. Norma neutrophils for adults equals 48-75%.
The increase in the number of neutrophils is:
- the beginning of the body to combat bacterial infection;
- intoxication;
- oncological diseases;
- heart disease and blood vessels.
Decrease says:
- lack of vitamins;
- effects of chemotherapy;
- violations of bone marrow.
lymphocytes
Another group of cells responsible for immunity - lymphocytes. Increased number indicates the body fight the virus or bacterium. The rate for adults is 19-37%.
Reasons for the increase of lymphocytes:
- infectious diseases;

- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- allergic reactions;
- postinfectious state (some time after undergoing disease increased number of lymphocytes - norm).
Reduced lymphocyte levels at:
- viral diseases;
- reception potent drugs;
- complications of inflammatory nature.
eosinophils
Eosinophils are responsible for the destruction of harmful protein that has entered the body. Bone marrow continuously generates this kind of leukocytes. Increased production of these cells known as eosinophilia. It can occur in the continuous presence in cells such foreign proteins. The rate for adults, regardless of gender is 1-5%.
Eosinophils are growing at:
- allergies;
- Cancers and tumors;
- infections;
- the presence of parasites;
- diseases of the stomach and colon.
Lowering the level of eosinophils says:
- blood poisoning;
- malfunction of the endocrine system;
- a state of shock;
- poisoning by heavy metals.
monocytes
The largest cell krovi- monocytes. They are produced in the bone marrow and enter the blood in an immature form. This is the best condition to fight the foreign proteins. Norm hardly changes with age and is independent of gender, it is 3-11%. The waiting period for the lower limit of the child for women is 1%.

Monocytes were elevated in:
- cancers;
- viruses or infections;
- diseases of the digestive system.
The level is lowered in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- hormonal therapies;
- cases of anemia;
- radiation sickness.
The absolute absence of these cells in serum - an alarming sign. It may indirectly indicate the presence of a severe form of leukemia.
basophils
Basophils are produced in the bone marrow and are one of the types of white blood cells. Within these high-level components are contained. In all the defense mechanisms of the body, these cells are involved. The norm for men and women is 0.5-1%.
The reasons for raising the level of basophils are:
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- diabetes;
- cancers;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Hodgkin's disease.
Physiological growth of these cells in women may occur during ovulation or menstrual cycle.
Reduced basophil is determined by:
- increased emotional or physical stress;
- infectious diseases;
- Cushing's syndrome.

Physiologic decrease may occur in 1 trimester of pregnancy.
Platelets (PLT)
This colorless blood cells that have no nucleus. Responsible for vital function - clotting. If bleedings are adhered to each other to form a clot, thereby stopping the movement of blood.
The rate for men is 199-401 thousand. U / .mu.l. For women - 180-319 thousand. U / .mu.l. During pregnancy rate is reduced - 98-311tys. U / .mu.l. Menses also lead to a reduction index (76-221tys. U / l).
The reasons for increasing platelet considered:
- emotional overload;
- infectious diseases;
- blood loss;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases;
- anemia.
Reduced rate may, at:
- reception potent drugs;
- liver diseases;
- certain types of cancer;
- prolonged menstruation.
Total protein
This parameter is investigated and measured in blood chemistry. He reported on the proportion of organic proteins in the sample. Norma adults up to 60 years of age is 64-84 g / l. After 60 - 63-82 g / l. Deviations in the one and the other side is a pathology.
Improvement may be when:
- thick blood;

- disorders of the digestive system;
- autoimmune shifts;
- tumors;
- infectious diseases.
Level drops significantly, if present:
- diabetes;
- HIV;
- hepatitis;
- lack of protein in the diet.
Glucose
Blood glucose levels - an indicator to monitor which is necessary for each adult. Diabetes mellitus is not uncommon today. glucose Score affects health. The rate for males and females is 3,1-5,6 mmol / l.
Reasons for the increase are:
- diabetes;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- ailments of the liver.

glucose level drops, if any:
- low-carbohydrate diet;
- physical and emotional tension;
- chronic disease.
Uric acid
The contents of this parameter indicates a metabolic process. Uric acid is produced in the liver as a decay product of purines. The rate for men is 209-421 micromol / L. For women - 148-352 mmol / l.
Level increases when present:
- toxicosis;
- unbalanced diet;
- hypertension;
- excess weight;
- blood diseases;
- violation of the excretory system.
Reduced content of uric acid in:
- HIV infection;
- gene mutations;
- lack of enzymes required for purine metabolism.
Urea
blood analysis measure responsible for the normal functioning of the kidneys and liver. The compound is a diamide of carbonic acid.
The rate for adults varies by gender:
- for men: 3,8-7,3 mmol / l;
- for women: 2,1-7,7 mmol / l.
The reasons for the growth of the urea content:
- leukemias;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- violating the integrity of the skin (burns, wounds);
- internal bleeding.
Reasons for the decline:
- low-calorie food;
- during pregnancy;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- parasites;

