A sudden pain in the abdomen of a woman can signal the development of pathologies in the abdominal cavity. It is important to recognize the first symptoms of appendicitis in a timely and correct manner and call physicians as soon as possible. However, the disease in women has many features and causes some difficulties in diagnosis. That is why it is important to understand all its nuances.
Contents of
- 1 What is appendicitis, from which side is the appendix?
- 1.1 Acute appendicitis - video
- 2 Causes of inflammation in adults
- 2.1 Common causes of
- 2.2 Main female causes: monthly, anatomical features, pregnancy
- 2.3 Risk group
- 3 Symptoms of pathologyin girls and women
- 3.1 Symptoms of acute pathology
- 3.2 Symptoms of chronic form
- 4 Diagnosis: what studies can determine the presence of pathology
- 4.1 Differential diagnostics
- 4.2 Appendicitis features video
- 5 Treatment of appendicitis
- 6 Postoperative period
- 6.1 Dietary food after operation
- 6.1.1 Dietary food - photo gallery
- 6.2 Physical activity
- 6.1 Dietary food after operation
What is appendicitis, from which side is the appendix
At the blindguts have a rudimentary process, which is called an appendix. It is a hollow organ that ends with a "dead end" - it is closed from the end. His functions to this day doctors are not clear, so he is considered a rudiment.
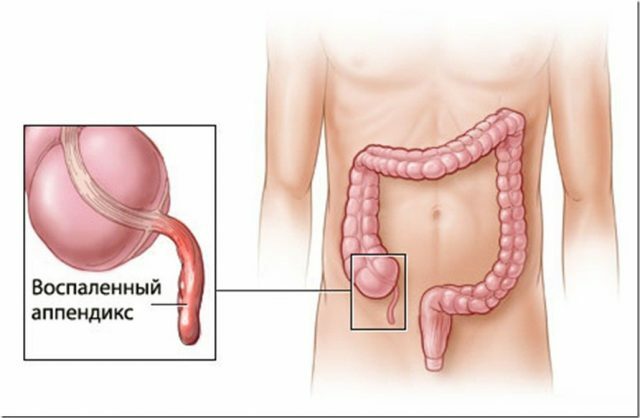
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix of the caecum
There are theories according to which the appendix helps to withstand loads, supports immunity, insures against certain diseases. This is a border guard between the colon and intestines. It protects the latter from the penetration of bacteria.
Sometimes, as a result of some reasons, the entrance to the appendix is clogged. However, the process continues to produce mucus, which now does not find an outlet. Against the background of such blockage, the rudiment inflames, its walls are stretched - appendicitis develops. If timely surgical care is not provided, the expanding process can burst. The contents spill out into the peritoneum, one of the most serious complications, peritonitis, develops.
The appendix has mobility. In addition, it can be localized in the body atypically. The wrong location of the appendix is often observed in women. In many cases, the pelvic site is localized, in which the process has a common network of vessels with the fallopian tube and ovary. And if a man's pain clearly indicates appendicitis, then a woman's discomfort in the same zone can signal problems with the reproductive organs of .
Acute appendicitis - video
Causes of inflammation in adults
Appendicitis develops in people of any age. Both men and women suffer from pathology. And in the latter, the disease is diagnosed 2 times more often than in the strong half. This is due to the anatomical structure of the female body.
Statistically, appendicitis usually worries patients of childbearing age( from 20 to 40 years).
Common causes of
Appendicitis can develop on a background:
- Infections. The disease can lead to inflammatory processes, which occur even in the remoteness from the appendix. Pathogenic bacteria are sometimes recorded with blood flow from such foci of infection as tonsillitis, inflammation of the tonsils.
- Chronic constipation. If the body does not excrete the feces in a timely manner, then they harden. Becoming dense, they overlap the mouth of the appendix, resulting in inflammation.

The development of appendicitis can result in chronic constipation of
- Parasites. The presence of helminths in the body can trigger the onset of the inflammatory-infectious process.
- Abnormal structure. By stagnation of the contents in the rudiment, a considerable length of the process or the presence of bends can lead.
Main female causes: monthly, anatomical features, pregnancy
Physicians associate the incidence of appendicitis in women with:
- Cyclical monthly changes. In the menstrual phase, there comes a period when the flow of blood to the internal organs of the pelvis increases. Mucous membranes swell and can have an irritating effect on the walls of the appendix.
