What is it? Portal hypertension is an increase in pressure within the portal( portal) vein, due to the occurrence of an obstruction to the normal flow of blood through it.
This condition is observed in certain diseases of the vessels and internal organs, the outflow from which enters the portal system. These are unpaired organs of the abdominal cavity - esophagus, liver, intestine, spleen, etc.
The syndrome of portal hypertension is a state of the body in which a number of specific clinical and morphological manifestations develop in response to the formation of portal hypertension.
For a better understanding of what portal hypertension is, its manifestations and methods of treatment, let's look at the development of the disease. For this, you will have to plunge a little into the anatomy and processes occurring in the body. .
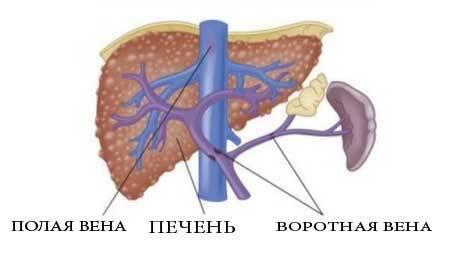
The liver is an organ with unusual, double blood loss. It receives both arterial and venous blood, which are mixed in the thickness of this organ. Such a system is necessary for the performance of the liver of its complex and diverse functions.
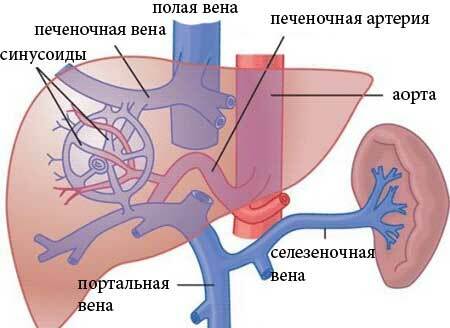
Venous blood from the intestine, spleen and stomach enters the liver through the portal vein. In the liver, this vein branches into smaller vessels, which form a dense network, the so-called sinusoidal capillary network.
It branches into the hepatic artery, which carries arterial blood to the liver from the aorta( oxygen and nutrients are supplied through this artery).In sinusoids, arterial and venous blood are mixed, which ensures the active work of hepatic cells( hepatocytes).
In the future, blood from sinusoids gathers into the hepatic veins, and they, in turn, carry blood into the lower vena cava. And she already comes to heart. This closes the circulatory circle involving the portal( portal) vein( see photo 2).
The portal vein has a connection with the system of hollow veins not only through the liver, but also in the form of communicating vessels - anastomoses that play an important clinical role. Violation of the permeability of the portal vein makes the blood seek other ways of outflow. And they are - it's an anastomosis.
Through them, blood enters the hollow veins by the principle of communicating vessels. In this case, specific manifestations arise that form a picture of this state.
There are 4 types of portal hypertension. This depends on the level of the location of the obstacle:
- The prehepatic, or prehepatic, form. It appears when the obstruction in the vessels is formed before they enter the liver;
- Intrahepatic - develops when an obstruction within the liver is formed. This is the most common option, which has a frequency of 80-90%;
- Superhepatic - with this form, blockage of blood flow takes place at the level of the vessels that exit the liver, that is, in the hepatic veins;
- Mixed form. It is a combination of an intrahepatic variant with a superhepatic or prehepatic form.
Contents
- 1 Causes of portal hypertension, the effect of liver cirrhosis
- 2 Signs of portal hypertension, photo
- 3 Diagnosis of portal hypertension
- 4 Treatment of portal hypertension
Causes of portal hypertension, the effect of liver cirrhosis
The causes of portal hypertension depend on the variant of this syndrome.
1. The pre-healed form of can develop as a result of the following causative factors:
- Congenital disorders of portal vein structure: cavernous transformation, aplasia, hypoplasia, portal vein atresia.
- Thrombus blocked blood flow - portal portal thrombosis. It is observed in inflammatory diseases, such as acute appendicitis with decay( destructive), pancreatitis, purulent cholangitis, acute cholecystitis, and also as a manifestation of thromboembolism.
- The compression of the portal vein with a large tumor or cyst of the pancreas, a parasitic cyst in alveococcosis. Also in these cases, secondary thrombosis of both portal and splenic veins is possible, which additionally forms portal hypertension.
2. The intrahepatic form of is due to changes in the structure of the hepatic tissue, due to diseases that disrupt the normal structure of hepatocytes.
Even the early stages are accompanied by portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis. This is the most frequent reason for the development of outflow violations in the portal system. With this disease, regenerate nodes are formed. They represent connective tissue structures, which externally squeeze the liver cells.
