Simple language about thyroid diseases in women. .
The thyroid gland takes part in all metabolic processes of the human body, is responsible for the growth of the organism, affects the operation of almost all systems. It produces three important hormones - thyroxine and triiodothyronine( T4, T3), calcitonin, which determine its functional activity.
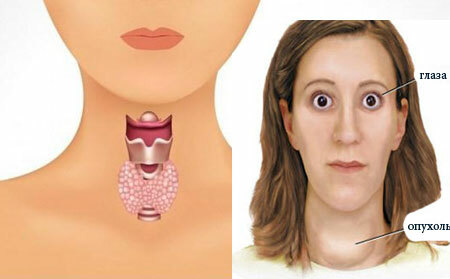
In the human body of iron is located on the neck in front of the larynx. It has two lobes and an isthmus connecting them. If you imagine it figuratively, it looks like the letter "H".Diseases of the thyroid gland take place in various forms and have a high prevalence.
In women, thyroid gland diseases are more common than in men. The high incidence is due to iodine deficiency in the territory of our country, as well as the lack of preventive measures for the replenishment of iodine deficiency.
Symptoms of thyroid disorders in women
Symptoms of thyroid disease in women may go unnoticed or are not given importance, since many diseases of the gland are prone to a sluggish chronic course.
Since the thyroid gland participates in metabolic processes, the first signs of thyroid disease indicate a metabolic disorder. The woman first thing to notice the causeless increase in weight, or, conversely, its decrease. Also, much will tell the hair, nails and skin.
An important sign that indicates a possible disease of the organ is a disorder of the cycle and the impossibility of conception.
In various diseases, the thyroid gland function may be exacerbated or extinguished. Two syndromes are developing, characterizing the functional activity of the organ - hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
- Hyperthyroidism
In hyperthyroidism, there is an increase in thyroid function - hormones are produced in quantities exceeding the normal values several times.
Hyperthyroidism can occur with diseases of the gland itself or in the case of disorders in the systems regulating its functioning( pituitary or hypothalamus).
More common thyrotoxicosis occurs in women at a young age. The increased amount of hormones promotes strengthening of metabolic processes and acceleration of reactions in organs and tissues. This can not but affect the health and general condition of a person.
Symptoms of hypersecretion T3 and T4:
- Weight loss with good appetite.
- Increased pulse, increased systolic pressure.
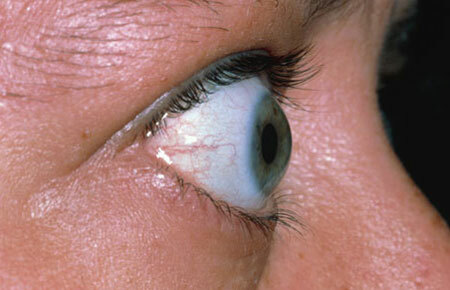
- Loss of vision and eyelashes( exophthalmos).
- Sleep disturbance, anxiety, irritability, trembling in the hands.
- Disorder of the monthly cycle until the disappearance of the monthly. Often there can be infertility.
- Increased sweating and poor health in hot weather. The skin is almost always wet to the touch.
- Fragility of nails and hair, the appearance of gray hair at an early age.
The thyroid gland is enlarged, in advanced cases the increase becomes noticeable to the naked eye.
- Hypothyroidism
The condition of hypothyroidism is directly opposite to hyperthyroidism. If, in hyperthyroidism, hormones are produced in a larger amount than the body needs, hypothyroidism shows a deficiency. At the same time, metabolic processes flow slowly, the disease develops too at a slow pace, for many years a woman can live with it, writing off the symptoms for fatigue or malaise.
Signs of hypothyroidism are associated with a deficiency of hormones T3 and T4:
- Weight gain due to delayed metabolism. At the same time, appetite is reduced.
- Addiction to edema.
- Women with hypothyroidism constantly experience a feeling of drowsiness, weakness.
- Arterial blood pressure lowered, bradycardia, heart rhythm disturbances.
- The skin of the body is prone to dryness, hair and nails are fragile.
- A woman is always cold, does not tolerate low temperatures.
- Female reproductive system suffers: monthly irregular, early onset of menopause, there is a tendency to neoplasm in the uterus and mammary glands.
- From the digestive side, there are disorders in the form of constipation, nausea, appetite is very poor.
The thyroid gland changes its size in the direction of decrease. In the absence of replacement therapy, atrophy of the glandular tissue occurs.
- Inflammation of the thyroid gland( thyroiditis)
The concept of "thyroiditis" includes a number of diseases, in the pathogenesis, which is the inflammatory reaction. Thyroiditis, depending on the course, is divided into acute, subacute, chronic.