- Close proximity of the genitourinary system and gastrointestinal tract. This close neighborhood, which is characteristic only of the female body, can lead to the spread of diseases from one organ to another. So, any inflammations occurring in the urinary, reproductive system( uterus, ovaries) can trigger appendicitis.
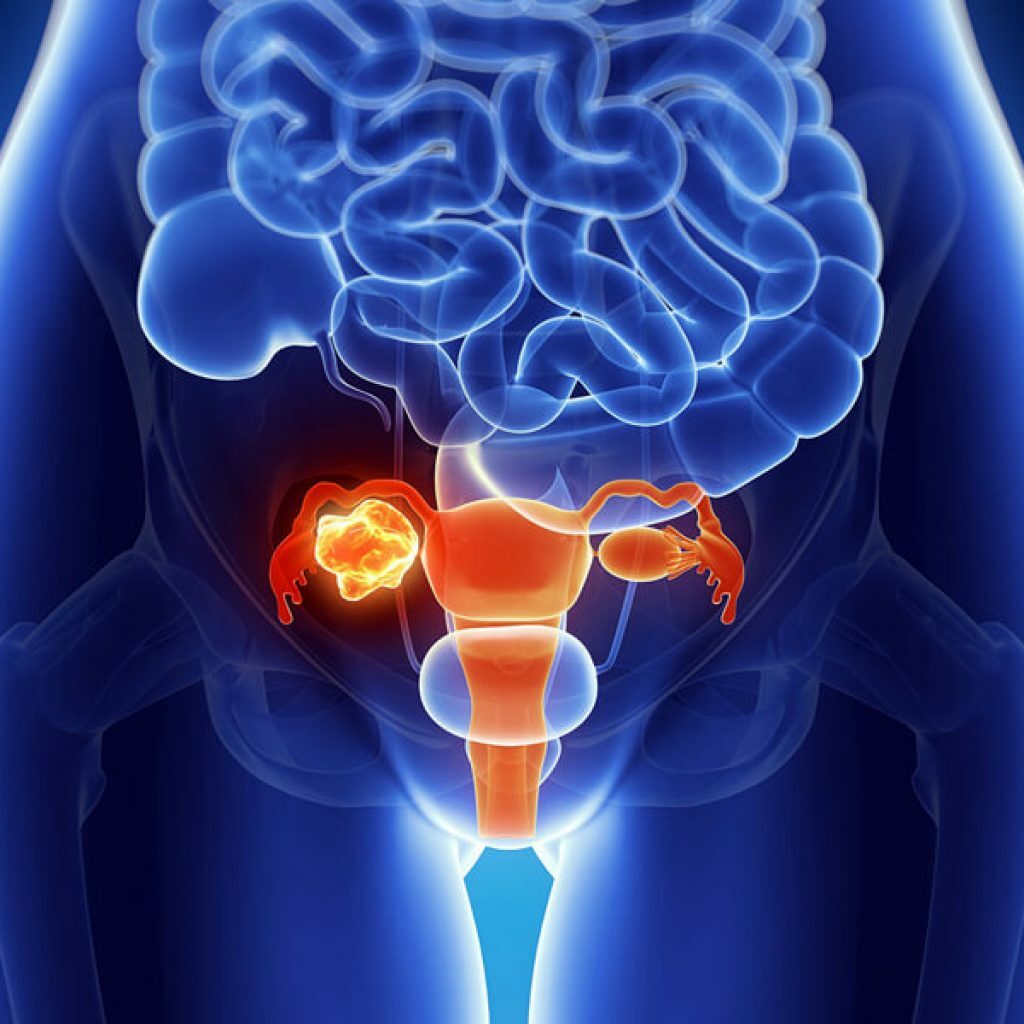
Inflammatory processes occurring in the reproductive system in a woman can lead to appendicitis
- Pregnancy. The enlargement of the uterus leads to squeezing and displacement of the internal organs. Blood supply to tissues may be impaired. Against the backdrop of such phenomena are able to develop a variety of pathologies, including appendicitis.
Risk group
The risk of developing appendicitis is noted in patients, more often in women, which are characterized by:
- Malnutrition. Appendicitis occlusion is observed in people who consume a lot of meat and practically do not eat foods enriched with fiber( bran, wheat, grain bread, broccoli, eggplant, cabbage, rice).It is the fiber that activates the peristalsis and helps to cleanse the intestines.
