Stroke - a neurological disorder characterized by acute cerebral ischemia due to vascular injury and bleeding in the brain or blockage of cerebral arteries at the background of atherosclerosis, thrombosis or embolism. The disease is always leaves a negative impact. Complications after a stroke can occur in the first hours and days after the attack, or a few weeks.

early consequences
Allocate following early complications of stroke:
- Swelling of the brain. Most often develops in hemorrhagic stroke. Edema may compress the most important centers that are responsible for breathing, temperature regulation and the work of the heart with blood vessels. Mechanism of development of edema in ischemic stroke It is associated with increased vascular permeability and the outlet of the plasma into the intercellular space. When hemorrhage (hemorrhagic stroke) edema develops at vascular damage and blood impregnating nervous tissue. Edema symptoms are impaired consciousness, movement, and visual disturbances, seizures, headaches, nausea and vomiting.
- Epileptiform seizures.
- Coma. It represents a profound disturbance of consciousness in which a person does not respond to external stimuli. Often preceded by stupor and coma stupor. It can last for years. Some people did not come out of the coma. The severity is assessed by the Glasgow Coma Scale. The main criteria are the speech, motor activity, and eye opening. At the heart of the coma on a background of a stroke is damage to the reticular pharmacy.
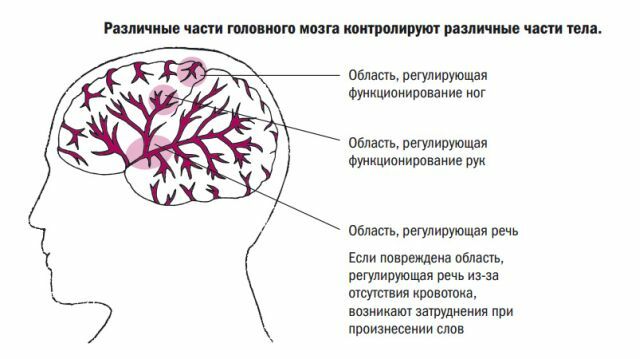
- Speech disorders. After a stroke is often observed aphasia (inability to fully enjoy their own speech and understand conversations others people), aprosodiya (violation of intonation, emotion and phonetics) and dysarthria (impaired pronunciation of sounds, inarticulate speech).
- Reduction or complete loss of sensitivity (anesthesia).
- Movement disorders. After a stroke in men and women are often observed paresis (partial restriction of movement) and paralysis (complete absence of movement). With the defeat of the left hemisphere of the brain disrupted the muscles of the right side of the body and vice versa. Possible monoparesis (limitation of movement in one limb), hemiparesis (volume reduction hands and feet movements on 1 side) and tetrapareses (defeat all 4 limbs).
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing food and water).
- Impaired hearing and taste.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs (intestines and bladder).
- Psycho-emotional disorders (psychosis, depression).
- Thrombosis and thromboembolism. Due to the slowdown of blood flow and blood thickening. Blood clots are often formed during ischemic insults cardiac (heart) etiology. Blood clots can break off, clogging the brain vessels. So develop thrombosis.
- Blurred vision.
- Pneumonia. Against the background of brain damage in stroke complicated by food intake, which can lead to its casting in the respiratory tract (trachea and bronchi). There also may get vomit. All this contributes to the development of aspiration pneumonia. It appears cough with sputum, chest pain, fever, wheezing, cyanosis of the skin and heart palpitations.
- Dislocation (offset) of the brain structures. Most often observed in cerebral hemorrhage. It formed a hematoma, which leads to displacement of structures and their squeezing.

late complications
By late complications include:
- Relapse (recurrence of the disease). The reasons may be non-compliance with recommendations of the doctor and medication dosage regimen, defective rehabilitation. Relapse is possible in a few years after the first attack of acute cerebrovascular accidents.
- Bedsores. Represent areas of tissue necrosis in areas of prolonged compression of skin. This is possible by immobilizing a person (with coma and paralysis of the legs). Thus compressed vessels, leading to ischemia and necrosis of cells. Bedsores often formed in the sacrum, shoulder blades, buttocks and limbs bend. They are round or oval. Bedsores occur gradually. In the last step in the process involves the surrounding tissue (tendons, bones and muscles). decubitus size often exceed 10-15 cm. From patients with an unpleasant (putrid) smell.
- Decreased attention and memory impairment.
- Vascular dementia. It is a condition characterized by a decrease in intelligence, thought disorders and social maladjustment. Dementia is more common in ischemic stroke. The reason - the massive loss of nerve cells. Dementia on the background of hemorrhage due to high blood pressure and vascular damage. Symptoms of dementia are: narrowing of the range of interest, inability to memorize information, speech, writing, and account, indifference to what is happening, emotional lability, aggression, crying and inability to self-service.
Stroke complications due to untimely and incomplete treatment. To reduce the risk of negative consequences and improve the health outlook, you need to quit smoking, to comply diet (to give up salt and fatty foods), eliminate stressful situations, avoid alcohol and take medications. Rehabilitation includes physiotherapy, exercises, rest in sanatoriums and limitation of physical activity.