 Children's cerebral palsy is a serious chronic disease. Cerebral Palsy combines a set of symptoms that are associated with impaired motor function of a person. Most often, the disease affects the fetus during its intrauterine development.
Children's cerebral palsy is a serious chronic disease. Cerebral Palsy combines a set of symptoms that are associated with impaired motor function of a person. Most often, the disease affects the fetus during its intrauterine development.
cerebral palsy is non-progressive, which means that the disease does not spread inside the body, it does not affect the healthy areas of the nervous tissue, it pinpoints damage to certain parts of the brain.
There is a disease on the basis of pathological processes occurring in the central nervous system. As a result, it becomes difficult for the child, or even impossible, to coordinate his movements. The range is quite wide: from mild disorders to complete immobility, depending on the degree of damage to the brain tissue.
Content
- Features of the classification of cerebral palsy
- Spastic diplegia
- double hemiplegia
- Hemiplegia
- hyperkinetic type of disease
- ataxic form
- Classification according to ICD-10
- Stages progress
- Diagnostic approach
- prevalence of various forms of violations
Features of the classification of cerebral palsy
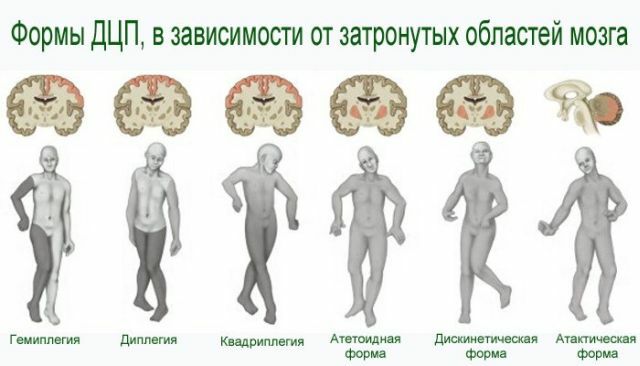
The nature and degree of damage as a basis forclassification of cerebral palsy. In Russia it is accepted to rely on the classification of Smirnova K.A.
According to this graduation, the following forms of cerebral palsy are distinguished:
- spastic diplegia;
- double hemiplegia;
- hemiplegia;
- hyperkinetic form;
- is atonically astatic.
Consider each type of defeat in more detail.
Spastic diplegia
Characteristic features:
- muscles of the lower and upper extremities in tonus;
- lower limbs are more affected;
- hands are more active and coordinated.
 Diplegia is a very common form of cerebral palsy, its symptoms are manifested to a certain extent already in newborns. Intellect is not affected, the child can be successfully taught.
Diplegia is a very common form of cerebral palsy, its symptoms are manifested to a certain extent already in newborns. Intellect is not affected, the child can be successfully taught.
Despite this, exceptions are still possible, there are separate cases when intellectual development is below the norm. There may be minor deviations in mental or speech development.
Spastic diplegia occurs most often in premature infants, but the main cause is cerebral hemorrhage and dilution of the nervous tissue. The brain department responsible for motor activity is affected.
Double hemiplegia
The characteristic of this form of cerebral palsy is as follows: 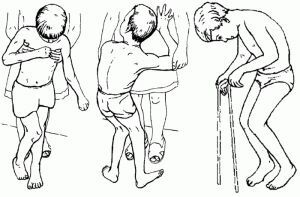
- severe hand dysfunction;
- severe lesion of the lower limbs;
- speech disorders;
- impossibility of self-service;
- atrophy of the optic nerves( in half the cases);
- hearing loss;
- Stiffness of muscles.
The heaviest of all kinds of infantile cerebral palsy. The child is not able to learn, moreover, he absolutely can not coordinate his movements. The reason is fetal hypoxia. The large hemispheres or the entire brain are affected.
Hemiplegia
Characteristic symptoms for this form of the disease:
- affects one side( right or left);
- intellectual development delay;
- deviations in mental development;
- characteristic gait( straightened leg with a bent hand);
- epileptic seizures are possible.
To some extent children with this type of cerebral palsy can be trained, but from peers they will noticeably lag behind. Hemiplegia arises after the transferred cerebral infarcts, hemorrhages in the brain. The cortex and subcortical structures are affected, which are responsible for motor activity.
Hyperkinetic form of the disease
Hyperkinetic form( dyskinetic form) of cerebral palsy has the following features:
- involuntary limb movements;
- wrong foot placement;
- violations of the correct posture of the spine;
- slow motion;
- convulsions;
- speech impairment.
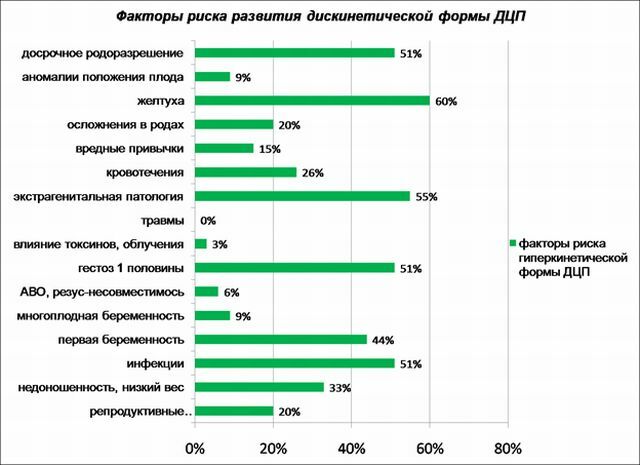
The cause is a hemolytic disease complicated by nuclear jaundice. The subcortical structures are affected.
Ataxic form
Atonic-astatic form( ataxic) Cerebral palsy:
- muscle tone decreased;
- pronounced tendon reflexes;

- cases of speech disturbance are frequent;
- coordination of movements is completely broken;
- lacks a sense of balance;
- may be a concomitant disease - oligophrenia;
- defects of intellectual development;
- violation of speech activity.
The cause of the disease is birth trauma, hypoxia, ischemia. The cerebellum is amazed.
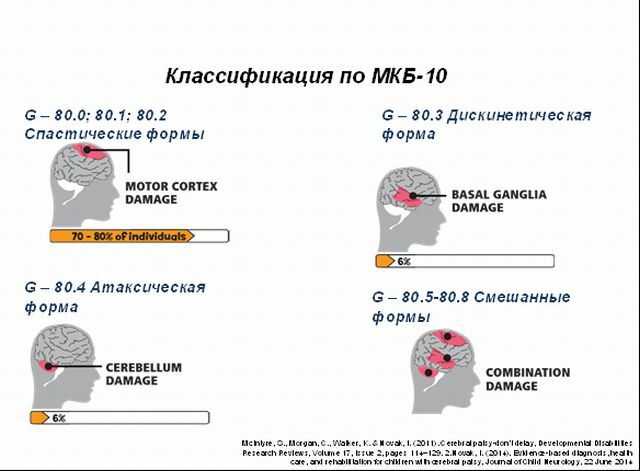
ICD-10 classification
According to the international classification of ICD-10, there are some refinements that complement the classification of cerebral palsy Smirnova, they are concerned with the localization of the lesion. So:
- spastic type, is subdivided in turn into hemiplegia, diplegia, monoplegia, quadriplegia.
- is a hyperkinetic type.
- is an atactic type.
- is a combinative type.
Some signs of infantile cerebral palsy are well marked from birth. But the doctor issues the final diagnosis after carrying out all the necessary studies during the first two years of the child's life. In cases where symptoms are poorly expressed, the diagnosis will be made when the baby is 5 years old.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a physician needs to conduct some research to study: the
- motor abilities of the child;
- disorders of muscle tone;
- level of mental development;
- degree of mental development;
- carefully study the medical history;
- to conduct additional diagnostic studies.
Progress stages
Children's cerebral palsy has three stages according to the nature of the symptoms:
- The first symptoms begin to appear in a baby under five months of age. This is the early stage .At this stage, there are obvious deviations in the child's physical development, which can be expressed in the following: the baby does not hold the head, does not follow the objects, does not reach for them, mostly only one hand is active, or only the hands are effective with less mobility of the lower limbs. All these symptoms at the early stage usually do not strike the eye, although in some cases, even in this period can be clearly seen. At this stage, the baby is prescribed treatment, basically, it includes massage and physiotherapy exercises.
- The second stage is the initial , the pathology has not yet been fixed, but has already been expressed more clearly. Muscle tone is very weak or vice versa, it is elevated. Age - up to three years.
- The third stage of the is late. The pathology is fixed and well marked, features of mental and mental development are formed. Age - over three years.
Diagnostic approach
 It is quite difficult to diagnose a disease at an early stage in the life of a baby. And yet, the initial symptoms begin to make themselves felt from the first months of life. The main thing is not to miss the moment and recognize them in time.
It is quite difficult to diagnose a disease at an early stage in the life of a baby. And yet, the initial symptoms begin to make themselves felt from the first months of life. The main thing is not to miss the moment and recognize them in time.
The spastic form of the disease can be diagnosed already in the first half of the child's life. This form has characteristic manifestations, which are well defined in the very first months: increased muscle tone in combination with pathological reflexes.
Hemiplegia manifests itself at the age of 5 - 7 months.
The anatomically-astatic form of cerebral palsy becomes more pronounced after seven months. Differential diagnosis of this form is rather complicated, due to the similarity of its symptoms with the symptoms of other diseases.
Until the age of six months, the baby can not notice any disorders, and only as it grows, symptoms gradually appear. Most often they are associated with mental development disorders, neurological disorders occur. The child has outbreaks of unreasonable aggression, increased excitability. There are verbal disorders, motor disorders, loss of balance.
The hyperkinetic form of the disease is determined somewhat later - by the beginning of the second year of life.
Additional diagnostics are performed using the following instrumental methods:
- computed tomography of the brain;
- encephalography;
- ultrasound of the brain;
- electromyography;
- craniography, etc.
The results of the study provide information on the depth of changes in the nervous system, determine the severity and severity of the lesions of a particular area of the brain, and identify other disorders.
For the diagnosis of cerebral palsy, it is sufficient to have specific motor disorders in the child at the initial stage of the disease development. As an additional measure of research, MRI of the brain is done, which allows to evaluate the type of damage and to determine the specific site of the brain lesion. 
Such a study is necessary in order to exclude the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms. For the same purpose, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Children's cerebral palsy is not a progressive disease, its symptoms do not increase with time, and the patient's condition does not deteriorate with time. If the opposite happens, then most likely the disease has a different nature.
The same symptoms as in infantile cerebral palsy have the following diseases:
- traumatic and non-traumatic brain injury;
- early autism;
- phenylketonuria;
- lesions of the spinal cord;
- schizophrenia and the like.
Prevalence of various forms of violation of
Children's cerebral palsy is a common disease. According to approximate calculations, one thousand healthy children account for up to 3 patients with cerebral palsy. If we consider the data on the prevalence of forms of cerebral palsy, it can be noted that
- is the spastic diplegia among all forms,
- is the second place - hemiparetic form,
- the third - double hemiplegia,
- the fourth - atonic-astatic form,
- , and finally, the fifth place inthe prevalence of cerebral palsy has a hyperkinetic form of the disease.

Hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy - destiny of girls
Boys are much more likely to suffer spastic diplegia and double hemiplegia, girls often have a hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy.
If we compare the overall ratio of boys to girls with cerebral palsy, it turns out that boys make up 58.1%, girls - 41.9%.
Children's cerebral palsy is an incurable disease, but this does not mean that its treatment does not need to be done at all.
Patients need help from both doctors and educators, so that they can achieve the best possible results with this disease and can adapt to the environment as far as possible. For these purposes, it is necessary to identify the disease as early as possible and begin treatment.