Acute thyroiditis is the result of the penetration of infectious agents into the tissue of the thyroid gland. This can occur with injuries in the neck, as well as during the spread of infection from nearby organs, for example, with purulent angina, pneumonia, etc.
The main symptoms, as with any infectious disease, will be pain in the projection of the gland, highbody temperature, weakness. In blood tests, signs of acute inflammation( an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in ESR).When touching the area of the thyroid gland, pain is noted in the affected area, sometimes it is possible to feel the focus of purulent tissue destruction( abscess).
In this place, a soft tissue with a characteristic feeling of fluid motion is felt, in medicine this phenomenon is called a symptom of fluctuation.
Subacute thyroiditis is observed after viral diseases. Women complain of pain in the neck, which can spread to the jaw, ear, neck, thereby making it difficult to diagnose. The body temperature rises. In blood tests, there may be signs of inflammation, or may not be.
Chronic thyroiditis has two forms:
- Fibrous;
- Autoimmune.
Fibrous thyroiditis is called Ridel's goiter. This is a fairly rare form of goiter, which is characterized by replacement of the glandular tissue with a coarse connective tissue, into which the proteins subsequently drop out, and it resembles a cartilaginous structure.
The thyroid gland becomes like a stone, its functions gradually fade away, hypothyroidism develops.
The causes of this pathology are unknown. Petrified and enlarged iron can press on the organs of the neck, which is dangerous for the patient's life.
The most important for the female population is the disease - chronic autoimmune thyroiditis.
For unknown reasons, this pathology occurs in women 8 times more often than in the opposite sex. The disease was studied and described by a doctor from Japan, in honor of whom this variant of thyroiditis was called Hoshimoto's goiter.
Zob Hashimoto occurs due to disorders of the immune system. The development of antibodies against the gland tissues begins. With what it is connected, it is not completely clear. Women after the age of 50 are ill.
The trigger mechanism can be thyroid injuries, thyroid surgery, as well as infectious diseases, environmental degradation, etc. Zob Hashimoto is inherited by next generations.
The disease has a prolonged course. The gland tissue thickens, replaced by a connective tissue. At the initial stages of the disease, there may be signs of hyperthyroidism due to compensatory mechanisms, but as a result, the gland functions are extinguished, the symptoms of hypothyroidism increase.
- Goiter and thyroid nodules
The goiter is called thyroid disease, accompanied by an increase in the thyroid gland. When the nodes are formed in the gland, the disease is called nodular goiter. In this case the node can be in a single copy, several nodes can be formed, sometimes there are so many nodes that they weld together, forming conglomerates.
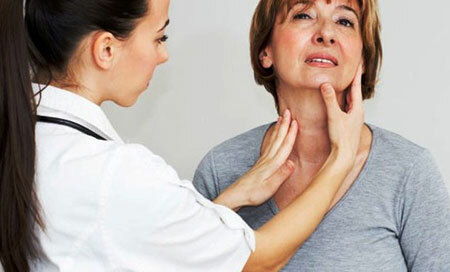
Nodes are easily probed by manual examination. Treatment depends on the nature of the nodes. They can be benign and malignant.
For detailed symptoms and treatment methods, see Endocrinology or the tag Thyroid
Methods for diagnosing the thyroid in various pathologies
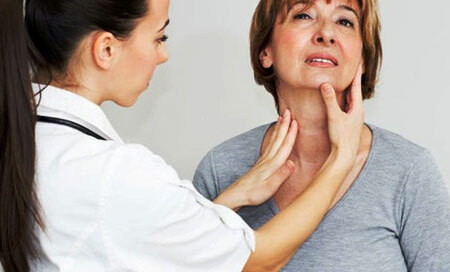
After examination and palpation, the endocrinologist will refer to the following studies:
- Determination of the level of iodine-containing hormones in the blood. Quantification will reveal an increase or decrease in function.
- ultrasound. Perhaps, the most accessible and simple way of diagnostics with high informativeness.
- Scintigraphy. It is based on the use of radioactive isotopes. You can see the structure of the gland, evaluate the changes in tissue.
- Thermography. Research is carried out in infrared rays. It is based on the fact that the affected areas and neoplasms in the tissue have a temperature different from healthy tissues.
- MRI.By informative method is similar to ultrasound, but more costly.
- CT.Very informative, but not cheap method of research.
- Puncture biopsy for further histological examination. The origin of the test tissue is determined: malignant or benign.
The number of studies depends on the diagnosis of the patient and is determined by the doctor.
Thyroid pathologies are treatable. It is important for a woman to see a doctor at the first symptoms of a thyroid gland. With weighed heredity or living in endemic areas, it is necessary to visit an endocrinologist for an examination for prevention purposes.