- Hereditary predisposition. Physicians argue that inflammation of the appendix is more common in people who carry certain antigens genetically incorporated.
- Lifestyle. Significantly increase the risk of development of pathology permanent stress, prolonged fatigue, smoking, alcohol abuse.
Signs of pathology in girls and women
Appendicitis often occurs in acute form. But sometimes there can be a chronization of the process. These forms have different manifestations, so it is necessary to consider them separately.
Symptoms of acute pathology
The clinical picture of a typical appendicitis is cyclical:
- Catarrhal stage. This is the onset of a disease that can last for 12 hours. For the catarrhal stage, the following course is typical:
- in the first hours of development of inflammation appears:
- soreness in the region of the stomach, reminiscent of gastritis;
- discomfort usually appears in the evening or at night;
- pain is of a non-intensive, dull character;
- nausea, one-time vomiting is possible;
- after a few hours, the following symptoms are noted:
- pain covers the lower right corner of the abdomen( with the natural location of the appendix);

Pain with appendicitis covers the lower right corner of the abdomen
- discomfort acquires an oppressive, pulsating character;
- the intensity of pain gradually increases;
- urination becomes more frequent, diarrhea is possible;
- the temperature rises;
- pain covers the lower right corner of the abdomen( with the natural location of the appendix);
- after 6-12 hours from the onset of inflammation, there are such signs of pathology:
- intoxication of the body: high weakness, malaise, excruciating dryness in the mouth, increased heart rate;
- pain is intense and difficult to bear;
- abdomen is soft, but pressing on the right side causes severe discomfort.
- in the first hours of development of inflammation appears:
- The phlegmonous stage. It usually comes to the end of the first day. The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain localized in the right ileal zone;
- discomfort has a pronounced pulsating character;
- nausea is present constantly;
- tachycardia reaches 90 beats / min;
- temperature ranges from 38-38,5 C;
- the right abdominal area is tense and practically does not participate in the respiration process.
- Gangrenous stage. If the patient has not been previously operated on, then the following clinical picture develops on day 2-3:
- pain is reduced as a result of death of appendix cells;
- intoxication is increasing, often vomiting, pronounced tachycardia;
- temperature decreases, sometimes even below 36 C;
- abdomen is swollen, there is no peristalsis;
- touching the area of appendix location causes severe pain.
- Perforating stage. By the end of the third day, the perforation( rupture) of the appendix wall usually occurs. The patient has such a clinical picture:
- acute pain with increasing intensity;
- is a constant discomfort, there are no periods of relief;
- repeated vomiting;
- tense and swollen abdomen with complete absence of peristalsis;
- temperature rises to critical values;The
- plaque on the tongue becomes brown.
When the wall of the appendix is perforated, the temperature rises to the critical values of
The above dates and stages of the clinical picture are conditional. Sometimes there is a lightning or latent development of appendicitis.
Especially dangerous are cases with atypical location of the appendage. Symptomatic in such situations can be significantly different. Pain can localize:
- in the hypochondrium on the right;
- in the lower back;
- in the crotch or pubic region.
Quite often inflammation of the appendix develops during menstruation. As noted above, the proximity of the right ovary to the vermiform appendix is to blame for this. And since some women experience aching pain during menstruation, many of them may not even suspect appendicitis.
During the period of menstruation, such characteristics can be observed:
- severe pain;
- nausea, vomiting, which appeared even during the catarrhal stage.

Some women often experience pain during menstruation, so they can not determine the inflammation of the
Sometimes young girls encounter so much pain during each menstrual period that suspicion of appendicitis arises. Such patients need to consult a doctor. As a rule, after the delivery, the severity of discomfort is significantly reduced.
Signs of acute appendicitis in young girls have a more acute and pronounced character than in women after childbirth.
Symptoms of chronic form
Chronicization of the process is very rare.
This appendicitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Sluggish inflammatory process, in which there is aching pain. Periodically, the patient feels a strong paroxysmal discomfort in the right side.
- Pain can be localized in the navel area, cover the iliac zone. Sometimes it radiates into the leg, it feels in the lower back.

Periodic appearance of aching pain in the right abdominal zone of the
- is typical for chronic pathology. Periodically, the patient is tormented with constipation, which is followed by diarrhea.
- Pain in the abdomen increases with coughing, sneezing. Discomfort occurs after the act of defecation.
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle often develop.
- Women experience discomfort during or immediately after intercourse. Sometimes the proximity causes painful spasms
It is important to understand that all the "female" symptoms of appendicitis, such as a cycle disturbance, increased pain, the presence of vomiting, nausea from the first stages of inflammation can indicate the development of diseases in the reproductive system. Sometimes they indicate such dangerous conditions as torsion cysts, rupture of the ovary.
Diagnosis: which studies can determine the presence of pathology
In women, appendicitis is much more difficult to determine than in men. After all, under the guise of inflammation can hide a variety of gynecological pathologies. That is why, in the presence of pain in the abdomen, a woman is initially sent for examination by a gynecologist.
For the diagnosis of appendicitis the following measures are used:
- Interrogation of the patient. The doctor will clarify the nature of the pain, find out its localization, learn about additional symptoms. In addition, the doctor will ask questions about the menstrual cycle.
- Patient examination. The body temperature and heart rate are specified. Then the surgeon palpates the abdomen. There are specific signs that help diagnose appendicitis:
- pain intensification occurs during the raising of the right leg and pressure on the zone of the rectum;
- discomfort is much stronger if the patient lies on his back and flexes his legs in the knees;
- during the pressure on the area under the navel in the patient increases discomfort.
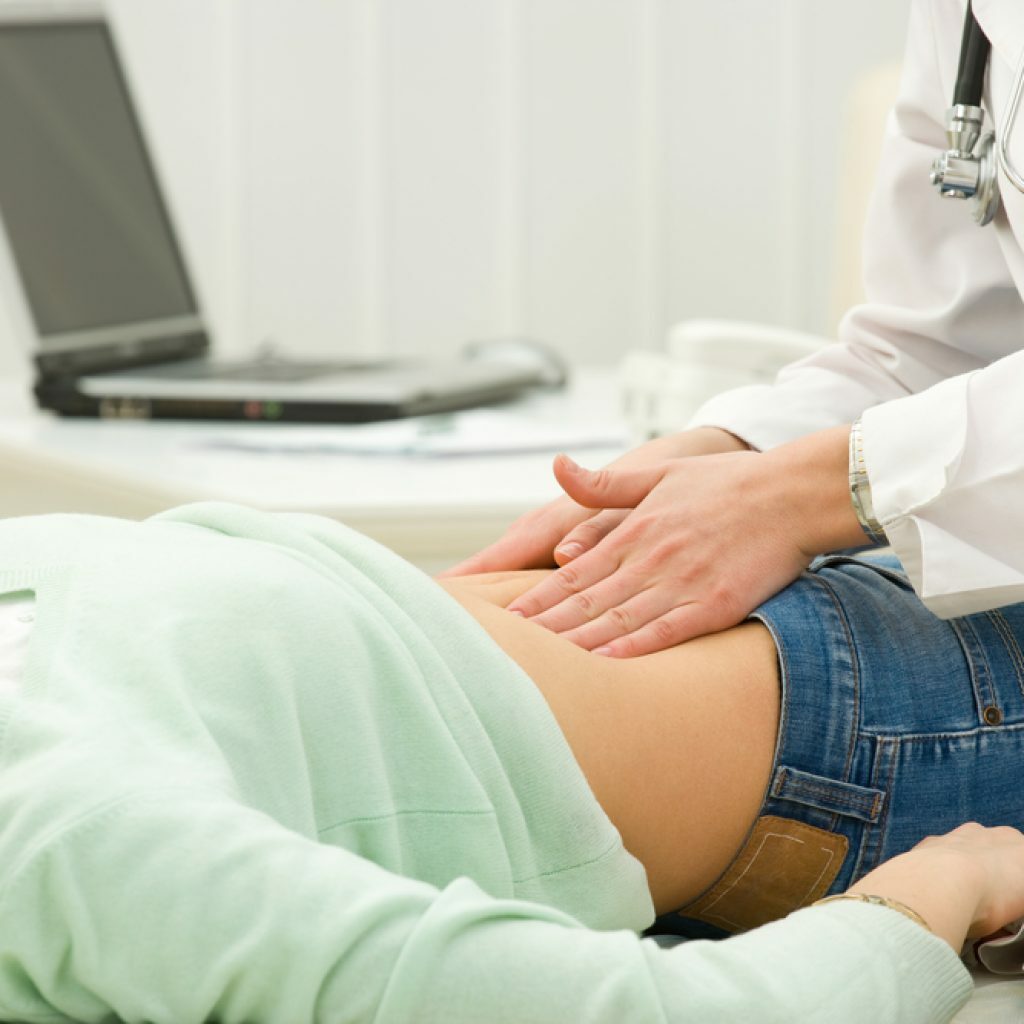

The surgeon palpates the abdomen to identify specific signs that help diagnose appendicitis.
- . Laboratory tests. The results of the blood test indicate inflammation in the body. The study of urine helps to suspect the pathology of the genitourinary system.
- Ultrasound examination. It is used if the patient is suspected of having gynecological diseases or disorders in the peritoneum, small pelvis.
- X-ray of the peritoneum. The study makes it possible to exclude the risk of intestinal obstruction.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. This method is used in the event that all the measures described above did not allow the pathology to be determined accurately. This is the most accurate method of diagnosis, which allows you to assess the condition of the appendix, pelvic organs and peritoneum.
Differential diagnosis of
Acute appendicitis in a woman must be differentiated from a variety of other pathologies, among which the following violations are most often observed:
- Painful menstruation. With appendicitis, painful sensations from the navel region extend into the right iliac zone. In the case of menstruation, the discomfort covers the lower back and the lower abdomen.
- Inflammation of the appendages or adnexitis. With this pathology, raising the right leg does not cause pain. In addition, adnexitis is characterized by the presence of discharge from the vagina, violation of the menstrual cycle and an increase in the appendages. Ectopic pregnancy. Discomfort radiates to the sacrum, the perineum, can give into the scapula. There are secretions in the form of blood clots.
- Rupture of the right ovary. There is a sharp pain in the lower abdomen after a physical or violent emotional load. The condition of a woman is rapidly deteriorating. Diagnosis of pathology allows examination by a gynecologist and ultrasound.
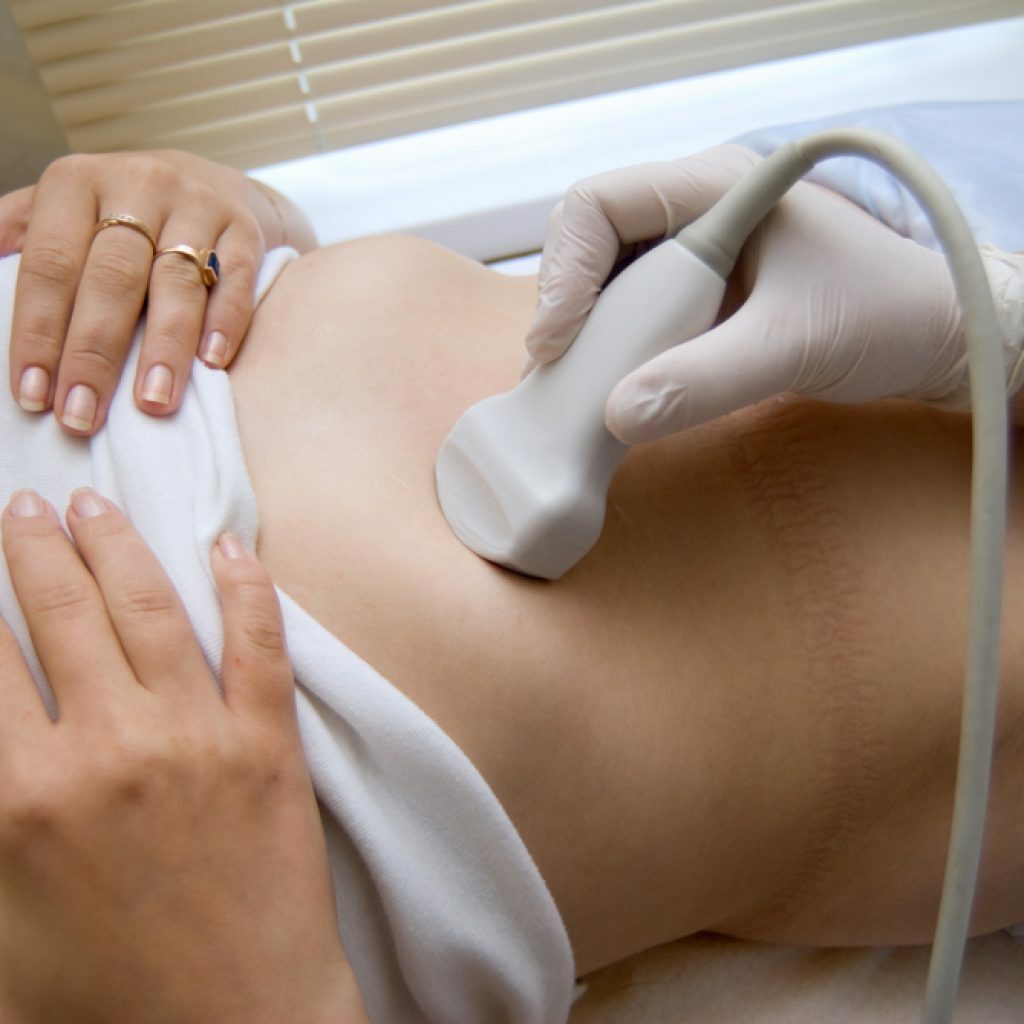
Ultrasonography helps to exclude gynecological diseases and pathologies of the abdominal cavity
Chronic appendicitis has a similar symptom with such pathologies:
- Pyelonephritis. On the kidney disease indicates an analysis of urine. Ultrasound is used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Peptic ulcer disease. If a pathology is suspected, a woman is prescribed gastroscopy. In the case of perforation of the ulcer, the feces acquire a black color.
- Chronic cholecystitis. Problems with the gall bladder can be indicated by vomit, in which there is no bile.
- Chronic gynecological pathologies. Such pathology gynecologist can suspect after the examination of the patient. For more detailed study, ultrasound is prescribed.
Distinctive features of appendicitis - video
Treatment of appendicitis
The only method of treatment for acute appendicitis is an operative procedure to remove the process. And the earlier it is carried out, the better the outcome of the disease.
The preparation for the operation includes several important activities that are most often carried out in an emergency:
- The patient's stomach is freed from the remnants of food. The patient is forbidden to drink water.
- In severe intoxication, intensive therapy is performed.
Depending on the stage of the course of the pathology, the intervention method will be chosen:
- Laparoscopy. The most preferred method of surgery. In the abdominal cavity several incisions are made, through which the instrumentation and the camera are inserted. Laparoscopy is possible only during the catarrhal stage, in which there are no complications. This method allows you to recover much more quickly after the operation. And, as a rule, already for 2-3 days the patient is discharged home.
- Laparotomy. Dissection of the peritoneum is carried out with a more severe course of appendicitis. Assign a phlegmonous, gangrenous stage, in the case of peritonitis. After the operation, drainage is inserted into the cavity. This is a more traumatic intervention. Approximately on the 7-10th day, seams are removed. And the patient is discharged for 10-14 days.
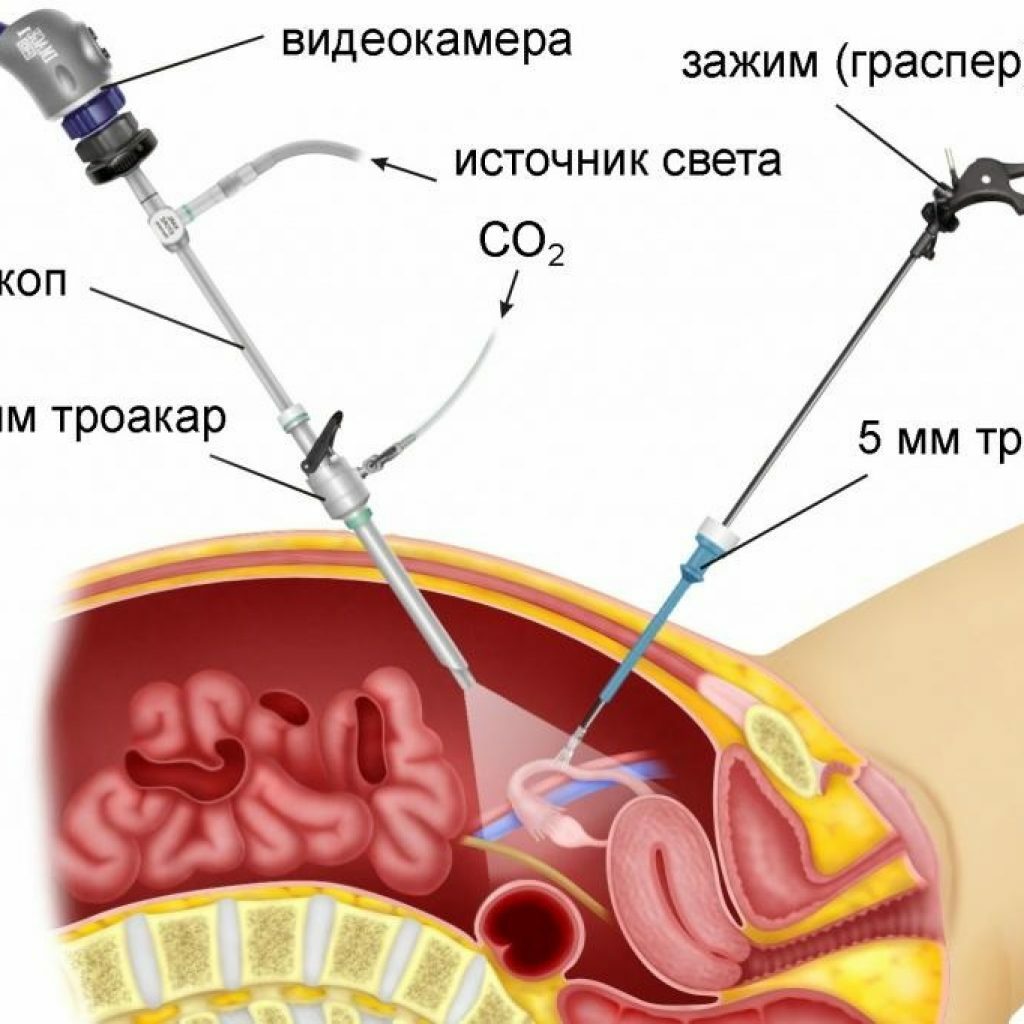
Laparoscopy - the least traumatic method of surgical intervention
After the operation, a woman can change her menstrual cycle. This is especially true for patients who have suffered a severe form of appendicitis. Such violations are temporary. The cycle is fully restored within 2-3 months.
Treatment of chronic form, if a woman does not have symptoms of inflammation, begins with the appointment of antibiotics. Such a pathology does not need an emergency operation. But doctors recommend not to delay and remove the appendix in the planned mode, without waiting for its inflammation.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In the case of suppurative inflammations, hormonal agents are included in the therapy. If necessary, blood filtration is prescribed-plasmaphoresis.
Dietary food after operation
After removal of the appendix, doctors recommend:
- For the first 12 hours. It is allowed to use only water without gas.
- After 12 hours. It is acceptable to use a small amount of berry, fruit jelly, chicken loose broth.
- On the 2nd day. In the diet can be introduced vegetable purees( only on water), sour-milk products, dietary meat( boiled).
- After a week. Meals are replenished with soups-mashed potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini. The menu is complemented by porridges: oatmeal, rice, buckwheat. Useful boiled meat, steam cutlets from chicken, beef. The patient recommends the use of low-fat dairy products.
From products that cause fermentation and gas formation in the digestive system, it is recommended to refuse( beans, cabbage, pickles, soda).
After about 2 weeks, the patient is allowed to gradually return to normal diet.
Dietary food - photo gallery
 The berry jelly is useful for the patient
The berry jelly is useful for the patient  The low-fat chicken broth
The low-fat chicken broth  is allowed. Potato puree cooked on the water can be already on the second day after the operation.
is allowed. Potato puree cooked on the water can be already on the second day after the operation.  After a week you can eat oatmeal
After a week you can eat oatmeal  Allowed the steam cutlets
Allowed the steam cutlets  The ration is supplemented with pumpkin soup
The ration is supplemented with pumpkin soup Physical activity
Postponed operation( especially laparotomy) can lead to adhesions, and sometimes hernias. To prevent the formation of such complications, doctors advise physical activity.
After surgery, a woman is recommended:
- Lifting from a bed. Raise is allowed by the end of the first day.
- Therapeutic gymnastics. Be sure to perform light exercises that allow the body to recover faster. Exceptions are sessions on the abdominal press.
- Walking. To prevent the formation of adhesions, it is recommended to walk unhurriedly.

After the operation, a woman is useful for walking.
- Exception of heavy loads. Within 6 weeks after the operation, internal tissues are fused. To protect the body from the formation of hernias during this period, it is necessary to refrain from heavy physical labor and lifting weights
It is rather difficult to prevent the development of appendicitis in a woman. After all, many causes can trigger an inflammatory process in a fragile organism. Therefore, you need to be careful about your health and, if there is a characteristic symptomatology, do not hesitate to visit a doctor.