- Parasites in the liver - echinococcosis, schistosomiasis;
- Polycystic, liver tumors, tumor metastases;
- Fibrosis of the liver;
- Toxic hepatitis, which occurs when taking a large amount of vitamin A, acute hepatitis;
- Fatty degeneration of the liver - accumulation of fat droplets in hepatocytes, leading to cell stretching and compression of their structures;
- Diseases of the bone marrow;
- Sarcoidosis, tuberculosis.
3. The superheated form of is the rarest. It occurs when an obstruction to the blood flow in the vessels that leave the liver - the hepatic veins. This form can occur in the following conditions:
- Chiari disease - inflammation of the inner lining of the hepatic veins, which leads to the formation of blood clots that block the flow of blood;
- Badd-Chiari Syndrome. In this condition, the inferior vena cava is blocked from the inside, due to the formation of connective tissue in the lumen of the vein, or when it is squeezed by a tumor, cyst, scars from the outside;
- Heart diseases: constrictive pericarditis, tricuspid valve insufficiency, right ventricular failure, etc.
4. Mixed form of may occur when a combination of diseases occurs. With this form, the worst prognosis, since the possibility of surgical treatment is severely limited. The main causative factors are:
- The emergence of portal vein thrombosis in combination with cirrhosis of the liver, which leads to the simultaneous or sequential formation of the prehepatic and intrahepatic forms.
- Secondary cirrhosis and superhepatic portal hypertension create first increased pressure in the hepatic veins, stagnation of blood in the liver, the development of changes in its structure, followed by the formation of intrahepatic portal hypertension.
5. Portal hypertension without obstruction to blood flow develops in the formation of a fistulous transition between the artery and the vein, through which there is an increased discharge of blood into the portal vein.
The most common fistula is formed between the splenic artery and the splenic vein.
Signs of portal hypertension, photo
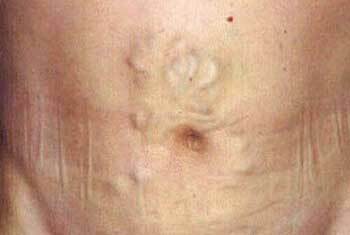
photo of characteristic signs of "Head of jellyfish"
Anastomoses between portal and hollow veins, through which the blood is discharged when a block in the portal system occurs, are located in 3 zones:
- The area of the lower part of the esophagus and the upper stomach;
- Lower part of rectum;
- Anterior abdominal wall.
Therefore, portal hypertension has the symptoms of altering the vessels in these areas:
- Esophagus dilatation;
- Hemorrhoids - dilated veins of the rectum;
- "Jellyfish head" - widening of the veins of the anterior abdominal wall;
- Increased spleen as a result of increased blood filling - splenomegaly, and as a result of the proliferation of its tissue - hypersplenism. The latter state is accompanied by the activation of splenic functions for the destruction of blood cells, so it often accompanies anemia and a decrease in the number of peripheral platelets;
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity - ascites.
As with the intrahepatic block, a part of the blood from the portal vein emerges, bypassing the liver - into the hepatic veins.
Blood, not falling into the liver, is not cleared, all harmful metabolic products enter the brain, and encephalopathy and other manifestations of intoxication syndrome develop.
The syndrome of portal hypertension will manifest itself as a complex of symptoms. So, in general condition there is weakness, malaise, fatigue.
Appear dyspeptic complaints - nausea, vomiting, discomfort, pain in the stomach and liver. At patients the appetite sharply decreases, down to refusal of food - an anorexia. The consequence of this will be a significant reduction in weight due to loss of fat and muscle.
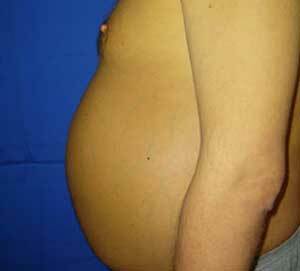
Syndrome of portal hypertension photo
On the skin itching is noted( due to a large intake of bile acids into the bloodstream irritating the sensitive nerve endings).Skin becomes icteric, sudden bruises may appear, and with vascular rupture, spontaneous bleeding from the mouth or from the perianal region occurs.
Appear edema on the legs, and with the appearance of ascites - greatly increases in the volume of the stomach. The cause of these signs is a decrease in the protein's protein-synthesizing function. As a result, the fluid easily exits into the interstitial space( the oncotic blood pressure decreases).
- The urine darkens. This is due to the entry into it of bilirubin, which turns into urobilin.
- With the development of hepatic encephalopathy, sleep is disturbed, the correct rhythm of sleep and wakefulness is lost, memory, thinking activity worsens. There may be violations of behavior and personality changes, up to a passing suicide.
- Sexual dysfunction and impotence develop, which is facilitated by a violation of the exchange of sex hormones in the liver. There may be muscle cramps, muscle atrophy, the development of Dupuytren's contracture - the "twisting" of the fingers.
The manifestations of portal hypertension in children will be minimal and, in general, the course of this syndrome is more favorable.
This is due to the fact that the pressure in the portal vein rises slightly, the blood goes around the obstruction on physiological bypass routes( still not closed in children), there are no marked violations of changes in liver function, ascites is rare.
However, in the absence of treatment, the disease begins to progress, despite the large compensatory capabilities of the child's body. It is necessary to quickly establish the cause and eliminate it.
Diagnosis of portal hypertension
The first stage is to survey and examine, identify the signs of this syndrome, liver diseases and other diseases. The laboratory study consists in conducting a general and biochemical analysis of blood and urine. Its results vary as follows:
- Portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis reveals a decrease in the number of platelets, at a late stage - anemia and a decrease in other blood cells.
- In hypersplenism, a decrease in all cellular elements - pancytopenia - will be detected.
- When hemochromatosis - an increase in hemoglobin in combination with a low color index.
- In alcoholic cirrhosis, a significant increase in the enzymes AsAT, AlAT, GGTP( gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase) is revealed.
- Primary biliary in liver cirrhosis is manifested by an increase in bilirubin, a decrease in albumin level, a significant increase in alkaline phosphatase, in the latter stage, there is a decrease in AST and ALT, which indicates the destruction of hepatocytes.
- Decrease in prothrombin index, if the index is below 60% - the forecast is unfavorable.
- In the blood, the level of albumins, creatinine, electrolytes, urea is determined. The obtained results are compared with special scales for the evaluation of the stage of the disease.
- In urine analysis: erythrocytes, leukocytes, protein, uric acid, creatinine. In ascites and edema, it is necessary to determine the amount of 24-hour urine.
The instrumental study consists in carrying out an ultrasound, which is very informative for this syndrome. It can be used as a screening method. When ultrasound is detected:
- changes in the volume of blood vessels;
- presence of bypass vessels;
- ascites;
- changes in the size and internal structure of the liver and spleen;
- determination of the presence of thrombi and blood flow velocity.
Also can be conducted: CT, MRI, radioisotope scanning.
The method, which allows to see the true picture of blood flow disturbance, is angiography - X-ray examination of vessels with the introduction of contrast medium.
For visual inspection of the esophagus, the EGF is performed. To clarify the causes of portal hypertension, a liver biopsy is performed with a subsequent microscopic examination of the tissues, as well as laparoscopy.
Treatment of portal hypertension
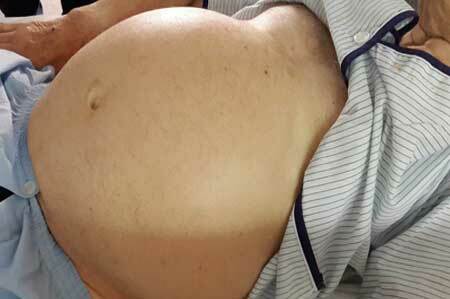
The complex of therapeutic measures consists in the treatment of the disease that caused the obstruction, as well as in the elimination of increased intra-portal pressure. In portal hypertension treatment is divided into conservative and surgical.
In the conservative treatment of portal hypertension, drugs that reduce the pressure in the portal system are used:
- Vasopressin leads to a reduction in arterioles, which reduces the flow of blood into the intestine and reduces pressure in the portal vein. Before its introduction it is necessary to remove an electrocardiogram, as it has a narrowing effect on the vessels of the heart.
- Somatostatin - increases the resistance of the arteries, affecting the smooth muscles, which leads to a decrease in pressure in the portal system. Synthetic analogue of this hormone is octreotide.
- Beta-blockers nonselective: propranolol, nadolol, timolol. In 30% of patients are ineffective. In addition, they have a side effect in the form of impotence.
- Nitrates: isosorbide-5-mononitrate, etc. They are an effective expander of veins. This group is used in combination with vasopressin.
Surgical treatment of portal hypertension consists in the artificial formation of detours for the removal of blood from the portal vein. With an intrahepatic obstruction, surgical treatment is performed only after the main process in the liver subsides, in the absence of manifestations of hepatic insufficiency.
The following operations are performed: portosystemic shunting, splenic artery embolization, omentorenopexy( hemming of the large epiploon to the liver and kidney, for the development of new vessels bypassing the portal vein).
Spleen removal reduces pressure in the portal system, but as an independent operation it is used only with hypersplenism.
In the treatment of portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis, the donor organ transplant has a good effect, with the development of irreversible changes in the liver with cirrhosis.
Complications of
Complications of portal hypertension are serious enough. They are represented by the following list:
- Bleeding from the enlarged and altered esophagus veins. This bleeding with portal hypertension is the most frequent and dangerous complication, resulting in 50% of deaths;
- Development of secondary cirrhosis of the liver in the sub-hepatic form of portal hypertension;
- Liver failure - liver failure;
- Spontaneous bacterial inflammation of the peritoneum;
- External and internal hernia due to ascites.