- poisoning;
- liver malfunction.
creatinine
Creatinine is a decay product of some of the reactions, is excreted in urine. Evaluates work excretory system (kidney). The rate for men is 62-125 mmol / l for women - 52-98 pmol / l.
Increases in the following reasons:
- low-calorie food;
- excessive exercise;
- side effects of medications (ibuprofen, tetracycline);
- excess weight;
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- adulthood.
Decreased creatinine at:
- 1 trimester of pregnancy;
- sudden weight loss;
- disorders of the kidney and liver;
- muscular dystrophy.
ALT aminotransferase (ALT) and AST (ACAT)
Alanine figure is estimated to be expanded blood test to detect failures of the liver. The enzyme aspartate aminotransferase - similar to the liver and heart muscle. If the rate of ALT greater AST, it speaks about the problems with the liver. If on the contrary - to attack the problems. Normal ALT for males is less than 41 U / l, for zhenischina - less than 33 U / l.
The reasons for the growth of ALT:
- viruses;
- liver disease;
- receiving drugs.
Reducing is not measured: the indicator must have a minimum value. Normal AST for males is less than 40 U / l for women - less than 32 U / l.
The reasons for the growth of AST:
- liver dysfunction;
- viruses.
Normally, AST should have a low value. During the period of gestation of the child AST index falls.
Cholesterol
This organic compound which is found in all body cells. Attention to this enzyme is increased in the past decade: talk about the benefits and dangers of cholesterol.

There are 2 types of this substance:
- high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or "good" cholesterol;
- low density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad" cholesterol.
Called their LDL obliged ability deposited on vessel walls. This leads to heart attacks and strokes. However, he and the other types of cholesterol are essential for human substances. It is only important not to allow the excess of their concentration in the blood.
Standards of cholesterol given in the table below:
| Normal Men, mmol / l | The rate for women, mmol / l | |
| total cholesterol | 3,58-5,19 | 3,58-5,19 |
| HDL | 2,26-4,81 | less than 3.51 |
| LDL | 0,7-1,71 | 0,9-1,87 |
The causes of high cholesterol:
- excess weight;
- fatty foods in the diet;
- age over 50 years;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- problems in the endocrine system.
Lowering cholesterol - is rare, but possible with memory disorders.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin - the enzyme responsible for the excretion of bile. It is an indicator of liver function. The rate for adults is 3,4-17,1 pmol / l.
Increase can indicate:
- jaundice;
- hepatitis;
- infectious mononucleosis.
- Gilbert's syndrome.

A lower value of bilirubin, usually means the analysis carried out incorrectly. Also affect the outcome before delivery can be drunk coffee, significantly reduces the level of this indicator.
Amylase
Amylase is a digestive enzyme. It is a defining component in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. The rate for adults is 29-101 U / l.
Increasing blood concentrations may occur when:
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the stomach;
- Injuries to the abdomen;
- neoplasms of the pancreas.
The level may be reduced when:
- toxicosis;
- hepatitis;
- dysfunction of the pancreas.
Minerals: potassium and sodium in the blood
Major cations defined in the biochemical analysis of blood - it's potassium and sodium. Sodium is found in the extracellular fluid. He is responsible for the formation of bones and is responsible for the nerve endings. Potassium is responsible for the acid-base balance. blood counts are normal adults should not extend beyond the sodium content of no more than 145-155 mmol / l; potassium - 3,35-5,28 mmol / l.
The causes growth of sodium concentration in blood:
- diseases of the excretory system;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- receiving hormonal preparations;
- the lack of water in the body.

Lower values occur when:
- sodium deficiency in the diet;
- disorders of the liver;
- renal dysfunction.
Causes of high potassium concentration in the blood:
- improper sampling of venous blood;
- genetic predisposition;
- reception potassium drugs prior to analysis.
Falling potassium concentration is at:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- reception diuretics;
- disruption of the heart.
Examined blood parameters is very important to keep under control. Any deviation from the norm could face a serious disorder or disease of an organ of an adult.
Registration of the article: Lozinski Oleg
Videos about normal blood parameters
Biochemical analysis of blood in health and disease: