All mothers know very well: babies with a 3-month-old age are vaccinated against diphtheria. The vaccine, including diphtheria-tetanus toxoid and anti-pertussis vaccine, is one of the most severe. Is vaccination necessary? Everyone will answer this question in the affirmative if they know what diphtheria is, its symptoms and causes of the disease, prevention and treatment.
Contents of
- 1 Diphtheria: what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of diphtheria
- 3 Symptoms of diphtheria by type of disease
- 4 Diagnosis of diphtheria: necessary analyzes
- 5 Treatment of diphtheria
- 6 Prevention of diphtheria
Diphtheria: what is it?
Diphtheria( diphtheria) is an acute infectious pathology, in 90-95% of cases, affecting the oropharynx with the formation of dense fibrinous films on the tonsils. Diphtheria lesions of the eyes, skin, genital tracts are much less common.
Considered earlier as a childhood infection, diphtheria has recently been increasingly registered in adolescents and adults. At the same time more and more serious complications of the disease are registered.
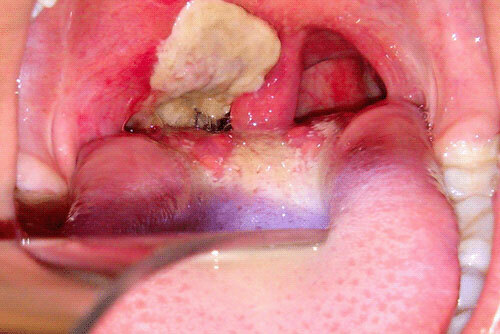
Diphtheria, photo of throat
In ancient times, the disease was called malignant angina, a deadly ulcer of the pharynx, the loop of the executioner. These awesome names accurately described the deadly risk of diphtheria infection in the absence of antidiphtheria serum and antibiotics.
In the development of the disease, the danger is not the causative agent itself, but the strong exotoxin that it emits. By toxicity, it is second only to the products of the life-activating pathogens of botulism and tetanus. Thus, the component of the diphtheria toxin hyaluronidase increases the permeability of the capillary wall and provokes the formation of fibrinogen in tissues surrounding the site of infection.
Then a pathological process includes necroxin, which regenerates fibrinogen into fibrin. At the same time on the surface of the focus of infection fibrin films are formed, tightly welded to surrounding tissues.
And the last, most dangerous component is actually a diphtheria toxin, the action of which is directed to small vessels, myocardium and nerve cells. It is his action that is more conducive to severe intoxication and complications in diphtheria.
Causes of diphtheria occurrence
Diphtheria is a contagious disease transmitted from a person( a patient or a carrier) to a person. Infection with diphtheria from animals is excluded.
The disease occurs when infecting bacillus Leffler - Gram-positive bacteria from the genus Corynebacterium. In the process of life, a bacillus may lose the ability to synthesize a toxin, forming nontoxigenic strains.
Infection can be infected by airborne droplets. Danger is represented as patients with diphtheria( the more severe the disease, the more the infectious agent releases the patient into the environment), and carriers that do not have external symptoms of infection.
Less commonly, infection occurs by contact( with eye / skin damage) through objects that have been used in a sick person, and through contaminated dairy products.
Symptoms of diphtheria by type of disease

The incubation of the digestion with diphtheria is 2-10 days. On the localization of the lesions, several forms of diphtheria are distinguished, each of which has distinctive features in the clinical picture.
Orthopharyngeal diphtheria is the most common type of lesion with the formation of an inflammatory focus in the oral cavity( tonsils) and pharynx. On external manifestations diagnose the following forms of oropharyngeal diphtheria:
Localized diphtheria
Begins with an increase in hyperemia and edema of tonsils, slight pain in the throat and a fever of 38-39 ° C.The primary picture of catarrhal diphtheria resembles angina, but initially the intoxication is less expressed. From banal tonsillitis, diphtheria is distinguished by a whistling noise, audible on inspiration, barking cough and problematic breathing.
With the rapid development of the disease in the lacunae of the tonsils, fibrinous islets are formed, at the same time the cervical lymph nodes are enlarged( mobile, practically painless), the swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa is increasing. Swallowing is difficult, although pain is less intense than with angina.
Pretty quickly, the islet form turns into a filmy one - on the tonsils, a dense coating of often white or gray color is formed. The removal of the diphtheria film with a spatula is difficult, ending with the bleeding of the tonsils.
Common diphtheria
Diphtheria raid spreads over the palatine tonsils, grasping the tongue and arches. This increases intoxication, there is pronounced weakness, pale skin, headache, soreness in the throat increases. Also, cervical lymph nodes that reach the size of a large bean become sensitive.
Toxic diphtheria
This form of diphtheria already very rapidly from the first hours. There is hyperthermia up to 40 ° C, a sore throat and neck. In the throat on the background of puffiness and hyperemia, a jelly-like plaque is formed in the form of a spider web, which becomes dense by day 3, acquires a dirty gray color and completely covers the soft / hard palate, tonsils, arches and tongue.
In case of toxic diphtheria, the appearance of transparent transparent discharge from the nose is possible, and fibrinous films often form on its mucous membrane. Nasal breathing is difficult, there is a nasal in the voice, and a sugary sweetish smell appears from the mouth.
Against the background of a visually defined edema of the neck, all groups of lymph nodes increase, forming a painful elastic conglomerate. On the development of puffiness neck distinguish toxic diphtheria:
- I degree - edema spreads to the middle of the neck;
- II degree - swelling reaches the clavicle;
- III degree - swelling captures the area below the clavicle.
More pronounced and symptoms of intoxication. The pronounced toxic effect provokes severe weakness and drowsiness from the first hours of the disease. High temperature and severe intoxication in children with diphtheria causes repeated vomiting, abdominal pain.
Hypertensive diphtheria( diphtheria croup)
The most severe form of diphtheria lesion, in which the symptoms of intoxication come to the forefront of the clinical picture. Significant swelling in the throat and large-scale film plaque are accompanied by critical hyperthermia, cyanosis, palpitation, convulsions and loss of consciousness.
The inflammatory process extends to the larynx, trachea and bronchial tree. In this case, all the symptoms of diphtheria develop rapidly, and a marked violation of cardiovascular activity often leads to a fatal outcome on day 2-3 of the disease.
This variant of the disease course is often observed in immunodeficiency and general weakness of the human body, requires the immediate introduction of antidiphtheria serum.
Hemorrhagic diphtheria
Characterized by multiple hemorrhages( hemorrhages) small in the form of a rash and extensive. Dense plaque due to impregnation with blood becomes brown. Possible development of bleeding gums, nasal and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Other localization diphtheria
Less frequently diagnosed forms of diphtheria infection occur with less severe symptoms, but are no less dangerous in terms of toxic effects. Distinguish the following types of disease:
- Diphtheria of the nose - against the background of the absence of intoxication from the nome, the serous, bloody mucus with an admixture of pus expires, and the nasal passages are covered with a filmy coating. The wings of the nose, chin, forehead and cheeks are covered with small erecting erosions, gradually drying up to form crusts. The localized form is not accompanied by an increase in temperature. With the development of a toxic form and the spread of the disease on the sinuses, there is pronounced edema on the cheeks and neck.
- Eye diphtheria - the catarrhal form is difficult to distinguish from ordinary conjunctivitis, and in the form of a film, pronounced edema of the conjunctiva and hardly removable whitish-gray films are observed. The toxic form of the disease gives the edema of all okolaglaznoy cellulose.
- Skin diphtheria - on the hyperemic background long unhealed sores with a dirty gray bottom are formed, surrounded by a dense infiltrative roller.
- Diphtheria of the genitals - typical of the secretions, painful urination and an increase in inguinal lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of diphtheria: necessary analyzes of
Not always in the clinical picture( especially with the catarrhal form of diphtheria), you can put an accurate diagnosis. Confirmation of the type of infection is carried out according to the following analyzes:
- general clinical blood test - gives signs of inflammation, but does not indicate an agent;
- plaque bacterioscopy - reveals Corynebacterium diphteriae of a distinctive species: paired bacterial sticks located in the letter V, with a bulbous bulge at the ends;
- bacteriological culture - cultivates colonies of microorganisms, however, the study takes time( for the purpose of treatment, no response is expected from seeding);
- serology - the detection of specific antibodies in the serum of blood( the method of RNGA, ELISA, etc.).
All people who have come into contact with the patient are subject to the examination for the prevention and subsequent treatment of diphtheria in the detection of bacterial transport.
Treatment of diphtheria
The earlier diphtheria is detected and the treatment is started, the less the risk of complications: paralysis of the respiratory tract, arms and legs, asphyxia, myocarditis. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital, the patient is placed in a separate box.
The therapeutic complex includes:
- Antidiphtheria serum for inactivation of toxin - dose, IM or IV method of administration is selected depending on the severity of the patient's condition.
- Rinse throat with antiseptics - soda, chamomile broth, eucalyptus.
- Antibiotics - penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines for 5-7 days.
- In / in detoxification - Reopoliglyukin, plasma.
- Symptomatic therapy - antihistamines, vit. C and group B, with the stenosis of breathing - Euphyllin, Prednisolone.
- Plasmapheresis, hemosorption - is suitable for toxic form.
- Resuscitation - with the development of an infectious-toxic shock.
Diphtheria prophylaxis
inoculation with diphtheria, photo
- Vaccination of children according to age schedule with DTP, Pentaxim, ADS-M vaccines( allowable temperature after diphtheria vaccination for 2-3 days).
- Vaccination of medical workers, school staff, caterers.
- Detection of bacteriocarrier by clinical examination.
- Inpatient treatment of carriers of toxigenic strains of the diphtheria bacillus.
- Disinfection in the source of infection.